Users Online
· Members Online: 0
· Total Members: 188
· Newest Member: meenachowdary055
Forum Threads
Latest Articles
Articles Hierarchy
PY0018 Python COPY File using shutil.copy(), shutil.copystat()
Python COPY File using shutil.copy(), shutil.copystat()
Python Copy File Methods
Python provides in-built functions for easily copying files using the Operating System Shell utilities.
Following command is used to Copy File
shutil.copy(src,dst)
Following command is used to Copy File with MetaData Information
shutil.copystat(src,dst)
Here are the steps to copy file in Python
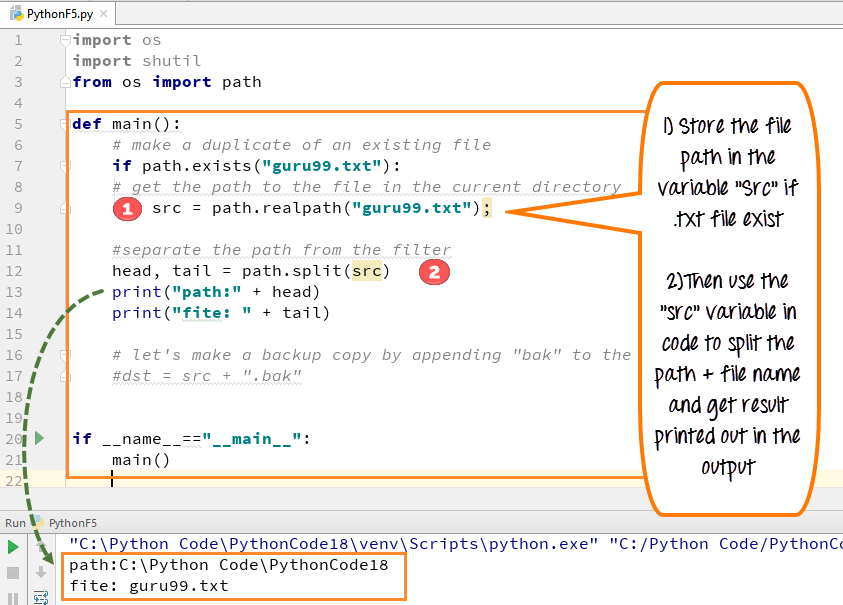
Step 1) Before, we copy a file, we need to get the the path to the original file in the current directory. In the code -
- Declaring variable
- Applying split function on variable
Code Explanation
- First we are going to check that our "guru99.txt" file exists or not. Since we have created guru99.txt file earlier, we know it exists, and we will carry on further with the code
- We store the file path in the variable "src" if your file exist
- Once we get the path, we going to separate the path and the file name
- For that, we are going to use the split
path.splitfunction on source variable - Code when executed prints out "file name" and "file path" separately
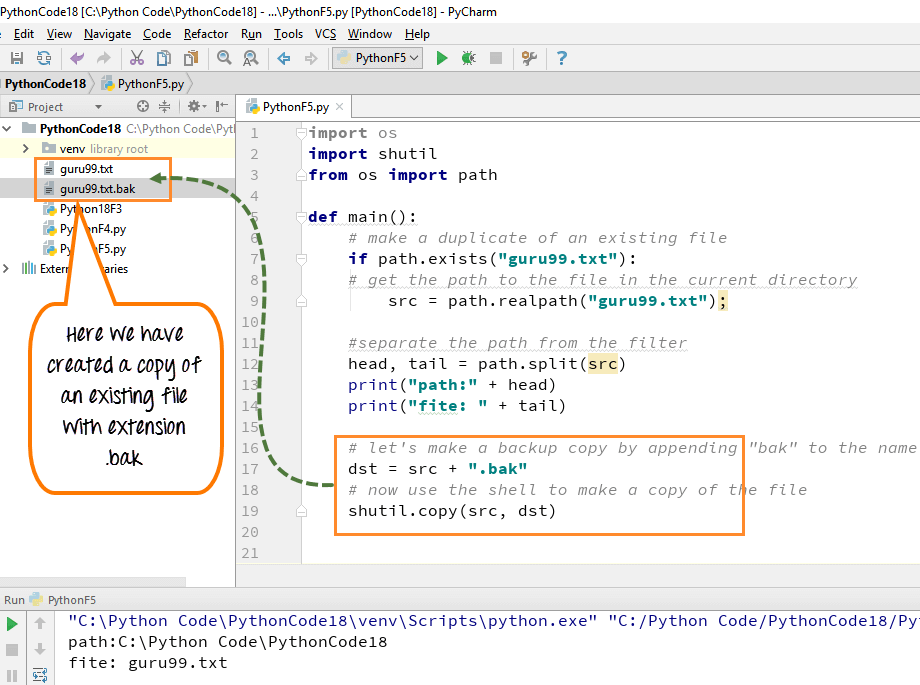
Step 2) We use Shutil Module to create a copy of the existing file. Here we used to create a copy of our existing file "guru99.txt."
Code Explanation
- Take the original file name "guru99.txt" and add letters .bak at the end "guru99.txt.bak". This name with .bak extension is going to be our duplicate copy
- And then we going to use utility's copy function to copy from source to the destination
- When you run the code, you will see a duplicate file with .bak extension is created on right-hand side of the panel
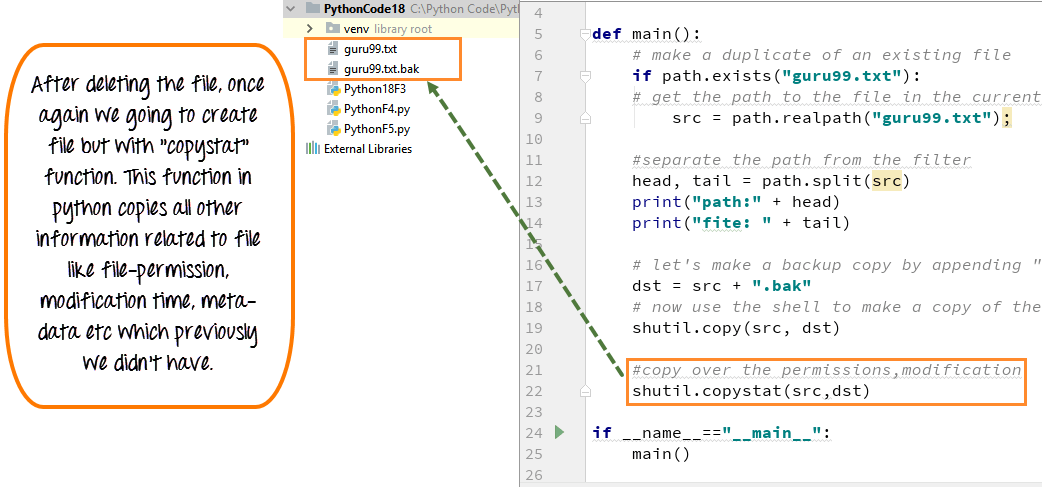
Step 3) Copy function only copies the content of the file but no other information. To copy meta-data associated with the file, file permission and other information you have to use "copystat" function. Before we run this code, we have to delete our copy file "guru99.text.bak".
Once you deleted the file and run the program it will create a copy of your .txt file but this time with all the information like file permission, modification time and meta-data information. You can go to your O.S shell to verify the information.
Here is the code
import os
import shutil
from os import path
def main():
# make a duplicate of an existing file
if path.exists("guru99.txt"):
# get the path to the file in the current directory
src = path.realpath("guru99.txt");
#seperate the path from the filter
head, tail = path.split(src)
print("path:" +head)
print("file:" +tail)
#let's make a backup copy by appending "bak" to the name
dst = src+".bak"
# nowuse the shell to make a copy of the file
shutil.copy(src, dst)
#copy over the permissions,modification
shutil.copystat(src,dst)
if __name__=="__main__":
main()
Step 4) You can fetch the information about the text file last modified
-
Code Line#15- It tells the day, date, month, year and time when .txt file (guru99) was last modified. We use the path module to get the file modification time details, and then we are going to use the time classes c time function to convert that into a readable time. So when we run the code, we can see the file guru99.txt was last modified on Mon, Jan 8th at 13:35 2018.
-
Code Line#17- It does the same thing giving information about file modification, but it has a different format to represent it. Here we use Get Modification Time function (path.getmtime("guru99.txt")). Now instead of using the c time function we going to use From Time Stamp function and going to construct a date time object. In output, you can see file modification time detail is printed out in different format 2018-01-08, 13:35:51.334072
Here is the code
#
# Example file for working with o.s path module
import os
from os import path
import datetime
from datetime import date, time, timedelta
import time
def main():
# Get the modification time
t = time.ctime(path.getmtime("guru99.txt.bak"))
print(t)
print(datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(path.getmtime("guru99.txt.bak")))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Summary
- To create a copy of the existing file by use code shutil.copy (src,dst)
- To copy all the information of original file to duplicate file like file permission, modification time or meta-data information by use code shutil.copystat(src,dst)