In the business world, risk management is the forecasting and evaluation of financial as well as capital risks together with the identification of procedures to avoid or minimize their impact.
Threats or risks can come from a wide variety of sources including financial uncertainty, legal liabilities, management errors, natural disasters, and other accidents.
Cyber security threats which put IT and data at risk have also become a top risk management priority for many organizations.
To mitigate these risks, a risk management plan includes companies' processes for identifying and controlling threats to all aspects of their business including the items mentioned above as well as proprietary corporate data, customer information, and intellectual property.
Every business, both big or small, faces the risk of unexpected events that could cost the company money or even their livelihood – small businesses do it informally, while enterprises codify it.
Risk management allows organizations to identify, plan and prepare for the worse case scenario and often, times protects them in the long run.
Risk management is important because it tells businesses about the threats in their operating environment and allows them to preemptively mitigate risks. In the absence of risk management, businesses would face heavy losses because they would be blindsided by risks.
Benefits of Risk Management:
- Establish procedures to avoid potential threats and minimize their impact should they occur and cope with the results.
- Confident in business decisions because organizations understand the associated risks and how to prevent them.
- Corporate governance principles that focus specifically on risk management can help a company reach their goals.
- Creates a safe and secure work environment for both staff as well as customers.
- Decreases legal liability while increasing stability of business operations.
- Protection from detrimental events.
- Helps establish a solid insurance plan and identify insurance needs for protection but also to save on insurance premiums.
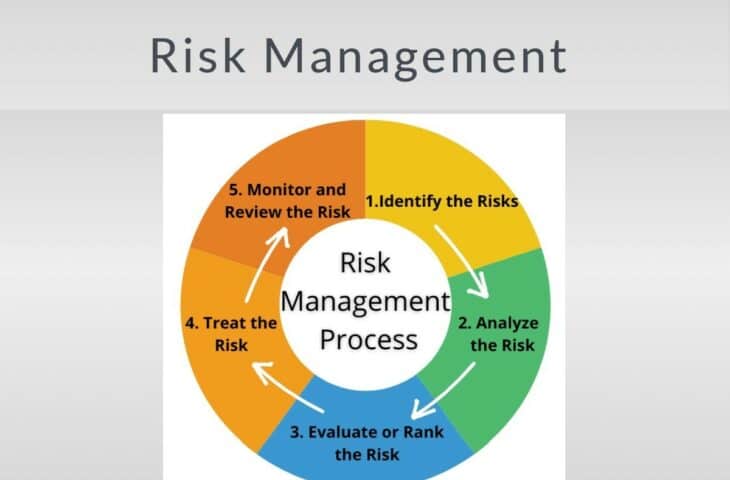
5 Steps for Risk Management
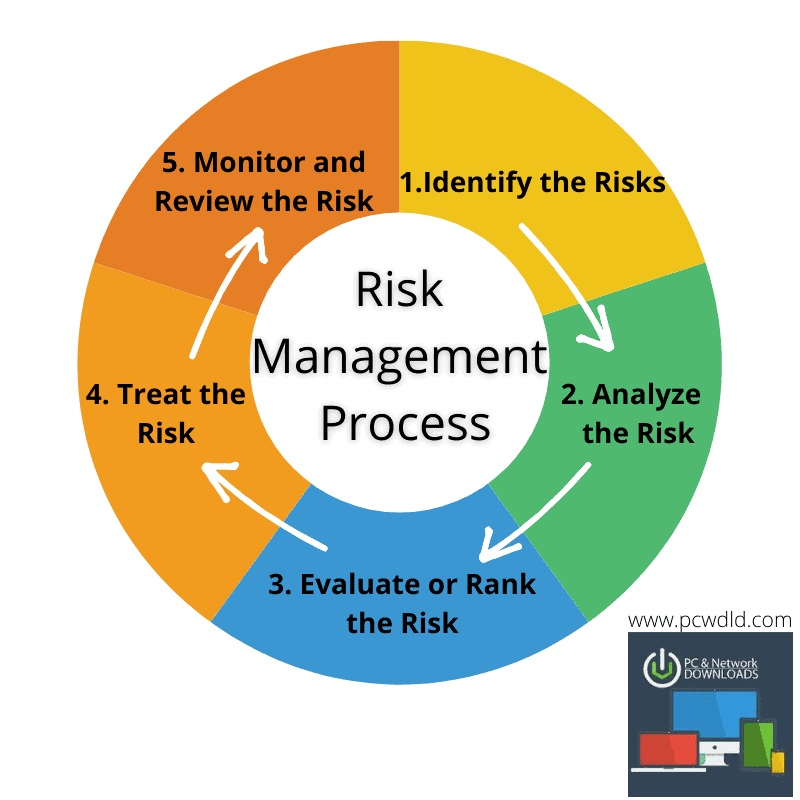
1. Identify the Risks
The four main risk categories of risk are hazard risks, such as fires or injuries; operational risks, including turnover and supplier failure; financial risks, such as economic recession; and strategic risks, which include new competitors and brand reputation.
Being able to identify what types of risk you have is vital to the risk management process.
Organizations can identify their risk through experience and internal history, consulting with an industry professional, and external research.
Other ways to identify risk within an organization includes interviews, group brainstorming, and focus groups.
Once an organization identifies their risk in each category, they can then analyze the risk in more detail.
Risks management is an important process because it empowers a business with the necessary tools so that it can adequately identify and deal with potential risks.
2. Analyze the Risk
In many cases, problem resolution involves identifying the problem and then finding an appropriate solution.
However, before figuring out how best to handle risks, a business should locate the cause of the risks by asking the question, “What caused such a risk and how could it influence the business?”
For example, to determine the severity and seriousness of the risk it is necessary to see how many business functions the risk affects.
When a risk management solution is implemented one of the most important basic steps is to map risks to different documents, policies, procedures, and business processes.
This means that the system will already have a mapped risk framework that will evaluate risks and let you know the far-reaching effects of each risk.
Some questions to consider when analyzing risk include:
- What can go wrong?
- How will it effect the organization?
- What can be done?
- If something happens, how will the organization pay for it?
3. Evaluate or Rank the Risk
Risks need to be ranked and prioritized from most severe to lowest level of risk.
Risks that can be catastrophic to the organization are ranked highest while risks that simply just cause an inconvenience are ranked lower on the list.
By knowing the level of the risk and the impact it will have on the organization, management knows how best to intervene if an when a series of risks occur.
4. Treat the Risk
Now that your organization has identified the risks and ranked them in order of high to low, each risk needs to be eliminated or contained as much as possible.
This is usually done by connecting with the experts in each department or field to which the risk belongs to.
Meeting with individuals to discuss the risk and solution is key to understanding how to eliminate or contain as well as treat the risk should it happen.
5. Monitor and Review the Risk
Unfortunately, there are some risks that cannot be completely eliminated and risk management isn't something that has a start and finish, or end result.
It is an ongoing process within an organization that is constantly changing.
The organization, its environment, and its risks are constantly changing, so the process should be consistently revisited.
If an organization gradually formalizes its risk management process and develops a risk culture, it will become more resilient and adaptable in the face of change.
Monitoring risks also allows your business to ensure continuity.
Here is a short video that does a great job of touching on the different steps for Risk Management:
Approaches to Risk Management
Once the organizations specific risks are identified and the risk management process has been implemented, there are a few different strategies that that be used for different types of risks.
Keep in mind that each risk is unique and may have a different approach for risk management, so don't feel the need to fit each risk into each category.
These approaches are simply a few ways that you can handle risks, but there is no right or wrong solution or method.
Risk Avoidance
Risk avoidance doesn't mean you are avoiding risks when they happen, it actually means avoiding a risk from happening, or prevention in other words. A risk avoidance strategy is designed to deflect as many threats as possible.
This is done to avoid disruptions to business, costly damages, and down time.
Risk Reduction
Adjusting certain aspects of project plans, company processes, and infrastructure can help reduce certain risks.
By doing so, sometimes companies are able to reduce certain risks and this is another approach to risk management.
Making adjustments to reduce risks is a great strategy and can help make your processes more efficient as well.
Risk Sharing
Sometimes risks are shared by different departments, customers, vendors, or external organizations.
Finding out where the risks are shared and working on solutions is a great way to mitigate and manage the risk.
Risk Retention
One of the reasons for ranking risks on a level of high to low is to determine if a risk is worth it from a business standpoint.
Sometimes companies will retail a certain level of risk if the anticipated profit is greater than the costs of the potential risk.

Conclusion
For a business, assessment and management of risks is the best way to prepare for eventualities that may come in the way of progress and growth.
When a business evaluates its plan for handling potential threats and then develops structures to address them, it improves its odds of becoming a successful entity.
If and when risks arise, your organization will be prepared to handle the situation and bounce back with little or no impact from the event.
Risk Management FAQs
What are some common risk management techniques?
Common risk management techniques include:
- Risk avoidance: This involves avoiding the risk by not engaging in activities that could trigger the risk.
- Risk reduction: This involves taking steps to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk, such as implementing safety measures or increasing insurance coverage.
- Risk transfer: This involves transferring the risk to another party, such as through insurance or outsourcing.
- Risk acceptance: This involves accepting the risk and taking no action to control or mitigate it.
Who is responsible for risk management in an organization?
The responsibility for risk management in an organization can vary depending on the size and structure of the organization. In some organizations, risk management is the responsibility of a specific department, such as finance or operations, while in others it is a shared responsibility across the organization. Regardless of the specific arrangement, senior management and the board of directors are typically responsible for ensuring that effective risk management practices are in place.
What are some popular risk management tools?
Some popular risk management tools include:
- RSA Archer: A cloud-based platform for managing risk, compliance, and audit activities.
- MetricStream: A cloud-based platform for managing governance, risk, and compliance activities.
- Qualys: A cloud-based platform for managing security and compliance risks.
- BMC Control-M: A job scheduling and automation tool that includes risk management capabilities.
- LogicManager: A cloud-based platform for managing enterprise risk and compliance activities.