Users Online
· Members Online: 0
· Total Members: 188
· Newest Member: meenachowdary055
Forum Threads
Latest Articles
Articles Hierarchy
How to use Jupyter Notebook with AWS and Docker
How to use Jupyter Notebook with AWS and Docker
This is a step by step tutorial, to used Jupyter Notebook on AWS
If you do not have an account at AWS, create a free account here.
We will proceed as follow
- Part 1: Set up a key pair
- Part 2: Set up a security group
- Part 3: Launch instance
- Part 4: Install Docker
- Part 5: Install Jupyter
- Part 6: Close connection
PART 1: Set up a key pair
Step 1) Go to Services and find EC2
Step 2) In the panel and click on Key Pairs
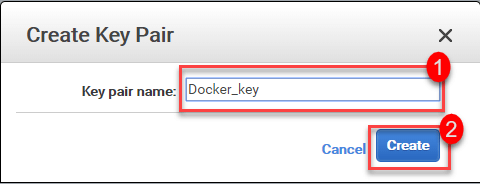
Step 3) Click Create Key Pair
- You can call it Docker key
- Click Create
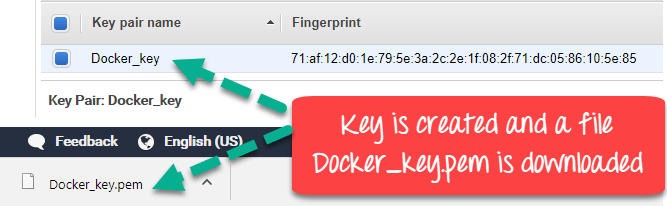
A file name Docker_key.pem downloads.
Step 4) Copy and paste it into the folder key. We will need it soon.
For Mac OS user only
This step concerns only Mac OS user. For Windows or Linux users, please proceed to PART 2
You need to set a working directory that will contain the file key
First of all, create a folder named key. For us, it is located inside the main folder Docker. Then, you set this path as your working directory
mkdir Docker/key cd Docker/key
PART 2: Set up a security group
Step 1) You need to configure a security group. You can access it with the panel
Step 2) Click on Create Security Group
Step 3) In the next Screen
- Enter Security group name "jupyter_docker" and Description Security Group for Docker
- You need to add 4 rules on top of
- ssh: port range 22, source Anywhere
- http: port range 80, source Anywhere
- https: port range 443, source Anywhere
- Custom TCP: port range 8888, source Anywhere
- Click Create
Step 4) The newly created Security Group will be listed
Part 3: Launch instance
You are finally ready to create the instance
Step 1) Click on Launch Instance
The default server is enough for your need. You can choose Amazon Linux AMI. The current instance is 2018.03.0.
AMI stands for Amazon Machine Image. It contains the information required to successfully starts an instance that run on a virtual server stored in the cloud.
Note that AWS has a server dedicated to deep learning such as:
- Deep Learning AMI (Ubuntu)
- Deep Learning AMI
- Deep Learning Base AMI (Ubuntu)
All of them Comes with latest binaries of deep learning frameworks pre-installed in separate virtual environments:
- TensorFlow,
- Caffe
- PyTorch,
- Keras,
- Theano
- CNTK.
Fully-configured with NVidia CUDA, cuDNN and NCCL as well as Intel MKL-DNN
Step 2) Choose t2.micro. It is a free tier server. AWS offers for free this virtual machine equipped with 1 vCPU and 1 GB of memory. This server provides a good tradeoff between computation, memory and network performance. It fits for small and medium database
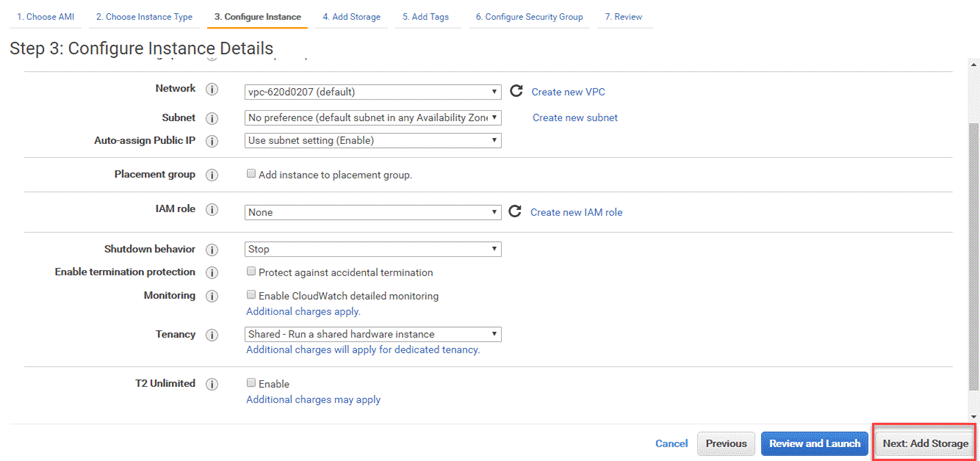
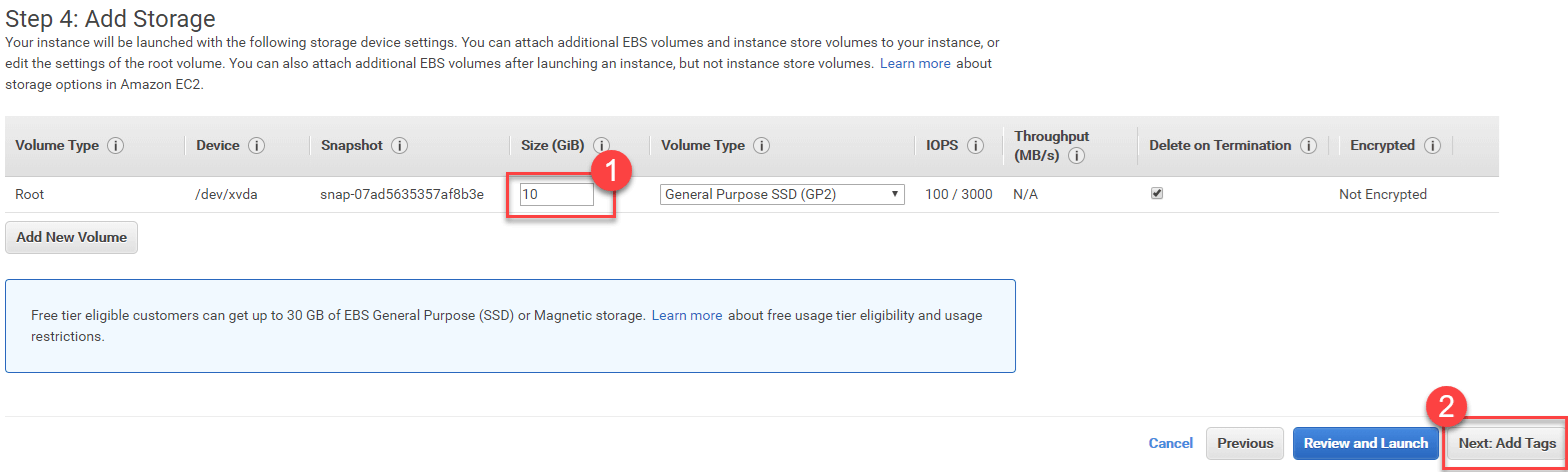
Step 3) Keep settings default in next screen and click Next: Add Storage
Step 4) Increase storage to 10GB and click Next
Step 5) Keep settings default and click Next: Configure Security Group
Step 6) Choose the security group you created before, which is jupyter_docker
Step 7) Review your settings and Click the launch button
Step 8 ) The last step is to link the key pair to the instance.
Step 8) Instance will launch
Step 9) Below a summary of the instances currently in use. Note the public IP
Step 9) Click on Connect
You will find the connection detials
Launch your instance (Mac OS users)
At first make sure that inside the terminal, your working directory points to the folder with the key pair file docker
run the code
chmod 400 docker.pem
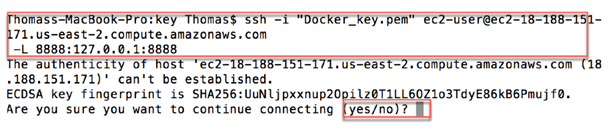
Open the connection with this code.
There are two codes. in some case, the first code avoids Jupyter to open the notebook.
In this case, use the second one to force the connection.
# If able to launch Jupyter ssh -i "docker.pem" ec2-user@ec2-18-219-192-34.us-east-2.compute.amazonaws.com # If not able to launch Jupyter ssh -i "docker.pem" ec2-user@ec2-18-219-192-34.us-east-2.compute.amazonaws.com -L 8888:127.0.0.1:8888
The first time, you are prompted to accept the connection
Launch your instance (Windows users)
Step 1) Go to this website to download PuTTY and PuTTYgen PuTTY
You need to download
- PuTTY: launch the instance
- PuTTYgen: convert the pem file to ppk
Now that both software are installed, you need to convert the .pem file to .ppk. PuTTY can only read .ppk. The pem file contains the unique key created by AWS.
Step 2) Open PuTTYgen and click on Load. Browse the folder where the .pem file is located.
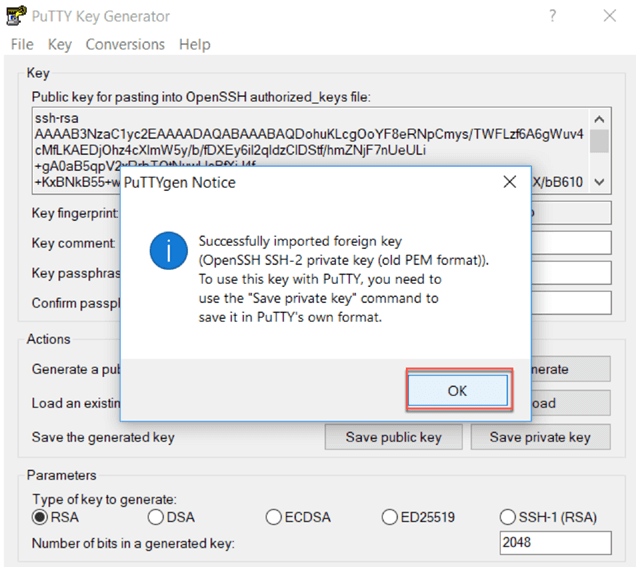
Step 3)After you loaded the file, you should get a notice informing you that the key has been successfully imported. Click on OK
Step 4) Then click on Save private key. You are asked if you want to save this key without a passphrase. Click on yes.
Step 5) Save the Key
Step 6) Go to AWS and copy the public DNS
Open PuTTY and paste the Public DNS in the Host Name
Step 7)
- On the left panel, unfold SSH and open Auth
- Browse the Private Key. You should select the .ppk
- Click on Open.
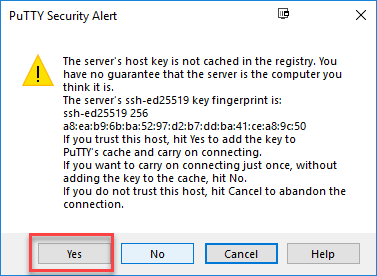
Step 8)
When this step is done, a new window will be opened. Click Yes if you see this pop-up
Step 9)
You need to login as: ec2-user
Step 10)
You are connected to the Amazon Linux AMI.
Part 4: Install Docker
While you are connected with the server via Putty/Terminal, you can install Docker container.
Execute the following codes
sudo yum update -y sudo yum install -y docker sudo service docker start sudo user-mod -a -G docker ec2-user exit
Launch again the connection
ssh -i "docker.pem" ec2-user@ec2-18-219-192-34.us-east-2.compute.amazonaws.com -L 8888:127.0.0.1:8888
Windows users use SSH as mentioned above
Part 5: Install Jupyter
Step 1) Create Jupyter with a pre-built image
## Tensorflow docker run -v ~/work:/home/jovyan/work -d -p 8888:8888 jupyter/tensorflow-notebook ## Sparkdocker run -v ~/work:/home/jovyan/work -d -p 8888:8888 jupyter/pyspark-notebook
Code Explanation
- docker run: Run the image
- v: attach a volume
- ~/work:/home/jovyan/work: Volume
- 8888:8888: port
- jupyter/datascience-notebook: Image
For other pre-build images, go here
Allow preserving Jupyter notebook
sudo chown 1000 ~/work
Step 2) Install tree to see our working directory next
sudo yum install -y tree
Step 3)
- Check the container and its name (changes with every installation) Use command
docker ps
- Get the name and use the log to open Jupyter. In the tutorial, the container's name is vigilant_easley. Use command
docker logs vigilant_easley
- Get the URL
Step 4)
In the URL
http://(90a3c09282d6 or 127.0.0.1):8888/?token=f460f1e79ab74c382b19f90fe3fd55f9f99c5222365eceed
Replace (90a3c09282d6 or 127.0.0.1) with Public DNS of your instance
Step 5)
The new URL becomes
http://ec2-174-129-135-16.compute-1.amazonaws.com:8888/?token=f460f1e79ab74c382b19f90fe3fd55f9f99c5222365eceed
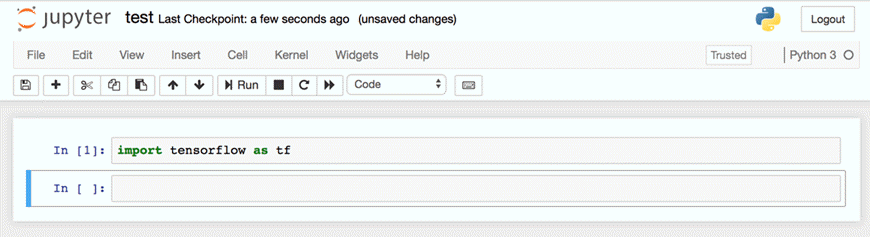
Step 6) Copy and paste the URL into your browser. Jupyter Opens
Step 7)
You can write a new Notebook in the work folder
Part 6: Close connection
Close the connection in the terminal
exit
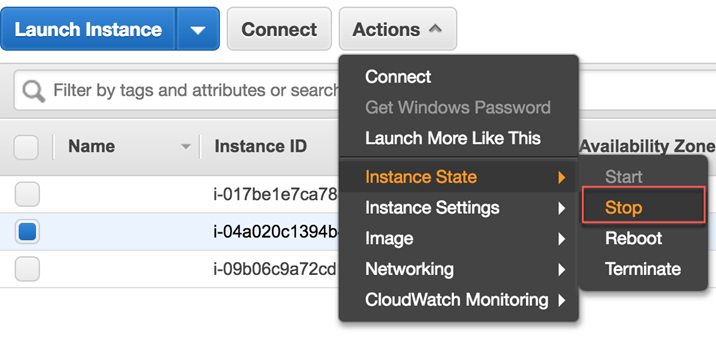
Go back to AWS and stop the server.
Troubleshooting
If ever docker doesnot work, try to rebuilt image using
docker run -v ~/work:/home/jovyan/work -d -p 8888:8888 jupyter/tensorflow-notebook