Users Online
· Members Online: 0
· Total Members: 188
· Newest Member: meenachowdary055
Forum Threads
Latest Articles
Articles Hierarchy
SAP HR Module 2 PA01 SAP HCM Personnel Administration
SAP HCM Personnel Administration
Welcome to the tutorial about SAP HCM Personnel Administration in SAP HR module. After completing this tutorial you will get knowledge about main processes in Personnel Administration submodule of SAP HCM. SAP HCM Personnel Administration consists of many individual pieces of information that are stored, updated and maintained for each employee in SAP HCM module.
SAP HCM Personnel Administration (PA) processes are important as this is the core submodule containing data for the rest of SAP HCM submodules and not only them. It also essential for the integration between HCM and the rest of SAP modules (e.g., FI). Accurate maintenance of the Personnel Administration (PA) master data is a prerequisite for time management and payroll, for personnel development and learning solutions, and for integration with CRM and finance. And vice versa – incorrect PA master data could cause issues in payroll calculation or in time recording, losing security access to SAP ERP or in travel booking tools.
Employee data in SAP HCM Personnel Administration
Employee data in Personnel administration is stored in so-called Employee Data Infotypes. Data fields are gathered into data groups or information units according to their content. In Personnel Management, these information units are called information types or infotypes for short. For example, individual information, such as last name, first name and date of birth, is defined in data fields.
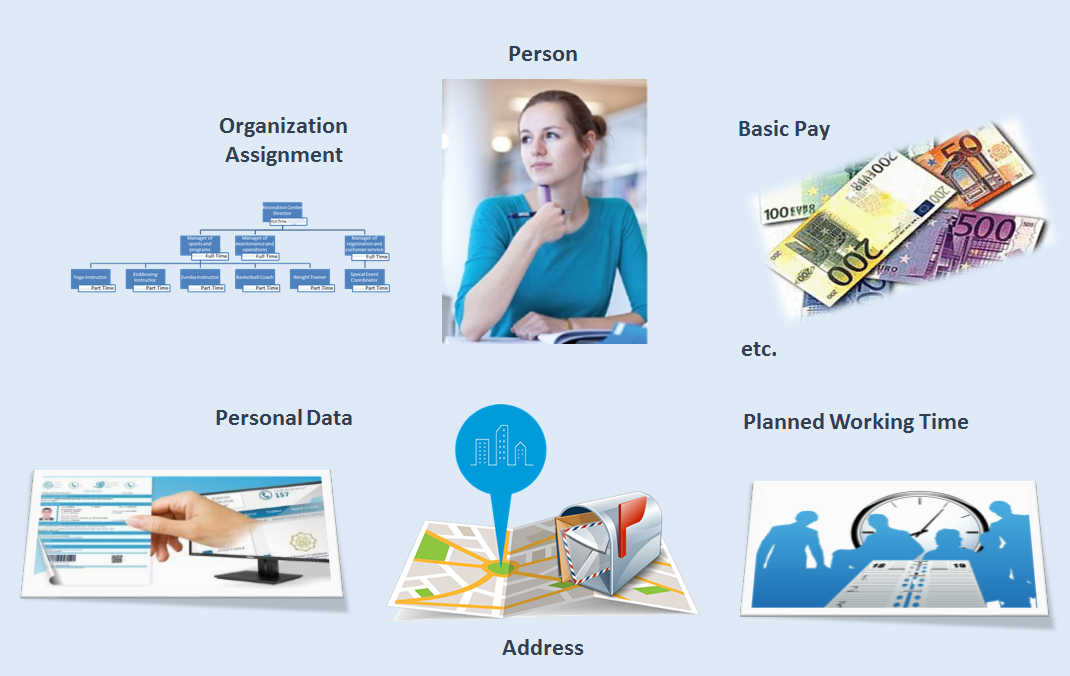 SAP HCM Personnel Administration Employee data Infotypes
SAP HCM Personnel Administration Employee data Infotypes
The infotype is displayed to the end user in the form of a data entry screen that has data entrance logic error checking. Personal data is stored in logical groups. For example, place of residence, street and house number make up the employee’s address and are stored (together with additional data) in the Address infotype. Infotypes have free text names and 4-digit codes. For example, the code of Addresses infotype is 0006.
Infotypes
The system stores 4 digit numbers as well as a description for infotypes. If you know the number you can enter it directly in the infotype field, press Enter and the text for the infotype will be displayed.
If the infotype number is not known or the infotype that you wish to use is not on a static menu, then use the icon of possible entries for drop-down selection on the infotype field to display a list of infotypes. The default listing of infotypes is in numerical order. You can also create a personal ‘hit list’ of infotypes.
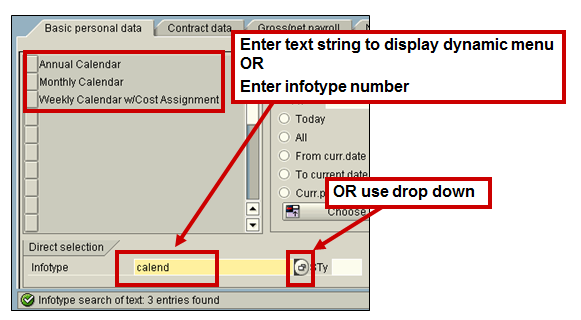 Search for an infotype (Transaction code PA20 or PA30)
Search for an infotype (Transaction code PA20 or PA30)
A subtype is a subdivision of infotype data, i.e. it is a way of storing infotype data in separate groups. Using the Address Infotype as an example, each different type of address is stored in a subtype, for instance, Permanent Address, Emergency Address and Temporary address.
The data entry screens and controlling parameters for each subtype, within an infotype, could contain slight differences. For example, the data screen for Next of Kin addresses could contain additional data fields comparing to the screen for Home addresses. Both sets of addresses are held in a single infotype but are grouped together as subtypes.
Subtypes have their own independent history within an infotype, thus simplifying enquiry on a specific group of data within an infotype. The possible entries drop-down menu displays all subtypes relating to the infotype. The same search functions apply as with infotypes.
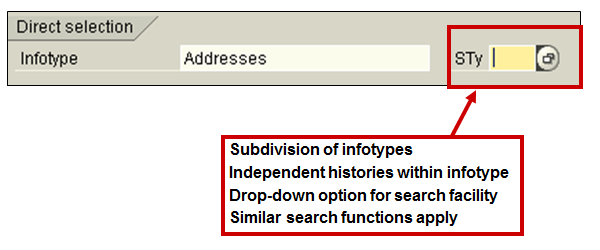 Infotype subtypes selection (Transaction code PA20 or PA30)
Infotype subtypes selection (Transaction code PA20 or PA30)
Main Infotypes in SAP HCM Personnel Administration
Main infotypes supported in SAP PA are:
Contract Data
Work contract – IT0016 Contract Elements (field Contract type)
Hiring Date – IT0000 Actions (Start date of hiring action)
Communication Data
E-mail – IT0105, subtype 0010 Email; subtype 0001 System User
Organizational Assignment
Org. Unit – IT0001 Organizational Assignment (field Org. Unit)
Position – IT0001 Organizational Assignment (field Position)
Cost Center – IT0001 Organizational Assignment (field Cost Ctr.)
Payroll Area – IT0001 Organizational Assignment (field Payr.area)
Personnel Structure
Personnel Area – IT0001 Organizational Assignment (field Pers.Area)
Personnel Subarea – IT0001 Organizational Assignment (field Subarea)
EE Group – IT0001 Organizational Assignment (field EE Group)
EE Subgroup – IT0001 Organizational Assignment (field EE Subgroup)
Emergency Contact
Address – IT0006 Addresses and subtype 4 – Emergency address incl mobile
Personal Data
Birth Date – IT0002 Personal Data (field Birth Date)
Marital Status – IT0002 Personal Data (field Mar. Status)
Address – IT0006 Addresses (subtype 1 – Permanent Residence)
Absence Days
Subtypes, periods, length – IT2001 Absences and IT2006 Absence Quota (Annually entitled vacation)
Organizational History
Based on correctly maintained relationships: Position and start date; Org Unit, Manager’s name & position; Email of the Manager (from the Manager’s IT 0105 Communication, subtype email)
Education Data
All data from IT0022 – Education
Base Salary Data
All data from 0008 – Basic Pay
Job Grade and reference salary
All Data from 1005 Planned compensation on the level of position
Previous employers or positions
All data from IT0023 – Other/Previous Employers & IT9963 Historical data
Accessing Infotypes
Selection of an infotype is obligatory to display a particular type of information for the employee. Menu tabs provide quick access to logically grouped infotypes. The quickest way to access an Infotype is to click on the selection box shown against the infotype description on a menu. The most usually accessed infotypes are showed on the menus. Menus are customer defined and can vary for different user types. If there are more infotype options available than space on the screen to show them, use the scrollbar existing on the right hand side of the individual menu.
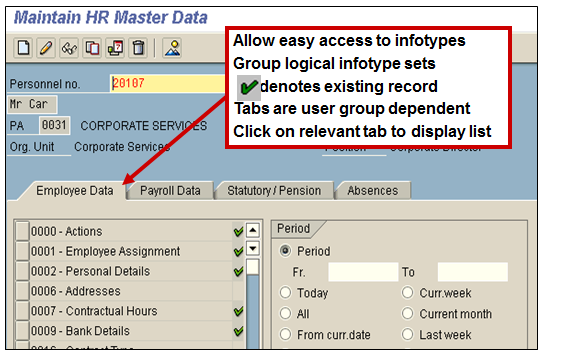 Infotype Menus (Transaction code PA20 or PA30)
Infotype Menus (Transaction code PA20 or PA30)
If the infotype is not shown on a menu, you can select it using text, numeric or other search methods. Enter the partial text of an infotype in the infotype field and press Enter. The system builds a temporary dynamic menu, displaying a list of infotypes that contain the partial text in their description.
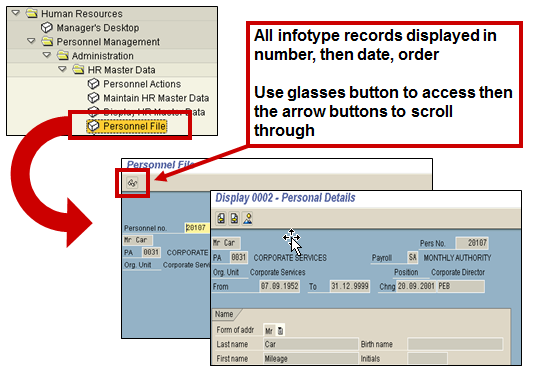 Employee Personnel File (Transaction PA10)
Employee Personnel File (Transaction PA10)
Assign Employees to Organizational Structure
The allocation of employees to the structures in their enterprise is of the utmost importance in Human Resources. It is the first step in entering personal data. You assign employees in the Infotype 0001. By doing this, you allocate employees to the enterprise, personnel and organizational structures.
Information about the organizational assignment of employees is of great importance for authorization checks, for the entry of additional data, and for Time Management and Payroll Accounting.
When you enter data for an employee in the Infotype 0001, Organizational Assignment, the employee is assigned to a company code, a personnel area, and a payroll area. You also assign employees to positions. This results in the assignment of employee to an organizational unit, a job, and a cost center.
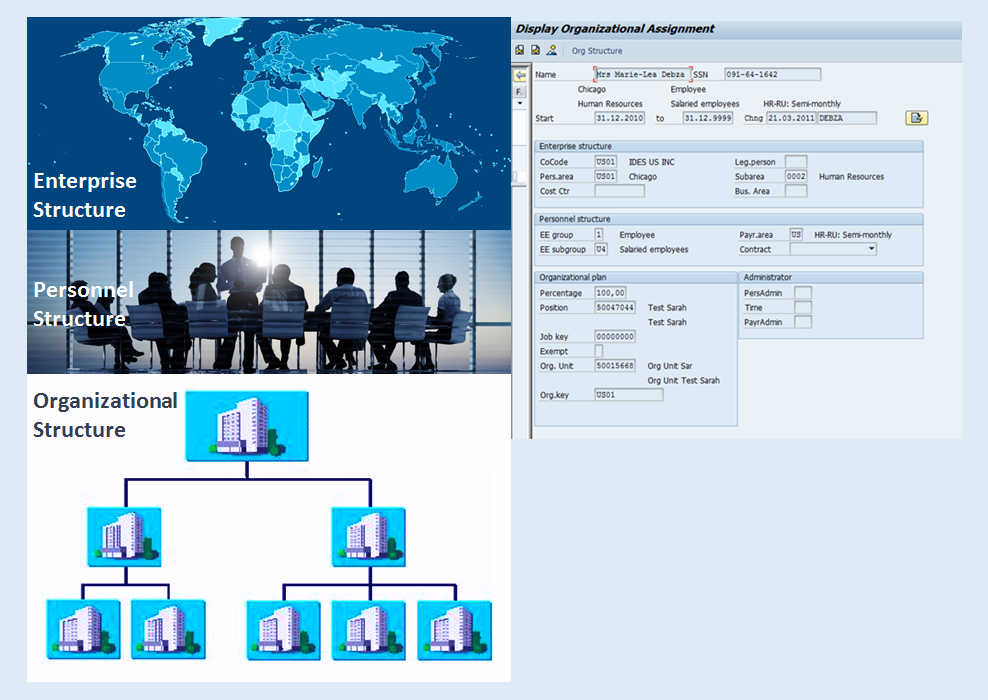 Structures in SAP HCM
Structures in SAP HCM
The Personnel Structure consists of the following elements:
- Employee group
- Employee subgroup
- Payroll area
- Organizational key
The employee group splits employees into various groups, like contractors and externals, active employees or retiree/pensioner.
Employees are distinguished further within the employee group. Active employees are differentiated according to their status – apprentice, hourly wage earner or salaried employee, for instance.
 Personnel Structure
Personnel Structure
Update of the employee data in SAP HCM Personnel Administration can be done in two ways:
1. Single Data Entry
You can edit one infotype at a time through the Maintain HR Master Data screen. For example, you would use this transaction to maintain an individual’s address information.
2. Fast Data Entry
Fast Data Entry lets you to maintain many infotypes for one employee, or the same infotype for many employees, inside one screen.
An example of maintaining several infotypes for one person is the Initial Data Entry transaction in the recruitment module. The Initial Data Entry screen lists many infotypes, letting you to enter numerous infotypes at once.
An example of entering the same data for many employees is the fast entry transaction.
Personnel Action
A Personnel Action is a set of infotypes that reflect specific personnel procedures. Each Personnel Action takes you through a logical set of infotypes, recognized as an infogroup. The infogroups are client defined and are designed to assist in the data input required for a specific personnel procedure. When you perform a Personnel Action, the first infotype in the sequential list is displayed on the screen for you to input the appropriate data entries.
It is common that during the hiring process, data is recorded for the above-mentioned infotypes. These infotypes, as well as the order in which they appear, can be customized to suit your organization’s requirements.
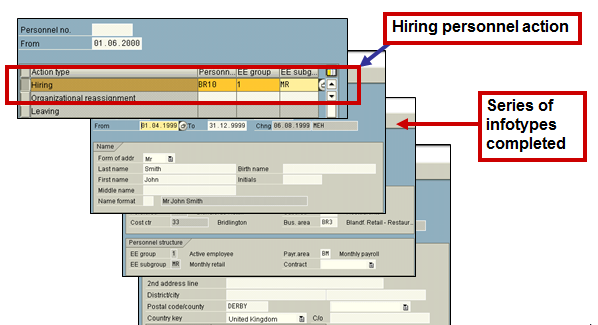 Sequence of Infotypes in a Personnel Action (Transaction PA40)
Sequence of Infotypes in a Personnel Action (Transaction PA40)
It is possible to interrupt an action and recommence it at a later stage.
Interrupting the Action
You should save the data entries made, and then click on the Exit button.
Re-starting the Action
To restart the interrupted action, you will need to re-enter the Personnel Actions menu or the Actions infotype via Maintain Master Data. Click the Execute info group button. This will take you through the sequence of infotypes again.
All infotype data that had been updated before the interruption will be displayed in CHANGE mode (if incorrect data had been entered it can be altered at this point). Infotypes that have not had data entered will be displayed in CREATE mode, ready for data input to be made.
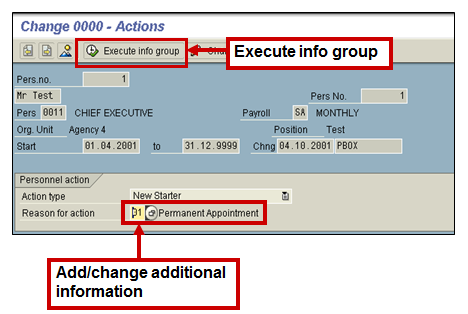 Restart Personnel Action (Transaction PA40)
Restart Personnel Action (Transaction PA40)
When an infotype is changed, the old data is not erased. Instead, it remains in the system so that you can perform historical assessments. Each infotype record is stored with a specific validity period. This means that the system can contain more than one record of the same infotype at the same time, even if their validity periods coincide.
If new information is entered and saved in an infotype, the system checks whether a record already exists for this infotype. If this is the case, the system responds based on guidelines, or time constraints set up for that particular infotype or subtype.
SAP assigns a start date and an end date to HR master data, as well as a large number of table entries. The payroll program requires these dates so that it can perform calculations for specific days, and retroactive accounting for previous periods.
If remuneration infotypes are changed, e.g. due to a salary rise, the system automatically recognises the fact that such changes have happened in the payroll past and triggers retroactive accounting.
Because of automatic retroactive accounting recognition, SAP does not allow you to change the payroll results yourself. Changes are applied by retrospectively changing employee master data and then running the payroll to apply the changes.
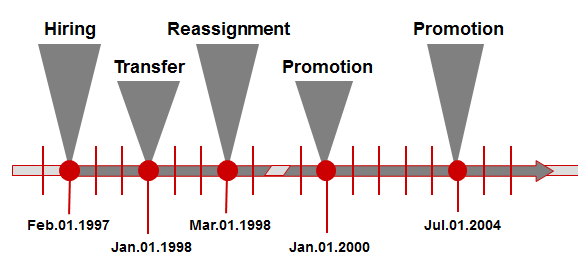 SAP HCM Personnel Administration Data Validity Periods
SAP HCM Personnel Administration Data Validity Periods
Time Constraint determines how often records for an infotype or subtype can be present at the same time. The system uses time constraints internally to ensure data integrity. Time constraints guarantee that exactly the data the system needs to be able to correctly process the employee data, handle personnel administration processes and run payroll for an employee is available in the system. Time constraints keep you from storing mutually incompatible data and prevent gaps from occurring in the data history.
You use time constraints to define the following:
- Whether an infotype record must exist for an employee in the system
- Whether further records of the same infotypes may exist
- Whether these records can overlap in the validity period.
For certain infotypes, different time constraints can be assigned in relation to the infotype subtype.
—

