Users Online
· Members Online: 0
· Total Members: 188
· Newest Member: meenachowdary055
Forum Threads
Latest Articles
Articles Hierarchy
SAP HR Module 4 TM13 SAP Absence Counting Rule
SAP Absence Counting Rule
Welcome to the tutorial on SAP Absence Counting Rule. This tutorial has more of a theoretical focus. The purpose is to convey the concept as well as the configuration of counting rules. There will be a follow-up to this tutorial that will put forth a practical illustration of absence counting.
In the tutorial on the configuration of absence types, we explained that a counting rule must be assigned to an absence type in order for it to be functional. To understand why this assignment is necessary, let’s revisit the three different units in which an absence is valuated. You may recall these definitions from the tutorial on SAP Time Management Infotypes.
Absence days – This is automatically calculated by the system as the number of planned working days during the absence period.
Calendar days – This is a count of the number of calendar days in the absence period, irrespective of the planned work schedule of the employee.
Payroll days / Quota used – This field indicates the number of days which will be deducted from the corresponding absence quota. It is also used in payroll. The calculation of this value can be customized based on the organization’s policy. It is precisely this customization that is carried out via counting rules. A point worthy of mention is that this field may also be seen with the label “Quota used” instead of “Payroll days”. This field label depends on the entry screen assigned to the absence type. We discussed the concept of entry screens in the absence type configuration tutorial. The field label “Quota used”, is displayed when the entry screen 2001 (Quota deduction) has been assigned to the absence type. This is the case when the absence type should be deducted from an absence quota.
Definition of SAP Absence Counting Rule
SAP absence counting rule is configured to count the duration of an absence so that it can be deducted from quota and/or valuated in payroll according to business requirements. The value thus counted is reflected in the “Quota used” field or the “Payroll days” field in the Absences infotype.
Configuration of SAP Absence Counting Rule
The configuration of counting rules can be carried out through the below steps.
Group Employee Subgroups for Time Quotas
To begin with, all employee subgroups that have the same absence and attendance quota types must be assigned the same grouping. To assign this grouping, follow the IMG path depicted in Figure 1.
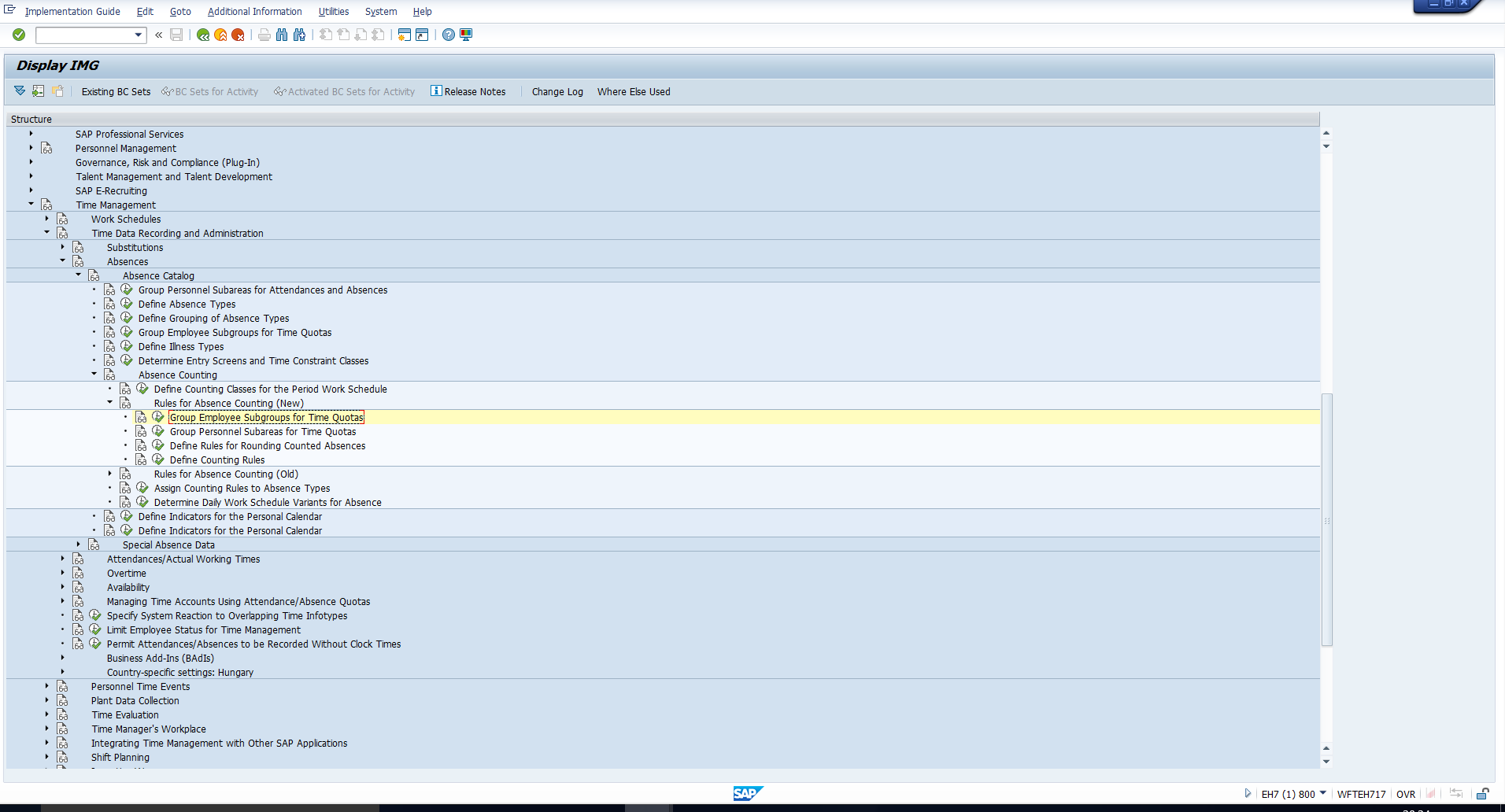 Figure 1: IMG Path to Group Employee Subgroups
Figure 1: IMG Path to Group Employee Subgroups
You will then be prompted to enter the relevant Country grouping, as illustrated in Figure 2.
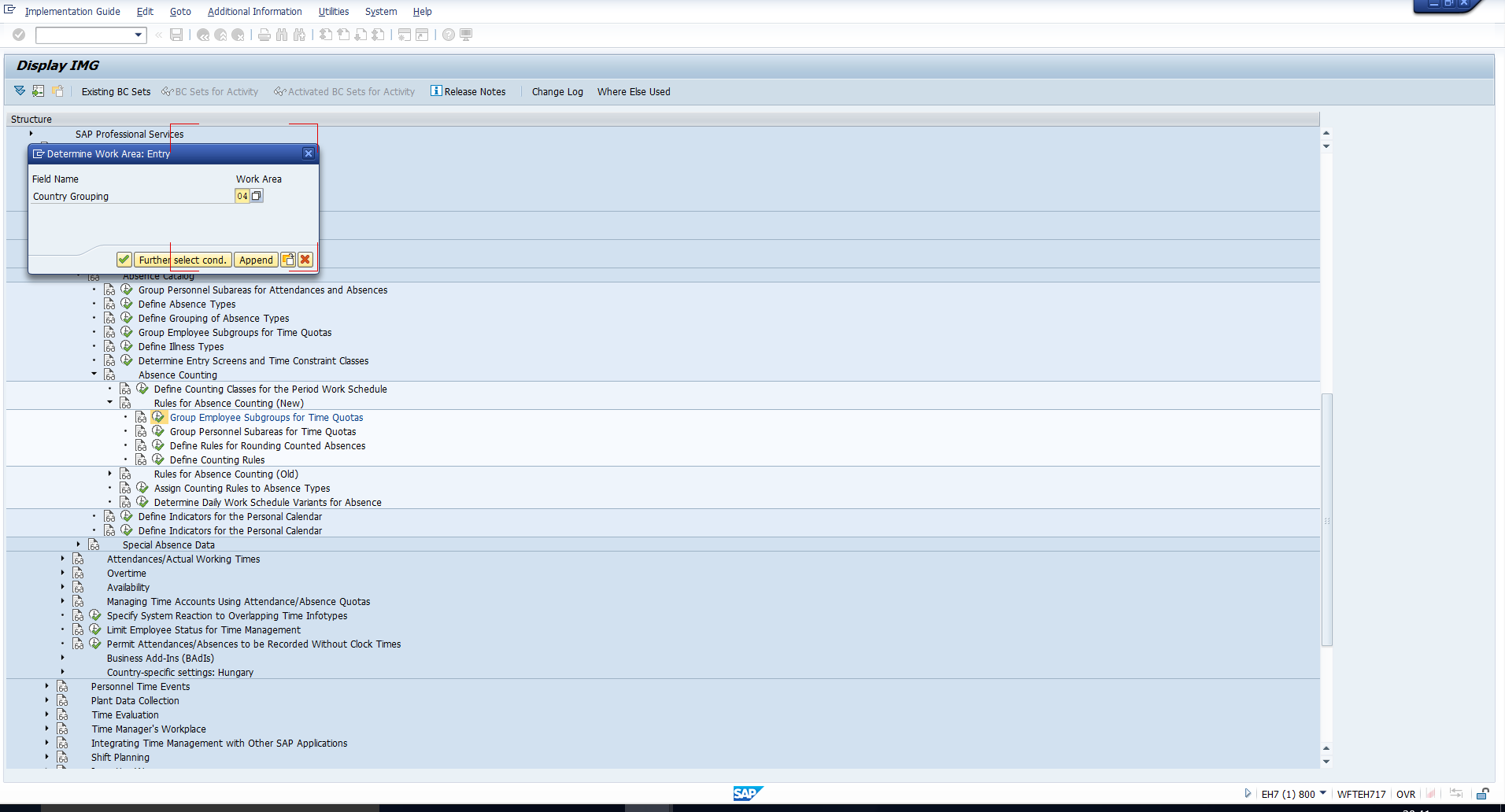 Figure 2: Enter Country Grouping
Figure 2: Enter Country Grouping
Once you enter the country grouping, you will see the screen depicted in Figure 3. Here you must assign a suitable grouping as required. Note that this must be done once for each employee subgroup, and not each time a counting rule is created. So, if the grouping has already been assigned to the employee subgroup(/s) for which the counting rule is required, you should simply make a note of this grouping as you will need it subsequently. For example, note that the grouping assigned to Employee subgroup ‘02’ is 1.
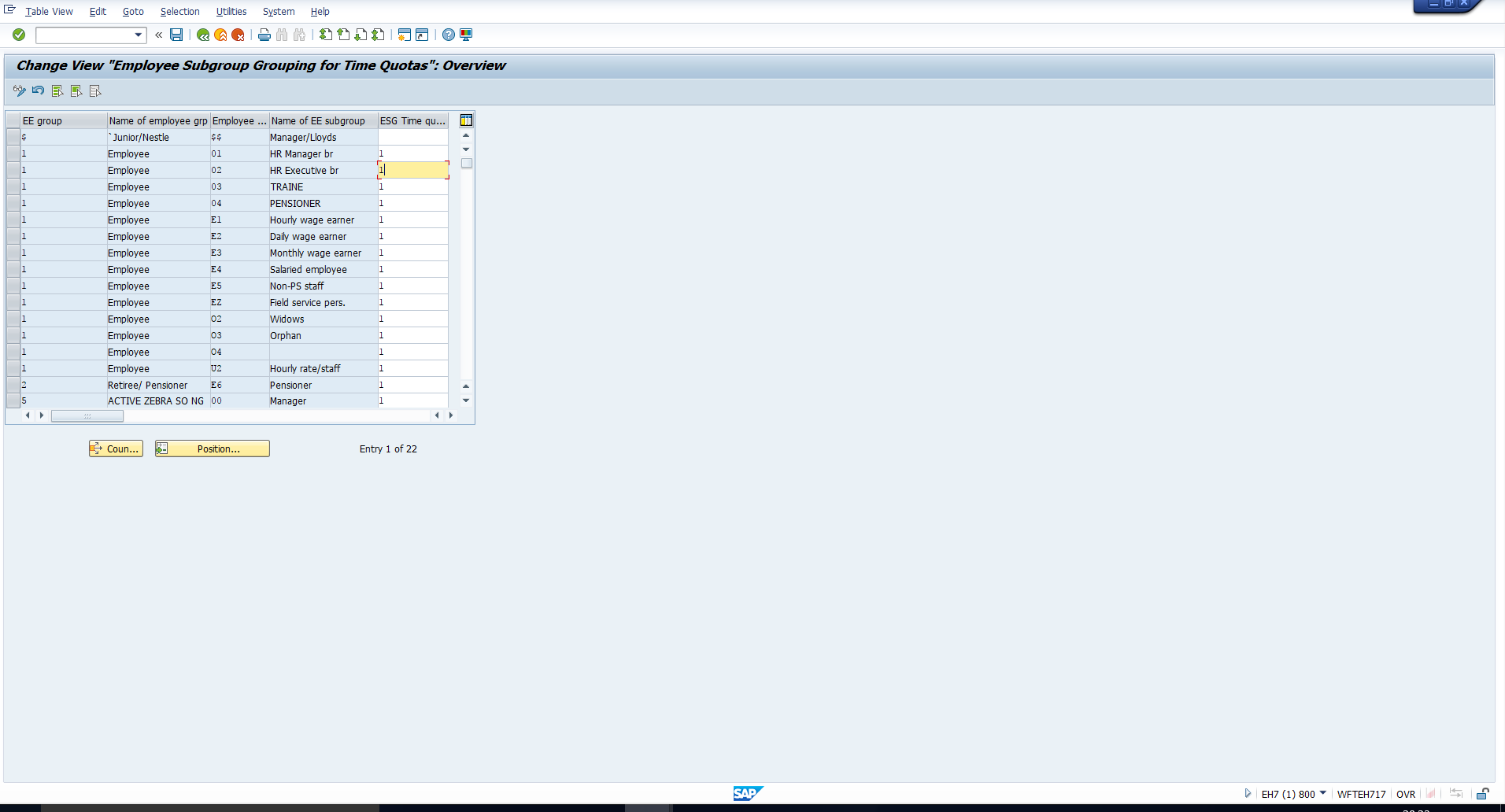 Figure 3: Assign Employee Subgroup Grouping
Figure 3: Assign Employee Subgroup Grouping
Group Personnel Subareas for Time Quotas
Next, all personnel subareas that have the same absence and attendance quota types must be assigned the same grouping. To assign this grouping, follow the IMG path depicted in Figure 4.
 Figure 4: IMG Path to Assign Personnel Subarea Grouping
Figure 4: IMG Path to Assign Personnel Subarea Grouping
Executing this activity takes you to the screen in Figure 5. As in the case of the employee subgroup groupings, assign a suitable grouping if not yet done for the personnel subarea. Otherwise, note the grouping that has already been assigned. For example, note that the grouping assigned to Personnel subarea 1235 under Personnel area 0004 is 01.
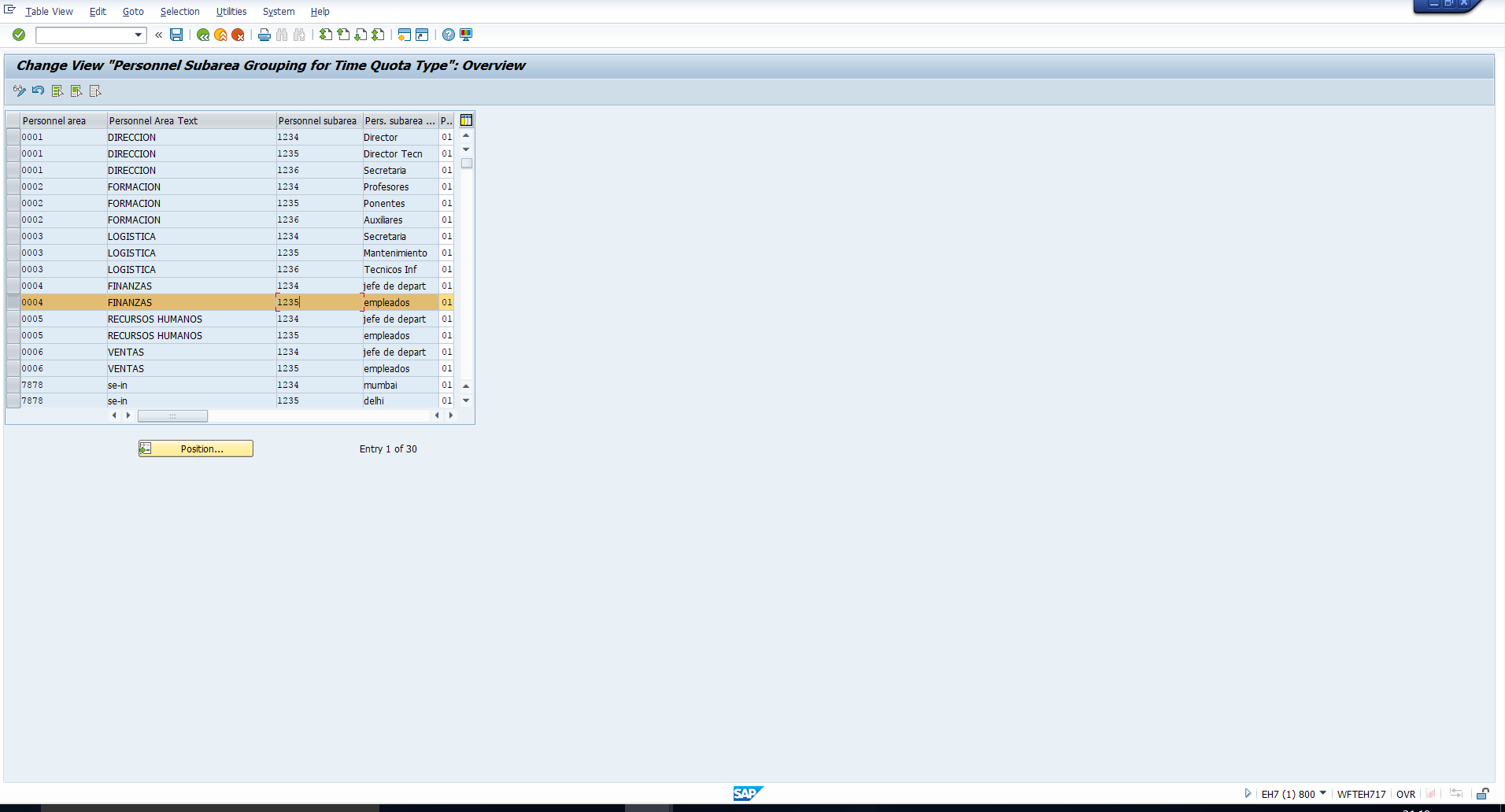 Figure 5: Assign Personnel Subarea Grouping
Figure 5: Assign Personnel Subarea Grouping
Define Counting Rules
To define a new SAP absence counting rule, follow the path depicted in Figure 6.
 Figure 6: Path to Define Counting Rules
Figure 6: Path to Define Counting Rules
The screen that follows is shown in Figure 7. Here you can see all the existing counting rules. Each is created for a combination of Employee subgroup grouping for Time Quotas and Personnel subarea grouping for Time Quotas. Assume that we want to create a new counting rule for the Employee subgroup grouping ‘1’ and the Personnel subarea grouping ‘01’ that we noted in the previous section. You can select any existing counting rule that exists for these groupings as we have demonstrated in Figure 7. Then click on the Copy icon, which we have highlighted below.
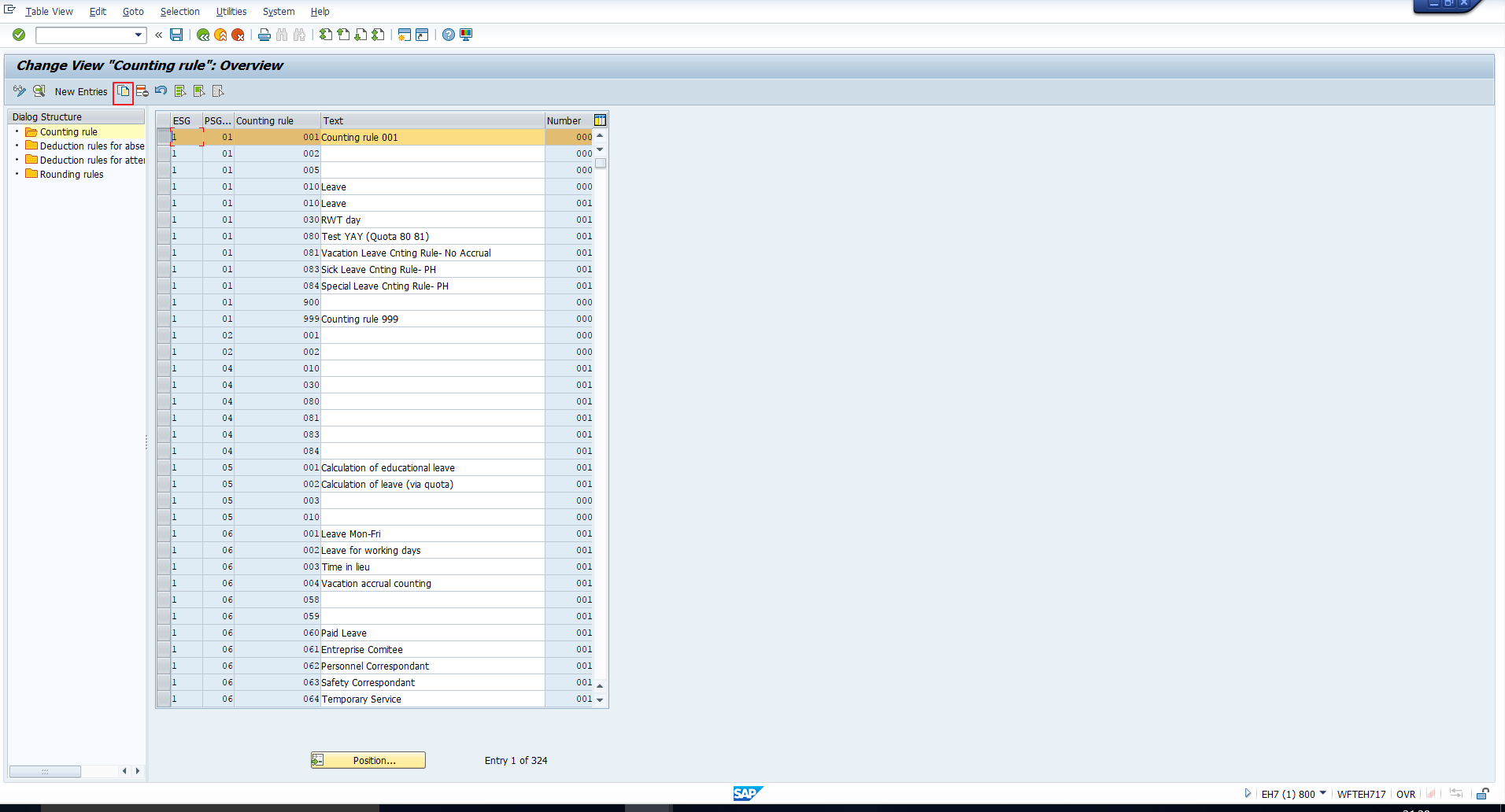 Figure 7: Copy SAP Absence Counting Rule
Figure 7: Copy SAP Absence Counting Rule
This takes you to the detailed view depicted in Figure 8. We’d like to point out that since we’ve used the Copy function, all the values get copied from the reference entry. You can then make changes to the new entry as required. Once you enter appropriate values in all fields and select the required boxes, click on the Save icon to save the counting rule. We will proceed to explain the significance of all the fields.
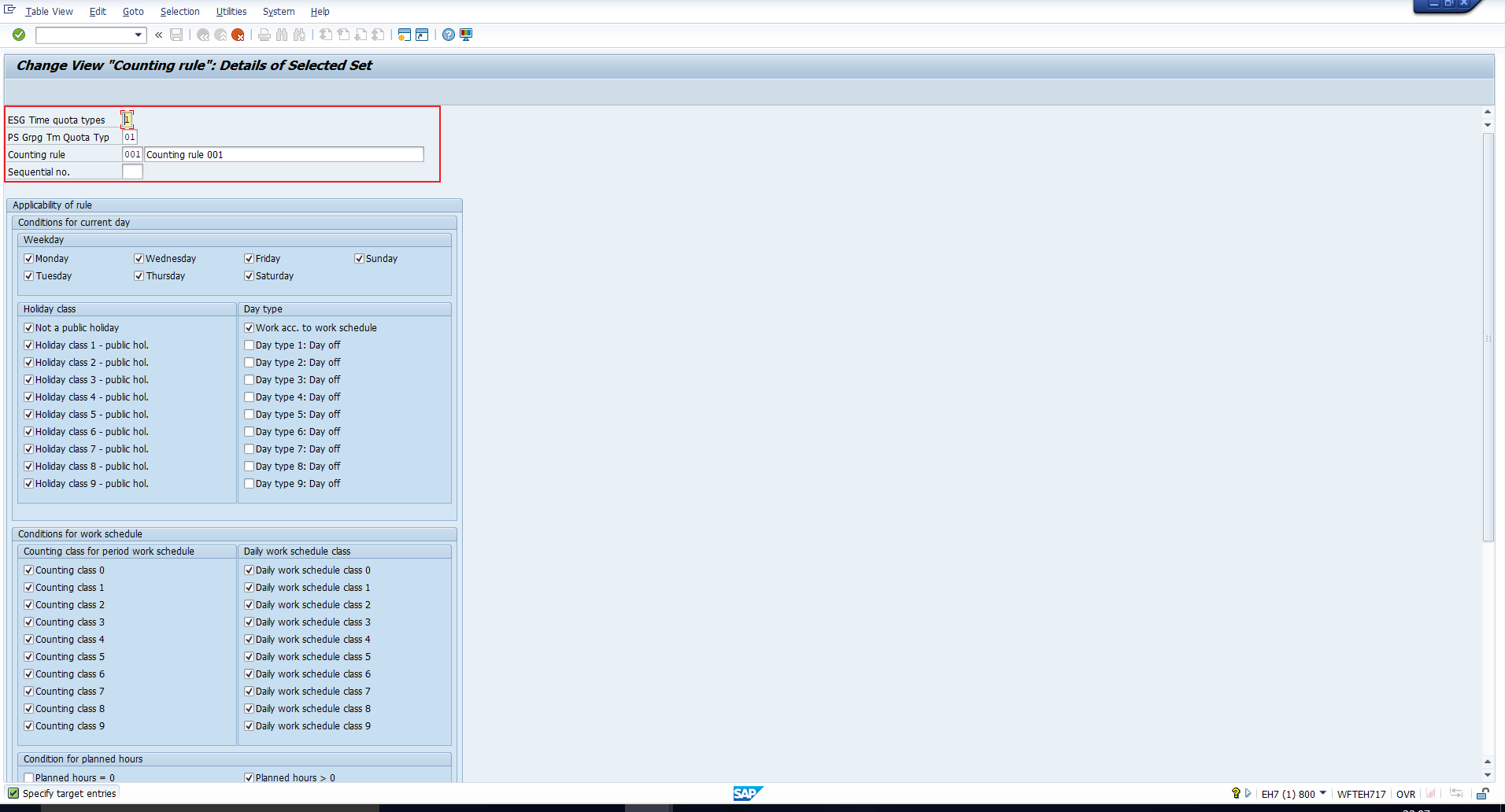 Figure 8: SAP Absence Counting Rule Details
Figure 8: SAP Absence Counting Rule Details
First, let’s understand the structure of the counting rule. Broadly, the screen is divided into the following sections.
HEADER
This section has been highlighted in Figure 8. It comprises the below fields:
ESG Time quota types – Specify the Employee subgroup grouping for which the counting rule is applicable.
PS Grpg Tm Quota Typ – Specify the Personnel subarea grouping for which the counting rule is applicable.
Counting rule – Assign a unique three-digit code and a suitable text to the counting rule.
Sequential no. – Since a counting rule can comprise one or more individual sub-rules, a sequence number must be assigned to each sub-rule. The system then sequentially runs through each sub-rule until it finds one that applies.
APPLICABILITY OF RULE
This section has been captured in Figure 9.
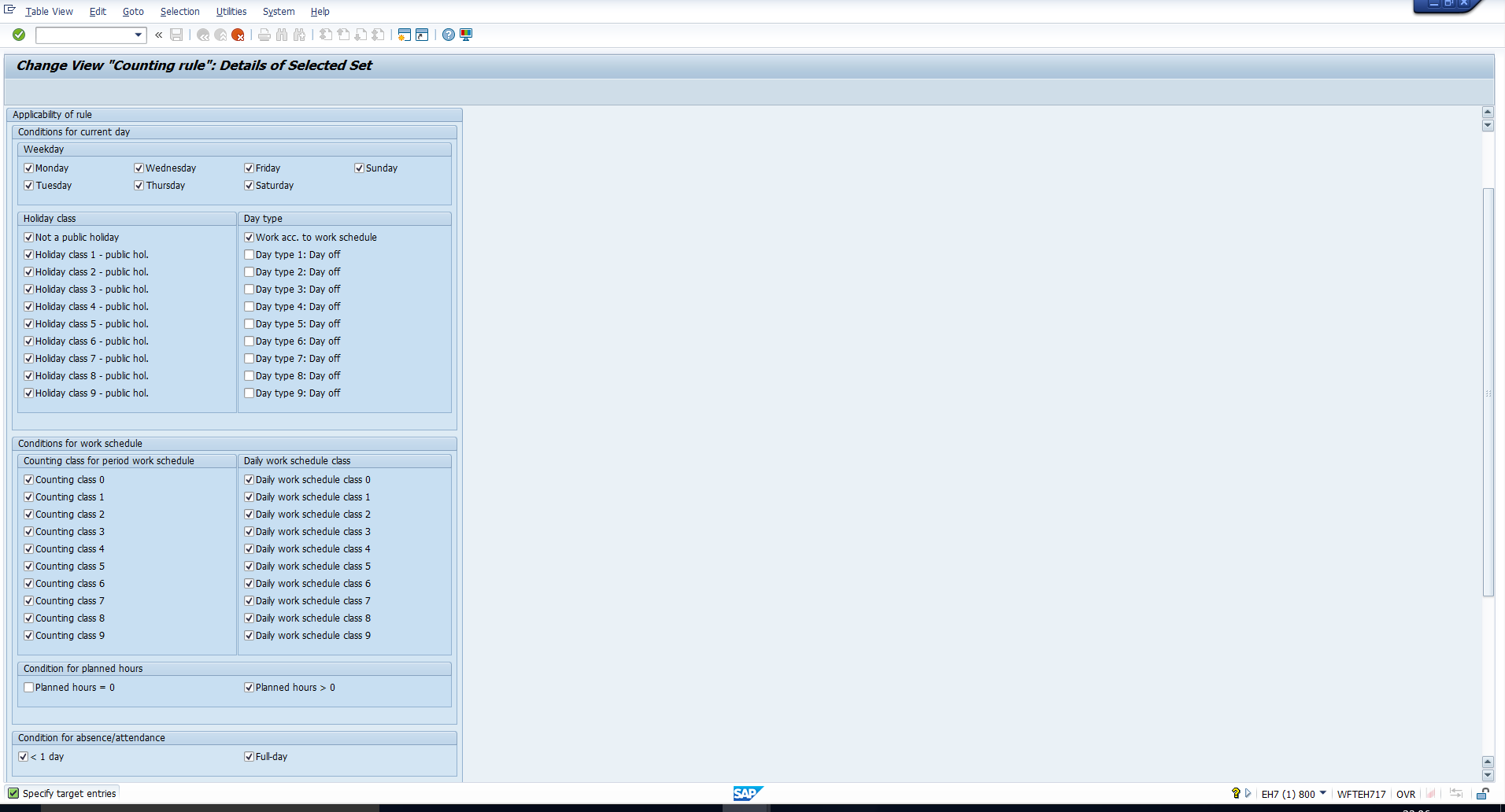 Figure 9: Applicability of Rule
Figure 9: Applicability of Rule
It is used to determine whether the counting rule is applicable to the particular absence scenario. It comprises the below sub-sections:
Conditions for Current Day
Here you must select the conditions for current day for which the counting rule and sub-rule are applicable. In other words, when an absence is entered in the absences infotype, for every day in the absence period, the system will check whether the day meets all the selected conditions in this section. If yes, the day will be counted in accordance with the rule specified in the Counting section below.
Weekday
You must select all the days of the week for which the counting rule and sub-rule are applicable.
Holiday Class
You must select all the holiday classes for which the counting rule and sub-rule are applicable.
Day Type
You must select all the day types for which the counting rule and sub-rule are applicable.
Conditions for Work Schedule
You can also restrict the applicability of the counting rule and sub-rule on the basis of Daily Work Schedule and Period Work schedule.
Counting class for Period Work Schedule
You can select all the Counting classes for Period Work schedule for which the counting rule and sub-rule are applicable. To do so, you must first assign Counting classes to Period Work schedules via the IMG path depicted in Figure 10.
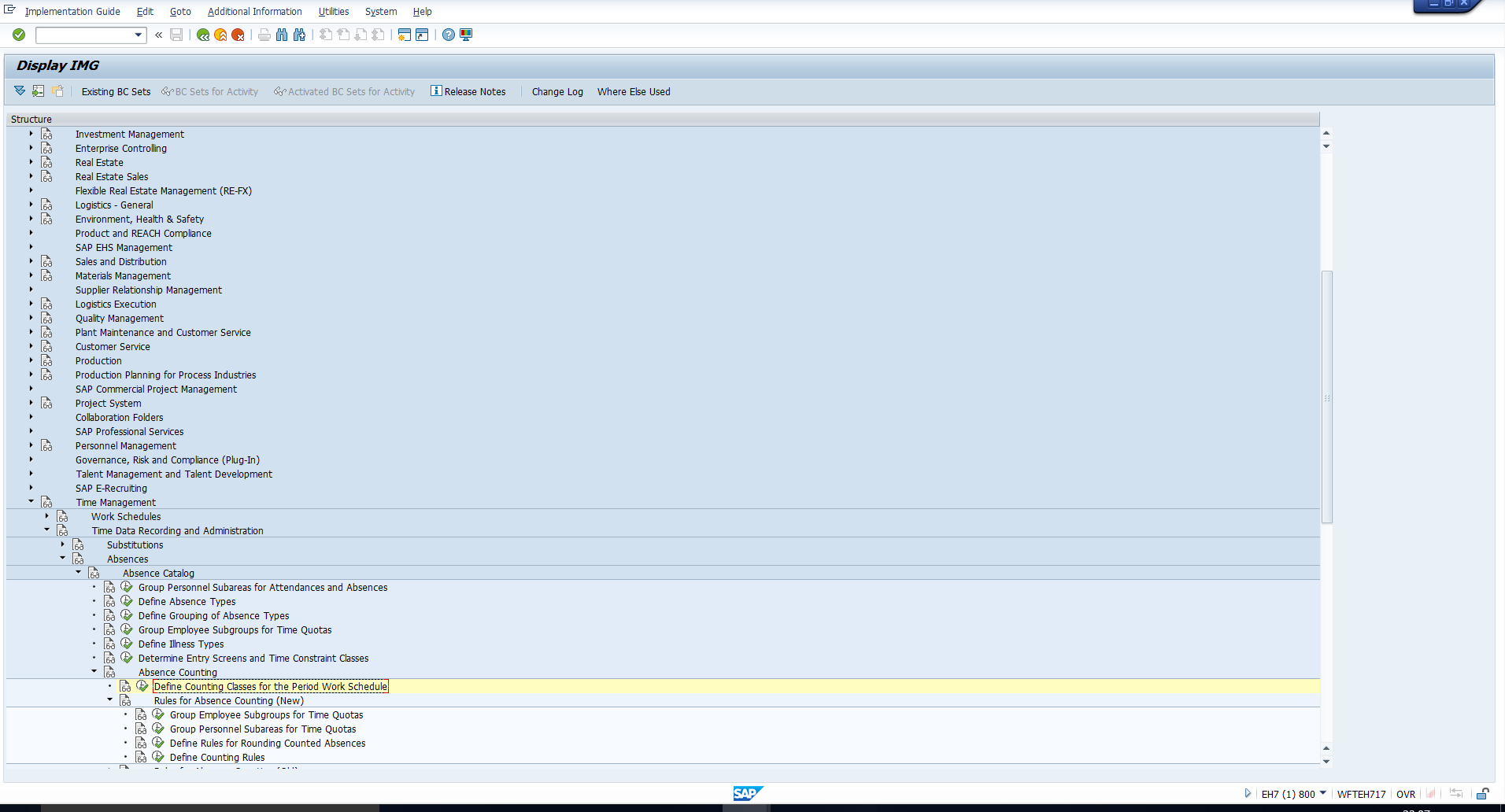 Figure 10: IMG Path to Assign Counting Class to Period Work Schedule
Figure 10: IMG Path to Assign Counting Class to Period Work Schedule
Daily Work Schedule class
You can select all the Daily Work Schedule classes for which the counting rule and sub-rule are applicable. Every Daily Work schedule is assigned a Daily Work Schedule class, as explained in the Daily Work Schedule configuration tutorial.
Condition for Planned Hours
You can specify whether the counting rule and sub-rule are applicable only if the Planned hours for the day are equal to 0, if the planned hours are greater than 0, or both.
Condition for Absence/Attendance
Here you can specify whether the counting rule is valid for partial-day absences, full-day absences or both.
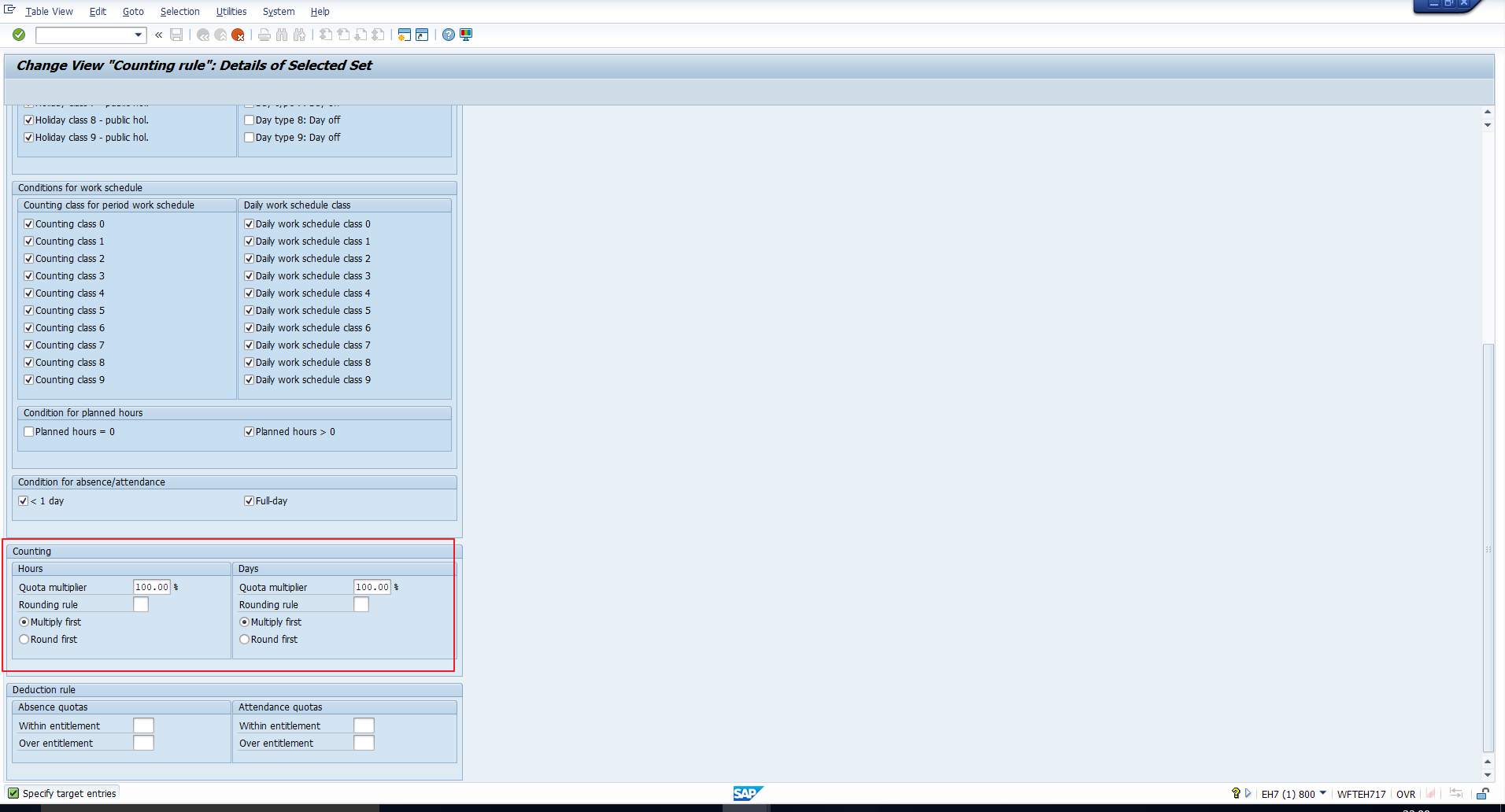
COUNTING
This section has been highlighted in Figure 11. This section serves to instruct the system about how to count the absence day if all the conditions in the Applicability section are satisfied.
Quota multiplier
Here you should enter a multiplier value to specify how the payroll days should be calculated from the absence days. The system uses this multiplier to calculate the payroll days as a percentage of the absence days. For example, if you enter the multiplier as 150, then the system calculates the payroll days as 150% of the absence days.
Rounding rule
As the name suggests, you can assign a suitable rounding rule to round the absence days up/down as per your requirement. We will explain the configuration of rounding rules in a separate tutorial.
Sequence of multiplication/rounding
You should specify whether the payroll hours/days should first be calculated using the quota multiplier, or whether the absence hours should first be rounded.
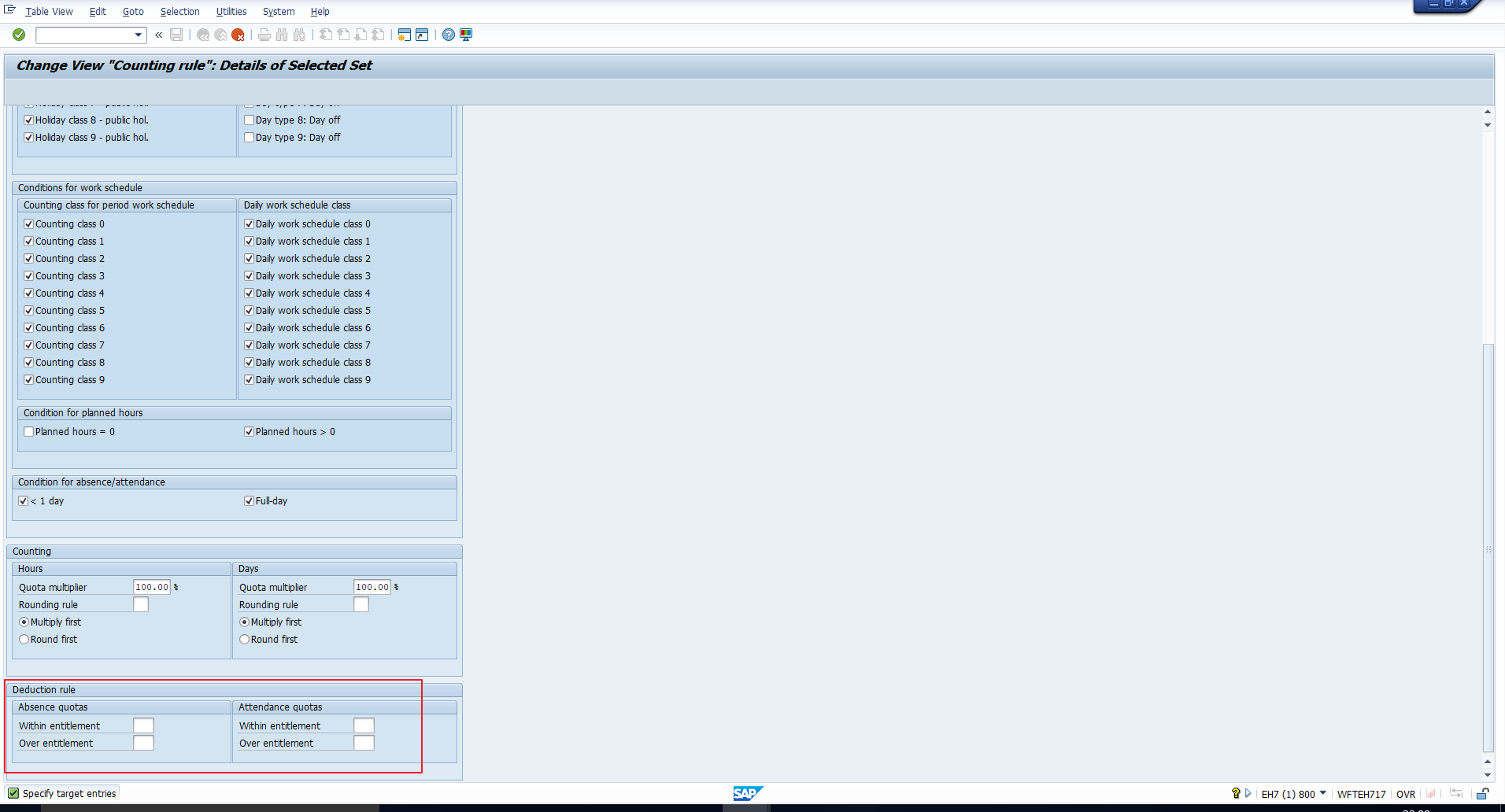
DEDUCTION RULE
This section has been highlighted in Figure 12. Here you assign the required Deduction rule to specify the sequence of absence quotas from which the absence must be deducted. If the absence type does not require Quota deduction, you can leave this blank.
We will cover the configuration of deduction rules in a subsequent tutorial.
Assign Counting rules to Absence types
Once the counting rule has been configured, you must assign it to the absence type via the IMG path depicted in Figure 13.
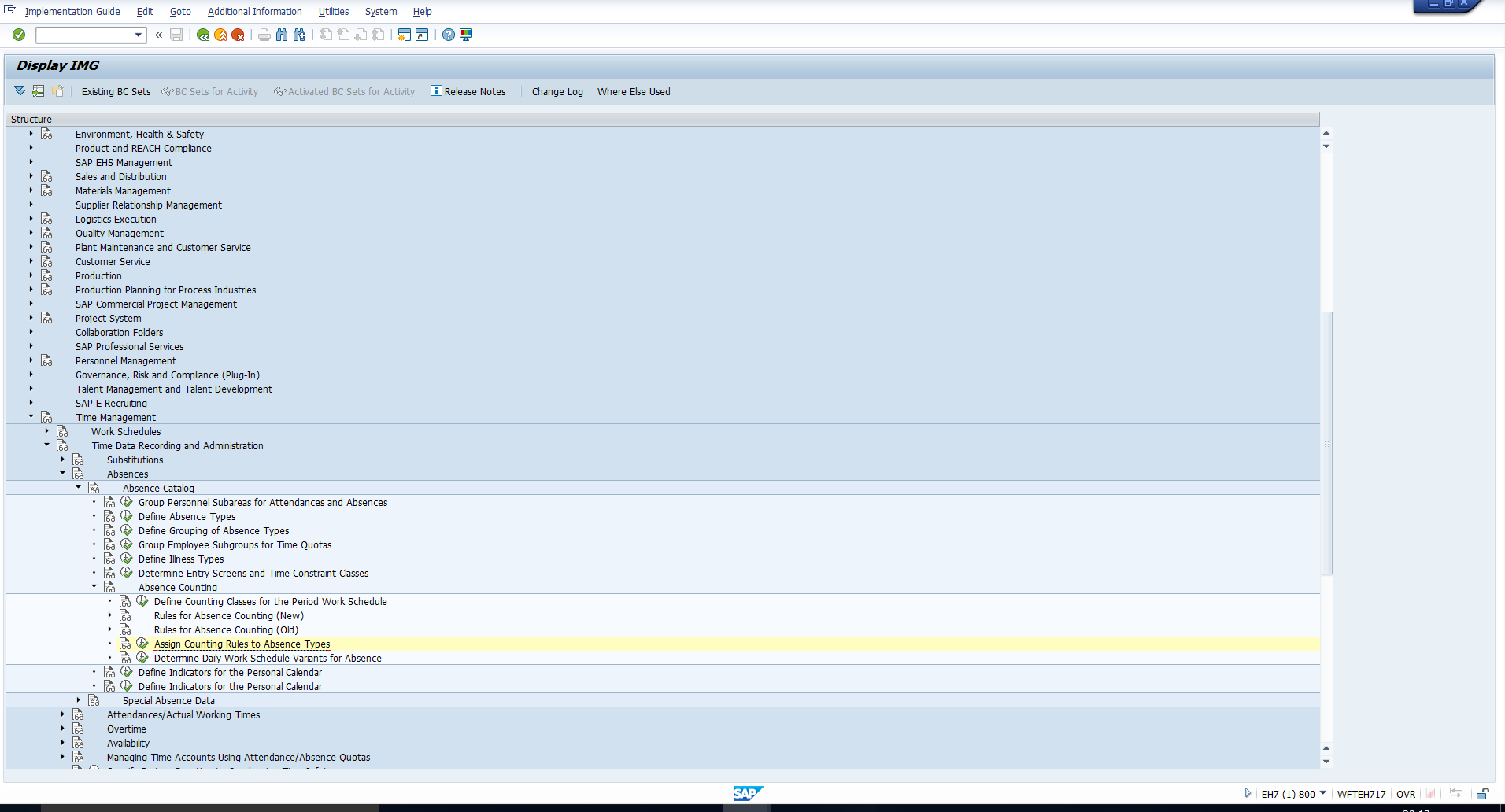 Figure 13: IMG Path to Assign Counting Rules to Absence Types
Figure 13: IMG Path to Assign Counting Rules to Absence Types
This will take you to the screen in Figure 14. Select the Personnel subarea grouping and the absence type for which you want to assign the counting rule. Then click on the Details icon.
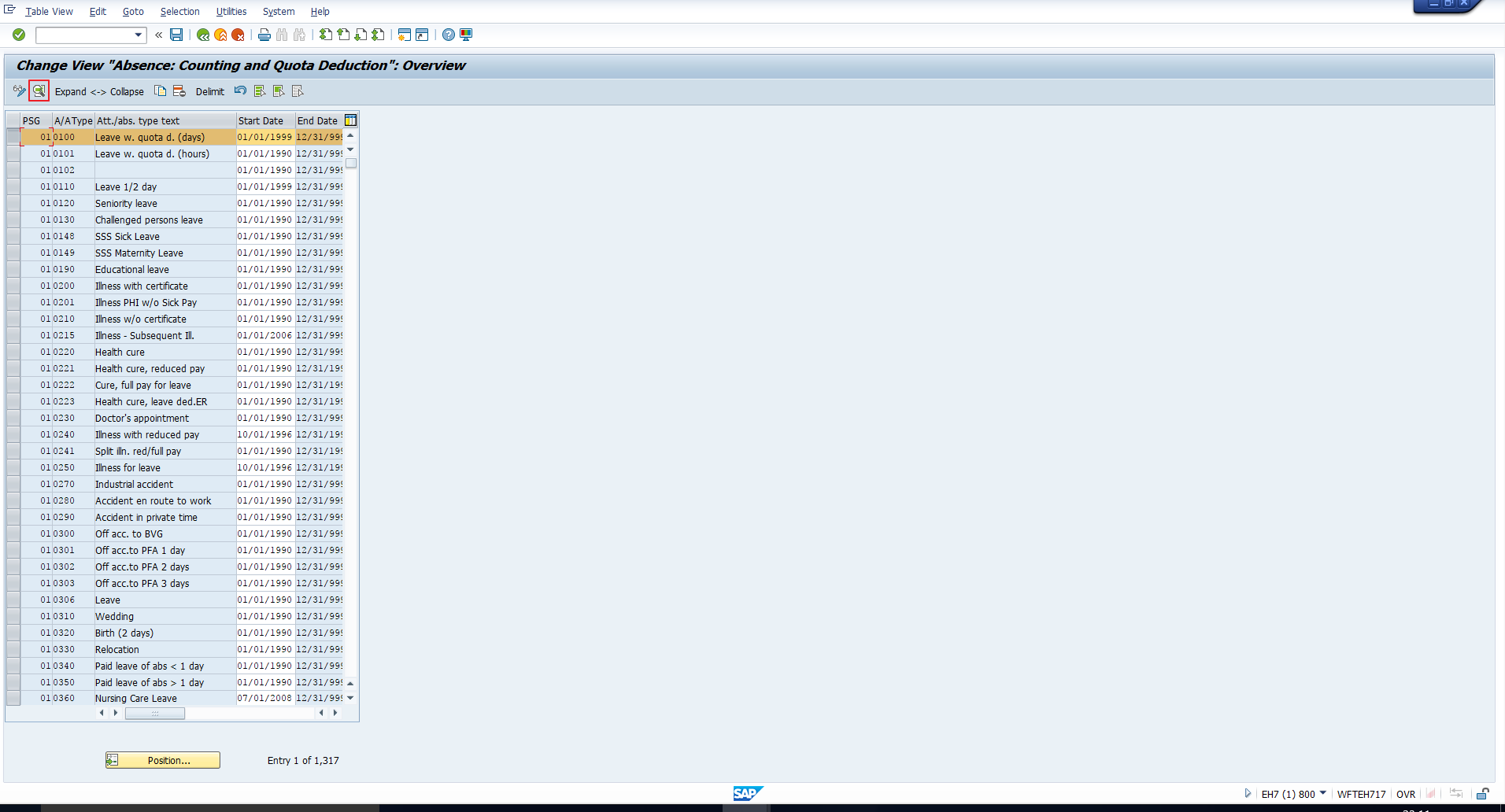 Figure 14: Absence Types Overview
Figure 14: Absence Types Overview
You will see the detailed screen as in Figure 15, where you can assign the newly created counting rule. Select the Quota deduction checkbox if the absence type should be deducted from a quota.
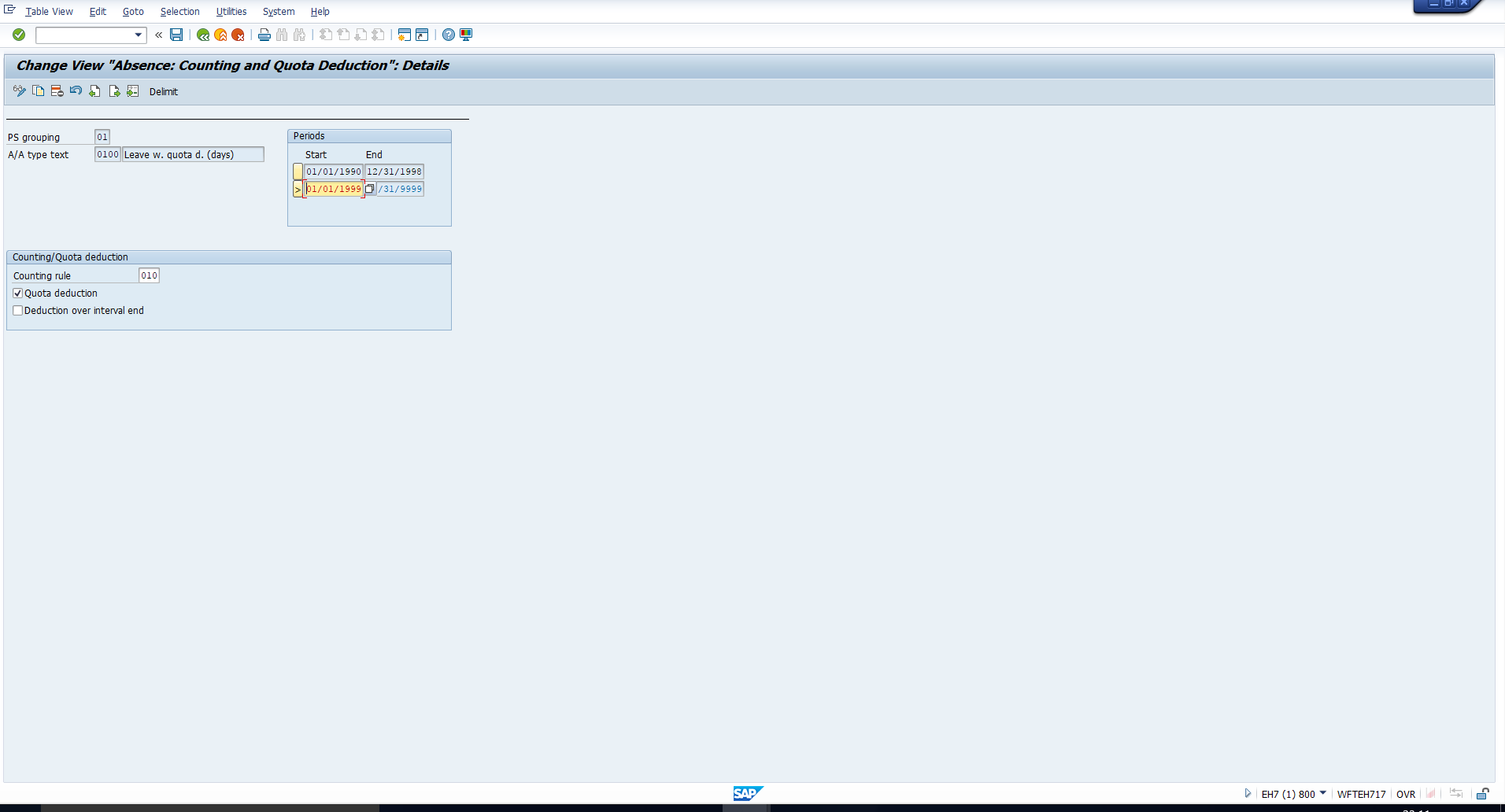 Figure 15: Assign Counting Rule
Figure 15: Assign Counting Rule
Then click on the Save icon to save the changes.
With this we would like to wrap up this tutorial. You should now understand how to perform configuration of SAP absence counting rule.