Users Online
· Members Online: 0
· Total Members: 188
· Newest Member: meenachowdary055
Forum Threads
Latest Articles
Articles Hierarchy
What is Jupyter Notebook? Complete Tutorial
What is Jupyter Notebook? Complete Tutorial
What is Jupyter Notebook?
A Jupyter notebook is a web application that allows the user to write codes and rich text elements. Inside the Notebooks, you can write paragraph, equations, title, add links, figures and so on. A notebook is useful to share interactive algorithms with your audience by focusing on teaching or demonstrating a technique. Jupyter Notebook is also a convenient way to run data analysis.
Jupyter Notebook App
The Jupyter Notebook App is the interface where you can write your scripts and codes through your web browser. The app can be used locally, meaning you don't need internet access, or a remote server.
Each computation is done via a kernel. A new kernel is created each time you launch a Jupyter Notebook.
How to use Jupyter
In the session below, you will learn how to use Jupyter Notebook. You will write a simple line of code to get familiar with the environment of Jupyter.
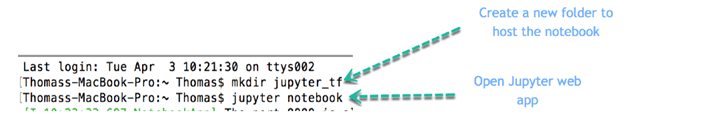
Step 1) You add a folder inside the working directory that will contains all the notebooks you will create during the tutorials about TensorFlow.
Open the Terminal and write
mkdir jupyter_tf jupyter notebook
Code Explanation
- mkdir jupyter_tf: Create a folder names jupyter_tf
- jupyter notebook: Open Jupyter web-app
Step 2) You can see the new folder inside the environment. Click on the folder jupyter_tf.
Step 3) Inside this folder, you will create your first notebook. Click on the button New and Python 3.
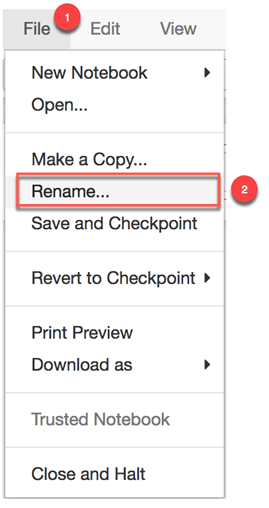
Step 4) You are inside the Jupyter environment. So far, your notebook is called Untiltled.ipynb. This is the default name given by Jupyter. Let's rename it by clicking on File and Rename
You can rename it Introduction_jupyter
In Jupyter Notebook, you write codes, annotation or text inside the cells.
Inside a cell, you can write a single line of code.
or multiple lines. Jupyter reads the code one line after another.
For instance, if you write following code inside a cell.
It will produce this output.
Step 5) You are ready to write your first line of code. You can notice the cell have two colors. The green color mean you are in the editing mode.
The blue color, however, indicates you are in executing mode.
You first line of code will be to print Guru99!. Inside the cell, you can write
print("Guru99!")
There are two ways to run a code in Jupyter:
- Click and Run
- Keyboard Shortcuts
To run the code, you can click on Cell and then Run Cells and Select Below
You can see the code is printed below the cell and a new cell has appeared right after the output.
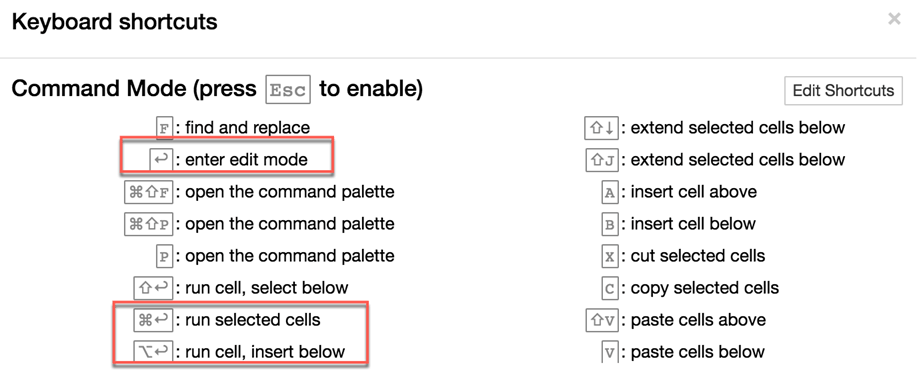
A faster way to run a code is to use the Keyboard Shortcuts. To access the Keyboard Shortcuts, go to Help and Keyboard Shortcuts
Below the list of shortcuts for a MacOS keyboard. You can edit the shortcuts in the editor.
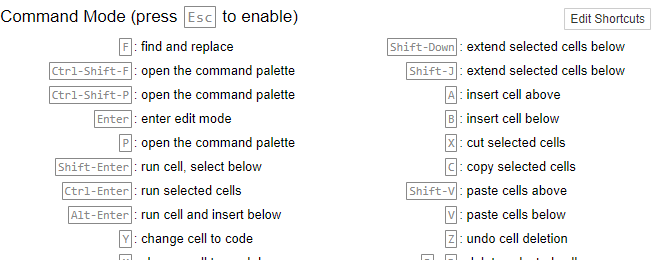
Following are shortcuts for Windows
Write this line
print("Hello world!")
and try to use the Keyboard Shortcuts to run the code. Use alt+enter. it will execute the cell and insert a new empty cell below, like you did before.
Step 6) It is time to close the Notebook. Go to File and click on Close and Halt
Note: Jupyter automatically saves the notebook with checkpoint. If you have the following message:
It means Jupyter didn't save the file since the last checkpoint. You can manually save the notebook
You will be redirected to the main panel. You can see your notebook has been saved a minute ago. You can safely logout.
Summary
- Jupyter notebook is a web application where you can run your Python and R codes. It is easy to share and deliver rich data analysis with Jupyter.
- To launch jupyter, write in the terminal: jupyter notebook
- You can save you notebook whereever you want
- A cell contains your Python code. The kernel will read the code one by one.
- You can use the shortcut to run a cell. By default: Ctrl+Enter