Users Online
· Members Online: 0
· Total Members: 188
· Newest Member: meenachowdary055
Forum Threads
Latest Articles
Articles Hierarchy
#CompTIA Security+ 501 exam Chapter04 Delving into Identity and Access Management Part 2
Chapter04 Delving into Identity and Access Management Part 2
Security Information and Event Management
Security information and event management (SIEM) is considered an IT best practice, and for regulated industries it is an audit compliance requirement. It supports IT service reliability by maximizing event log value and is used to aggregate, decipher, and normalize nonstandard log formats; it can also filter out false positives. The only time that an SIEM system will not provide the correct information is when the wrong filters are set in error:
-
Account management: In a multinational corporation that may have in excess of 50,000 users it is very important that account management policies are in place so that the directory service is kept up to date. Let us look at different account management tools and policies. An Active Directory query can be run against the system to discover accounts that have not been used for a certain period of time.
-
Account expiry: When companies employ temporary employees such as sub-contractors during the account creation phase an expiry date will be enabled. This is to prevent someone from trying to gain access to the company network once their contract has expired. Once the account hits the expiry state the account is automatically disabled, however, the IT team can reset the expiry date if the contract is extended. Here is an example of account expiry:
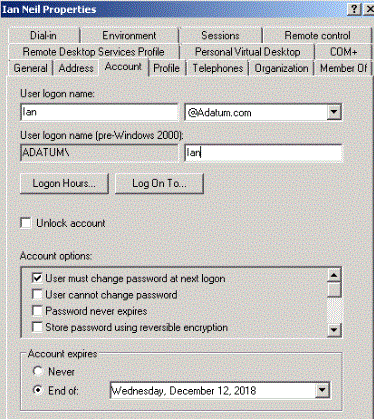
Figure 19: Account expiry
If a person moves department and their old account is still being used, then we should get an auditor who will perform a user account review.
-
Time and day restriction: Time and day restriction is set up for each individual user as a company may have many different shift patterns and may not wish their employees to access their network outside of their working hours. This prevents users coming in at 3 a.m. when nobody else is in at the company and stealing data:
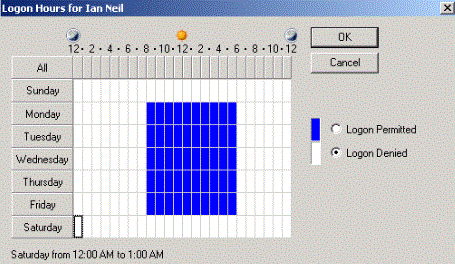
Figure 20: Time and day restrictions
For example, a toy factory may employ university students to work prior to the busy Christmas period with three different shift patterns, 6 a.m.-2 p.m., 2-10 p.m. and 10 p.m.-6 a.m. Each employee will have a time and day restriction in place so that they can log in only for their individual shift times.
-
Account lockout: To prevent dictionary and brute-force attacks, account lockout is enforced so that maybe three or five attempts to enter the password are allowed; once exceeded the account is disabled. This prevent hackers guessing an account password.
If a time restriction is to be placed on a group of contractors, rule based access control will be used. Time and day restriction can only be used for individuals.
Group based access control
When a company has a large number of users it is difficult to give each user access to the resources that they need to perform their job. Groups are created and they will contain all users in that department. For example the sales group will then contain all of the people working in sales and the group will be used to allow access to resources such as a printer or file structure. If you decide to use group-based access and you have new employees or interns you may create another group for them with lower permissions.
For example, in a large corporation there are 25 employees who work in marketing and need full access to the marketing file share. Next week they will have three new interns start with the company but they need only read access to the same share. We therefore create the following:
-
A global group called marketing is created; all 25 employees are added to the group. The group is given full control access to the data.
-
A global group called marketing interns is created; the three interns are added to the group. The group is given read access to the data.
If group-based access is used in the exam question, then the solution will be a group-based access solution.
Credential management
The details of usernames and passwords that someone uses to access a network or an application are called credentials. Users will sometimes have more than one set of credentials to access their local network, and their Facebook, Hotmail, or Twitter account. It would be a serious security risk to use the same account and password for any two of these. Windows 10 has a Credential Manager that can store credentials in to two categories: generic credentials and Windows 10. When you log in to an account and you check the box Remember Password, these details could be stored inside credential management to consolidate them. It can be for generic accounts used to access web portals or Windows 10 credentials:
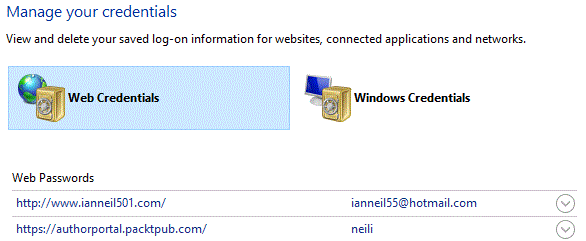
Figure 21: Credential manager
User account reviews
An auditor will carry out a user account review periodically to ensure that old accounts are not being used after an employee either moves department or leaves the company. The auditor will also ensure that all employees have the correct amount of permissions and privileges to carry out their jobs and that they don't have a higher level than they required. Least privilege is giving the person only the access that they require.
Practical exercise – password policy
In this practical exercise, you need to prevent users from resetting their account by using the same password. The company should not allow the users to change their password more than once every three days and these passwords need to be complex. A user must use a minimum of 12 passwords before they can reuse the original password. You need to prevent a hacker using more than five attempts at guessing a password:
-
On a Windows 10 desktop, type gpedit.msc or on a domain controller, go to Server Manager | Tools | Group Policy management. Edit the Default Domain Policy.
-
Under Computer Configurations, expand Windows Settings.
-
Select Security Settings.
-
Select Account Policy, then select Password Policy.
-
Select Password History and enter 12 passwords remembered—press OK.
-
Select Minimum Password Age. Enter 3 days—press OK.
-
Select Password must meet complexity requirements—select the radio button Enabled and press OK.
-
Go back to Account Policies and select Account Lockout Policies.
-
Select Account Lockout Threshold and change the value to five invalid logon attempts—press OK.
Review questions
-
What is the most common form of authentication that is most likely to be enter incorrectly?
-
When I purchase a new wireless access point what should I do first?
-
What is password history?
-
How can I prevent someone from reusing the same password?
-
Explain what format a complex password takes.
-
How can I prevent a hacker from inserting a password multiple times?
-
What type of factor authentication is a smart card?
-
How many factors is it if I have a password, PIN, and date of birth?
-
What is biometric authentication?
-
What authentication method can be used by two third parties who participate in a joint venture?
-
What is an XML-based authentication protocol?
-
What is Shibboleth?
-
What protocol is used to store and search for Active Directory objects?
-
What is the format of a distinguished name for a user called Fred who works in the IT department for a company with a domain called Company A that is a dotcom?
-
What authentication factor uses tickets, timestamps, and updated sequence numbers and is used to prevent replay attacks?
-
Which Stratum time server is the reference time source?
-
What is a ticket granting ticket (TGT) session?
-
What is single sign-on? Give two examples.
-
How can I prevent a Pass the Hash attack?
-
Give an example of when you would use Open ID Connect.
-
Name two AAA servers and the ports associated with them.
-
What is used for accounting in an AAA server?
-
What is the purpose of a virtual private network (VPN) solution?
-
Why should we never use PAP authentication?
-
What type of device is an iris scanner?
-
What can be two drawbacks of using facial recognition?
-
What is Type II in biometric authentication and why is it a security risk?
-
What is a time-limited password?
-
How many times can you use a HOTP password? Is there a time restriction associated with it?
-
How does a CAC differ from a smart card and who uses CAC?
-
What is port-based authentication that authenticates both users and devices?
-
What type of account is a service account?
-
How many accounts should a system administrator for a multinational corporation have and why?
-
What do I need to do when I purchase a baby monitor and why?
-
What is a privilege account?
-
What is the drawback for security if the company uses shared accounts?
-
What is a default account? Is it a security risk?
-
The system administrator in a multination corporation creates a user account using an employee's first name and last name. Why is he doing this time after time?
-
What two actions do I need to complete when John Smith leaves the company?
-
What is account recertification?
-
What is the purpose of a user account review?
-
What can I implement to find out immediately when a user is placed in a group that may give them a higher level of privilege?
-
What will be the two possible outcomes if an auditor finds any working practices that do not confirm to the company policy?
-
If a contractor brings in five consultants for two months of mail server migration, how should I set up their accounts?
-
How can I ensure that the contractors in Question 44 can only access the company network 9 a.m.-5 p.m. daily?
-
If I has a company that has five consultants who work in different shift patterns, how can I set up their accounts so each of them can only access the network during their individual shifts?
-
A brute-force attack cracks a password using all combinations of characters and will eventually crack a password. What can I do to prevent a brute-force attack?
-
The IT team have a global group called IT Admin; each member of the IT team are members of this group and therefore has full control access to the departmental data. Two new apprentices are joining the company and they need to have read access to the IT data—how can you achieve this with the minimum amount of administrative effort?
-
I have different login details and passwords to access Airbnb, Twitter, and Facebook, but I keep getting them mixed up and have locked myself out of these accounts from time to time. What can I implement on my Windows 10 laptop to help me?
-
I have moved departments but the employees in my old department still use my old account for access; what should the company have done to prevent this from happening? What should their next action be?
Answers and explanations
-
A password is most likely to be entered incorrectly; the user may forget the password or may have the caps lock set-up incorrectly.
-
When purchasing any device, you should change the default username and password as many of these are available on the internet and could be used to access your device.
-
Password history is the number of passwords you can use before you can reuse your current password. Some third-party applications or systems may call this a Password Reuse list.
-
Password history could be set up and combined with minimum password age. If I set the minimum password age to 1 day, a user could only change their password a maximum of once per day. This would prevent them from rotating their passwords to come back to the old password.
-
A complex password uses three of the following; uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and special characters not used in programming.
-
If I set up an account lockout with a low value such as three, the hacker needs to guess your password within three attempts or the password is lockout, and this disables the user account.
-
A smart card is multi-factor or dual factor as the card is something you have and the PIN is something you know.
-
A password, PIN, and date of birth are all factors that you know, therefore it is single factor.
-
Biometric authentication is where you use a part of your body or voice to authenticate, for example your iris, retina, palm, or fingerprint.
-
Federated services are an authentication method that can be used by two third parties; this uses SAML and extended attributes such as employee or email address.
-
Security Assertion Mark-up Language (SAML) is an XML-based authentication protocol used with federated services.
-
Shibboleth is a small open source Federation Services protocol.
-
Lightweight Directory Authentication Protocol (LDAP) is used to stores objects in a X500 format and search Active Directory objects such as users, printers, groups, or computers.
-
A distinguisher name in the ITU X500 object format is: CN=Fred, OU=IT, CN=Company, DC=Com.
-
Microsoft's Kerberos authentication protocol is the only one that uses tickets. It also uses time stamps and updated sequence numbers and is used to prevent replay attacks.
-
Stratum 0 is the reference time source. Stratum 1 is set up internally to obtain time from the Stratum 0.
-
A Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) process is where a user logs into an Active Directory domain using Kerberos authentication.
-
Single sign-on is where a user inserts their credentials only once and access different resource such as emails and files without needing to re-enter the credentials. Examples of this are Kerberos, Federated Services, and a smart card.
-
Pass the hash attacks exploit older systems such as Microsoft NT4.0, which uses NT Lan Manager. You can prevent is by disabling NTLM.
-
Open ID Connect is where you access a device or portal using your Facebook, Twitter, Google, or Hotmail credentials. The portal itself does not manage the account.
-
The first AAA server is Microsoft RADIUS, using TCP Port 1812—it is seen as non-proprietary. The second is CISCO TACACS+ and uses TCP Port 49. Diameter is a more modern secure form of RADIUS.
-
Accounting in an AAA server is where they log the details of when someone logs in and logs out; this can be used for billing purposes. Accounting is normally logged in a database such as SQL.
-
A VPN solution creates a secure to connect from a remote location to your corporate network or vice versa. The most secure tunneling protocol is L2TP/IPSec.
-
PAP authentication uses a password in clear text; this could be captured easily by a packet sniffer.
-
An iris scanner is a physical device used for biometric authentication.
-
Facial recognition could be affected by light or turning your head slightly to one side; some older facial recognition systems accept photographs. Microsoft Windows Hello is much better as it uses infrared and is not fooled by a photograph or affected by light.
-
Type II in biometric authentication is Failure Acceptance Rate, where people that are not permitted to access a tour network are given access.
-
Time based one time password has a short time limit of 30-60 seconds.
-
HOTP is a one-time password that does not expire until it is used.
-
A CAC is similar to a smart card as it uses certificates, but the CAC card is used by the military, has a picture, and the details of the user on the front and their blood group and Geneva convention category on the reverse side.
-
IEE802.1x is port-based authentication that authenticates both users and devices.
-
A service account is a type of administrative account that allows an application to have the higher level of privileges to run on a desktop or server. An example of this is using a service account to run an anti-visas application.
-
A system administrator should have two accounts: a user account for day-to-day tasks and an administrative account for administrative tasks.
-
When I purchase a baby monitor I should rename the default administrative account and change the default password to prevent someone using it to hack my home.
-
A privilege account is an account with administrative rights.
-
When monitoring and auditing are carried out, the employees responsible cannot be traced while more than one-person shared accounts. Shared accounts should be eliminated for monitoring and auditing purposes
-
Default accounts and passwords for devices and software can be found on the internet and used to hack your network or home devices. Ovens, TVs, baby monitors, and refrigerators are examples.
-
The system administrator is using a standard naming convention.
-
When John Smith leaves the company, you need to disable his account and reset the password. Deleting the account will prevent access to data he used.
-
Account recertification is an audit of user account and permissions usually carried out by an auditor; this could also be known as user account reviews.
-
A user account review ensures that old accounts have been deleted—all current users have the appropriate access to resources and not a higher level of privilege.
-
A SIEM system can carry out active monitoring and notify the administrators of any changes to user account or logs.
-
Following an audit, either change management or a new policy will be put in place to rectify any area not conforming to company policy.
-
The contractor's account should have an expiry date equal to the last day of the contract.
-
Rule-based access should be adopted so that the contractors can access the company network 9 a.m.-5 p.m. daily.
-
Time and day restrictions should be set up against each individual's user account equal to their shift pattern.
-
Account Lockout with a low value will prevent brute-force attacks.
-
Create a group called IT apprentices then add the apprentices accounts to the group. Give the group read access to the IT data.
-
The credential manager can be used to store generic and Windows 10 accounts. The user therefore does not have to remember them.
-
The company should have disabled the account. A user account review needs to be carried out to find accounts in a similar situation.

