Dot Net framework: It is a platform or a collection of many technologies integrated as a single technology for developing a powerful application. The Dot Net Framework can consider as a platform where multiple technologies/Languages can work together.
Framework: The framework is literally a platform for the software systems, which helps to re-use the pre-defined code. That means the framework encourages re-usability by providing support for code libraries and several scripting languages.
Execution of Non Dot Net applications
To understand the Dot Net framework better, let us compare the execution of the Non-Dot Net application with a Dot Net application.
Even before the Dot Net framework came into existence, we used to develop applications using VB6, VC++, etc. When these applications executed, their respective compilers used to generate an assembly, which is having an extension .dll or .exe depending on the type of application. For instance, when a windows application got compiled, we get a .exe. However, when a web application compiled, it generates a .dll file.
Here, VB6 or VC++ compiler’s task is to generate an assembly( language understood by the operating system, i.e., 0’s and 1’s). Because without a respective compiler, the operating system cannot understand the high-level language.
Without the compiler, it is practically impossible for us to convert the high-level language into 0’s and 1’s.
This compiler-generated assembly code is nothing but the Machine code/Native code.
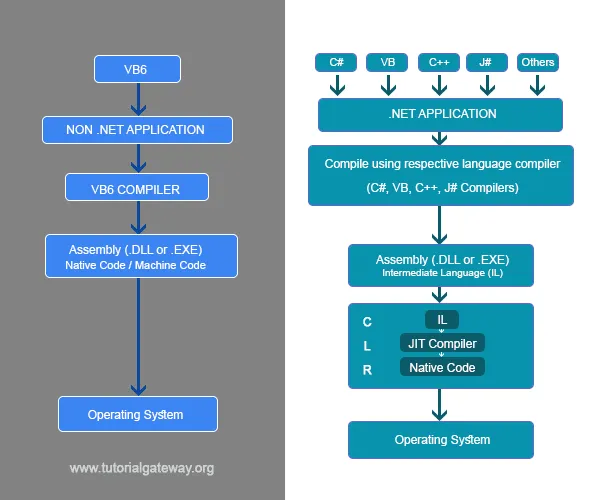
Execution of the Dot Net applications
The main difference in the execution of Non-Dot Net and Dot Net applications is that the compiler of the Dot Net applications like C#, VB, etc., will generate an Intermediate Language (IL) instead of the Native code.
This intermediate language also called as MSIL (Microsoft Intermediate language) / Managed code / CIL (Common intermediate language).
Here, the job of converting the intermediate language into the machine code is done by the run time environment called CLR (Common Language Runtime).
When we install C# Dot Net on a computer, two crucial components will automatically get install.
- Dot Net Framework Class Library.
- Common Language Runtime (CLR).
Within the CLR, there is another component called the JIT compiler. It takes the intermediate language as the input and generates Native code.
The main advantage of this run time environment is its portability. If the operating system is windows, then the runtime environment installed on that operating system is suitable for windows. But when it is Linux, the runtime environment installed on that operating system is suitable for Linux operating system. Which will convert the Intermediate Language(IL) into the native code, which the underlying operating system can understand.
Finally, we can say that as long as the CLR is present on any of those platforms, the Dot Net program get execute on that platform.
Another essential feature of the run time environment is Garbage Collection (automatic memory management). The garbage collector will restrict memory overflow exceptions by clearing the objects which are not in use. That means it will take care of the memory management. However, before the Dot Net environment or framework, we have the burden of memory management.

