In this chapter, we will be looking at our business environment to provide systems availability, selecting the most appropriate method for disaster recovery following a disaster. This will be broken down into four distinct sections, and you must understand each of them:
Implementing secure systems design
The importance of secure staging deployment concepts
Troubleshooting common security issues
Disaster recovery and continuity of operations concepts
Exam domain mapping
We will cover the following topics in this chapter:
Given a scenario, troubleshoot common security issues: Unencrypted credentials/clear text, logs and events anomalies, permission issues, access violations, certificate issues, data exfiltration, misconfigured devices, firewall, content filter, access points, weak security configurations, personnel issues, policy violation, insider threat, social engineering, social media, personal email, unauthorized software, baseline deviation, license compliance violation, (availability/integrity), asset management, and authentication issues
Given a scenario, implement secure systems design: Hardware/firmware security, FDE/SED, TPM, HSM, UEFI/BIOS, secure boot and attestation, supply chain, hardware root of trust, EMI/EMP, operating systems, types, networks server, workstation, appliance, kiosk, mobile OS, patch management, disabling unnecessary ports and services, least functionality, secure configurations, trusted operating system, application whitelisting/blacklisting, disable default accounts/passwords, peripherals, wireless keyboards, wireless mice, displays, Wi-Fi-enabled MicroSD cards, printers/MFDs, external storage devices, and digital cameras
Explain the importance of secure staging deployment concepts: Sandboxing, environment, development, test, staging, production, secure baseline, and integrity measurement
Explain disaster recovery and continuity of operations concepts: Recovery sites, hot site, warm site, cold site, order of restoration, geographic considerations, off-site backups, distance, location selection, legal implications, data sovereignty, continuity of operations planning, exercises/tabletop, after-action reports, failover, alternate processing sites, and alternate business practices
IT systems range from desktops and servers used internally to mobile devices, such as laptops that can also be used externally in unsecured environments, such as hotels and airports. We therefore need to harden the systems and operating systems so that they are as secure as we can possibly make them. There are various aspects that we need to look at, depending on the functionality of the device and where they are used. Let's look at all of the aspects that we need to take into consideration, and we will start with a system booting up:
Basic Input Output System (BIOS): The BIOS on every computer is different, depending on the manufacturer, with the BIOS chip on the motherboard giving instructions on how the computer boots up.
Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI): The UEFI is a modern version of the BIOS that is more secure and is needed for a secure boot of the operating system.
Secure boot and attestation: Some newer operating systems, such as Windows 10, can perform a secure boot at startup where the operating systems checks that all of the drivers have been signed—if they have not, the boot sequence fails. This can be coupled with attestation where the integrity of the operation is also checked before booting up.
Example: Your company is a multinational company that requires an operating system that can be used by both desktops and laptops that can provide both secure boot and attestation. Which operating system and feature will you choose and why? At the moment, we are using a BIOS to boot up from.
The first thing that we would do is upgrade the BIOS to UEFI so that it can provide a secure boot. The operating system selected would be Windows 10 as it provides a secure boot where the drivers need to be signed to allow boot up. We would then enable Device Guard, which logs the setting of the operating system and checks the integrity of the software and hardware, otherwise the boot sequence fails.
We need to protect our computer systems against someone stealing the data by stealing the device, re-installing the operating system, and stealing the data. We need to be able to secure the operating systems and hardware by encrypting them by using products such as Microsoft's Bitlocker. Let's look at some encryption methods:
Hardware root of trust: When we use certificates for FDE, they use a hardware root of trust that verifies that the keys match before the secure boot process takes place.
Full Disk Encryption (FDE): FDE uses X509 certificates to encrypt the full disk, but needs a TPM chip on the motherboard to store the keys. Sometimes, these can be referred to as Self-Encrypting Devices. When you boot up from the computer, you are asked for a password to access the system.
Trusted Platform Module (TPM): The TPM chip is stored on the motherboard and is used to store the encryption keys so that when the system boots up, it can compare the keys and ensure that the system has not been tampered with. If the system thinks that tampering has happened, it locks itself up. The only way that it is accessed is by entering the recovery keys, for example, with Bitlocker, it is a 48-character password.
Hardware Security Module (HSM): A HSM is similar to TPM chips except that is removable. The Key Escrow uses a HSM to store and manage private keys but smaller ones can be used for computers.
Exam tip:FDE needs either a TPM chip on the motherboard or a HSM.
Supply chain: It is vital that you have vetting for your supply chain as they may be given limited access to your network and maybe install hardware into your network. You need to ensure that the people working for them have been cleared and the systems that they put in have a certain level of security. You also need to ensure that the company has no bad credit rating and can always supply the hardware and services, even if a disaster occurs.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): EMI coming from motors, fluorescent lights, and radio frequencies interference could affect a systems performance and could cause jamming and prevent IT systems from working.
Electromagnetic Pulse (EMP): EMP is a strong burst of electric energy and causes damage, such as an electrostatic discharge that causes permanent damage. Other forms are military weapons that can cause nuclear explosions or lightning strikes that could have unprotected systems. Surge protectors, uninterruptible power supplies, shielding, and Faraday cages can be used to protect against EMP.
There are various operating systems, such as Linux, that are used by the cloud and many network appliances, and Microsoft has Windows 10 for desktops and laptops, and Server 29016 for servers. There is also Android for many phones, as well as Apples iOS for iPhones and iPads. Let's look at different uses of these:
Network: Network devices such as switches, routers, and firewalls all have some sort of operating system installed so that they can be configured. Normally, these are different versions of Linux, such as FreeBSD, Red Hat, CentOS, or Ubuntu.
Server: A server operating system needs to be secure as these can be used for databases such as SQL server or a mail server, such as Exchange 2016. The domain controller runs on operating systems such as Server 2016 and has a secure boot.
Workstation: Workstation operating systems such as Windows 10 are the most secure client operating systems. Windows 10 has a secure boot and has the ability to use Bitlocker, a version of FDE to protect against data theft.
Appliance: Security appliances are firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and intrusion detection systems are used to protect against attacks.
Kiosk: A Kiosk is a computer in a reception area or foyer; it is used to gain access of the building that you are visiting. Their functionality is limited and they would normally be a workgroup and not connected to the network.
Trusted operating system: A trusted operating system is a secure system normally used by the military where it has multiple layers of security, as it is used to access classified data. It is tied down tightly and changes to the operating system as controlled.
Mobile OS: Apple iOS is an operating system for mobile devices, such as the iPhone and the iPad, and Android is used by all other mobile telephones, such as Samsung.
It is important that we secure all of our IT systems against attacks. Let's now look at hardening the operating system to reduce the surface attack. Let's look at each of these in turn:
Disable default accounts/passwords: The first step when we receive an IT system or an IoT device would be to disable the default administrative accounts and then reset the default passwords to prevent unauthorized access to the system.
Disabling unnecessary ports and services/least functionality: A secure system should only have the minimal number of services enabled and should secure a firewall to block all ports, with the exception of those required for the applications running on them. The secure system should have only the functionality required for business purposes. It should not have any applications running except those authorized.
Exam tip:When receiving a new IT System or IoT device, you need to change the default administrator account and password.
Secure configurations: The military uses a STIG that outlines what setting should be enabled or disabled for a military system. Another reason to secure the configuration of an operating system is for compliance reasons, and periodically, you can use a compliance scanner to ensure that it is still secure.
Application whitelisting/blacklisting: Application whitelisting is a list of approved applications that can be installed onto an IT system. The application blacklist is a list of named applications that are forbidden. The most common reason why someone cannot run an application on an IT system is that it has not been added to the whitelist and not the fact it is on the blacklist.
Exam tip:When receiving a new IT system or IoT device, you need to change the default administrator account and password.
Patch management: Patch management is where updates are downloaded, then tested on an isolated system such as sandboxing, and when they have been thoroughly tested are then rolled out onto the IT systems. This ensures that the IT systems have no vulnerabilities.
Once we have looked at the security of the IT systems, we need to look at the vulnerabilities of the peripherals to see where they are vulnerable:
Wireless keyboards/wireless mice: Wireless keyboards/wireless mice should not be used on secure systems as they are not encrypted and could easy be intercepted by a wireless packet sniffer.
Displays: We need to ensure that we use display filters and do not have the displays facing outside windows. This is to prevent shoulder surfing.
Wi-Fi enabled MicroSD cards: Wi-Fi enabled MicroSD cards have the same vulnerabilities as wireless keyboard and mice, where the data can be intercepted by a wireless packet sniffer.
Printers/MFDs: Printers/multifunction devices are very vulnerable. For example, the printer may have data in the spooler waiting to be printed off and a scanner may have an image stored in their internal memory.
External storage device: External storage devices normally operate with a USB interface and therefore are easy to steal data from. The best way to protect against data theft would be to use Bitlocker-to-go, which encrypts the whole drive, or use a self-encrypting device.
Digital cameras: Digital cameras store information on memory cards that are very easy to remove from the camera. They may have pictures of documents that could be printed off very easily.
Before applications can be used in a production environment, we must ensure that they are as secure as possible to mitigate the risk of being attacked by an outside agency. We are going to look at three different aspects: sandboxing, environment, and secure baseline. Let's look at these in turn:
Sandboxing: Sandboxing is where we can install an application in a virtual machine environment isolated from our network so that we can patch, test, and ensure that it is secure before putting it into a production environment. In a Linux environment, this is known as Chroot Jail.
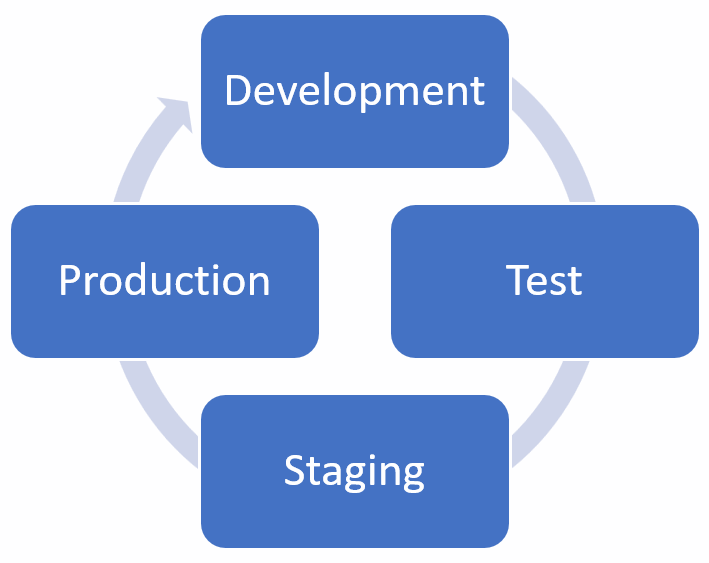
Environment: When we are designing an application, we need a secure staging environment to develop, test, and staging before moving it into production, so let's look at each of these in turn. The environment is shown in the following diagram:

Figure 1: Environment
Development: The first stage of developing an application is where the application developer will look to use the most secure programming language for the task in hand. The application will need different versions before it is fully created and these can be tracked by using version numbers.
Test: Software testers ensure that the functionality of the program fulfills the specifications. They may also employ a secure coding freelancer to carry out regression testing to ensure that the application is fit for production. At this stage, we are not looking at how it affects the production environment as this is completed at staging.
Staging: Staging is the process of rolling out the application to simulate a production environment where an end user will be asked to use the application to ensure that the data output is correct, before it is rolled out to the production environment. Those supporting the application will have training on the application so that they can support it when it is rolled out to production.
Production: The production environment is when the application goes live and end users will have the support of the IT Team. The end users will be asked to give as much feedback as they can should the application have any problems that have not been picked up beforehand.
Secure baseline/integrity: A secure baseline is a list of applications, patches, and the configuration of the applications that improves the security posture of the IT systems. We can use vulnerability scanners to identity any changes that might affect the integrity of the systems. File Checksum Integrity Verifier (FCIV) and System File Checker (SFC) can find identity changes in the integrity of the application.
On a day-to-day basis, the security team will come across some of the following issues, and we will look at how they can mitigate the risk caused by each of them:
Unencrypted credentials/clear text: Unencrypted credentials/clear text are a security risk as they can be intercepted by a packet sniffer or protocol analyzer. We should be using an authentication protocol such as Kerberos that is encrypted and encrypts data in transit.
Logs and events anomalies: There are many logs in a company, for example, firewall logs, antivirus logs, and event viewers on computers and servers, showing attempts to log into the network. The best way to prevent duplication of events and get real-time monitoring would be to install a SIEM system.
Permission issues: Permissions that are incorrectly set can give users more permissions than they need to do their job, but someone with more permissions will not let anyone know that this is the case. Audit user accounts and permissions on a regular basis to identify this.
Access violations: Access violations are where users are accessing data that they are not allowed to see, for example, someone may have access to the payroll file and can see the salaries of everyone in the company. Audit user accounts and permissions on a regular basis to identify this.
Certificate issues: When a new certificate is not working, we should first of all ensure that the certificate is valid and secondly check that it has been added to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities so that the computers trust the certificate provider —see the following screenshot:
Figure 2: Trusted Root Certification Authorities
Data exfiltration: Data exfiltration can be carried out by steganography, and the way to prevent this would be to use a stateful firewall to deeply inspect the data passing through it. Symptoms of steganography are that an image has changed color or a file has just grown that bit larger. We can also prevent someone from stealing data via email or by putting it on an external device; this would be by using Data Loss Prevention.
Exam tip:If a certificate does not work, ensure it is valid and add it to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities.
Asset management: One of the problems a company could face would be the loss and theft of assets. The first stage would be to create an asset register and have all devices asset tagged. We could use cable locks for desktops, laptops, and tablets. We could use Mobile Device Management to remote wipe stolen data and RFID to stop small devices leaving the company. We could use geotracking on the mobile devices so that the device can be found.
Authentication issues: One of the most common authentication issues facing a security team is passwords, where people either forget their password or input the password with the caps lock on and then try it three times and get locked out. Also, as it is a single factor, it is now longer secure enough on its own. Another method would be using biometrics, but even then, the biometric device could suffer from FAR and FRR. One of the best solutions of this would be to use smart cards that are dual factor authentication using certificates, as this would cause the least amount of support calls.
It is vital that all network appliances are properly configured or the company could be vulnerable to attack. Let's look at some of the appliances for this:
Firewall: The purpose of a firewall is to prevent unauthorized access to the network and it is vital that no one employee is responsible for maintaining the rules, and when new rules are added, a second member of the IT Team confirms that the rule is correct.
Content filter: If the UTM or Proxy server has the incorrect content filter set up, then employees may be able to access gaming sites while at work, which would then reduce the productivity of the workforce.
Access points: If the wireless access point was not set up properly, then it could mean that people would be able to access the company network from outside of the building. The wireless access point should be set up using WPA2-CCMP encryption coupled with disabling the SSID and enabling MAC filtering.
Weak security configurations: In general, if we set up IT systems with weak security configuration, then we are leaving the company open to attack. We should ensure that none of the systems use the default username and password and that we use a compliance scanner to ensure that the system is set up as securely as it can be.
Most cybercrime is successful due to the actions of people that work for the company, and therefore we need to set up policies to mitigate against any attack. Let's look at some of the personnel security issues facing the security team:
Policy violation: Companies write policies so that all employees know what is expected of them so that risks can be mitigated. During the induction period, the HR team makes the new personnel aware of, and read and sign the company policies. For example, if I am going to use email, there will be an email policy to guide me or if I am a remote user I am expected to use a VPN to gain access to the company when I am a remote user. Company employees should be reminded that failure to comply with company policies will be seen as a policy violation and could lead to disciplinary action and even being dismissed.
Insider threat: The insider threat is the hardest threat to stop as they may use someone else's credentials. You could install CCTV in all offices so that when the attack is carried out, you can see who is using the source computer at that time.
Exam tip: Accessing the company network externally with a secure connection or VPN is policy violation.
Social engineering: The most common social engineering attacks that affect a business would be tailgating and familiarity. We need to give users annual training, reminding them about the dangers of tailgating and no matter how friendly reception staff get with other employees, they should be aware of familiarity where people will try and access areas that they are not allowed to get into. The security team could give each person a smart card that could be used with a smart card access control system.
Social media: Data that is posted on social media can be used in social engineering attacks and some of the data can be used to try and crack passwords. Annual security awareness training should warn employees of the danger of posting information about the company.
Personal e-mail: We can use DLP templates to prevent sensitive and PII information leaving the company by email, but we cannot control personal email such as Gmail or Hotmail. The security team should use either UTM or a Proxy, and block the URL of personal email providers.
Software is no longer run locally, as some of it is now run or downloaded from the internet. Therefore, the security team needs to be aware of unauthorized software being installed on their IT systems. Let's look as some of the problems that are posed:
Unauthorized software: The symptoms of someone using unauthorized software is that the internet bandwidth is increasing while the disk space on the IT system is reducing. One of the best ways to stop this from happening it to use an application whitelist where only approved applications can be installed.
Exam tip:Someone downloading unauthorized software will increase the bandwidth and reduce the disk space.
Baseline deviation: When we roll out an image to the desktops, we know that they have the same baseline, but we need to ensure that we run a baseline visualizer tool that can detect the changes to the original baseline. We could also use a manual method of baseline comparison on a regular basis.
License compliance violation: The company purchases 10 licenses for an application and then installs it onto the approved desktops. When another member of the company manages to steal the license key and puts it in his desktop, the company has violated the license agreement and the company could face a regulatory fine. We could prevent this violation by installing the software on a share and limit the number of people using the share to equal the licenses that we have purchased. Another license violation would be for someone to install a cracked copy of software on a company's desktop. We could prevent the installation of unauthorized applications by implementing application whitelists.
It is important that if a company suffers from a disaster that they can be up and running as soon as possible. Disasters range from natural disasters such as hurricanes or floods, hardware failure, malicious insider attack, or accidental deletion of data. The main aim of a disaster recovery plan is to get the company back up and running so that it can generate income. Let's look at the different aspects of disaster recovery:
Business Impact Analysis (BIA): BIA looks at the monetary loss if a company is not up and running, coupled with the purchase of new equipment so that the business can continue to operate.
Recovery sites: There are three main types of recovery sites and these are hot, cold, and warm sites. Let's look at each of them:
Hot site: This site is up and running with staff loading the data into live systems on an hourly basis. This makes it the most expensive to maintain, but it has the fastest recovery. We may also use a cloud provider to host our hot site as it would allow us to be back up and running immediately.
Warm site: A warm site is similar to the hot site but data is backed up on a daily basis so it will take a little bit longer to get up and running than a hot site.
Cold site: A cold site is the cheapest to maintain as it has power and water but no staff or equipment, making this the slowest site to get up and running.
Order of restoration: Once a disaster has happened, it is important that we look at the services needed to get a company back up and running. We would rank them as critical, essential, or non-essential, and we would work on getting the most crucial service up and running first. However, if you are restoring from a differential or incremental backup, you would have to restore the full backup first and then the differential/incremental tapes required.
Exam tip:Cloud providers and multinational companies can only store data within the region that it was created in.
Geographic considerations: Where your data is located has a major impact on the restoration phase following a disaster, and we need to look at the impact of each of these. We will look at distance, off-site backups, and location selection:
Distance: We know that the fastest site to restore is a hot site, but if the hot site is 200 miles away, think of the logistics in getting the company personnel to that site. This may take a few days to organize.
Location selection: The location of the hot site is critical in how fast we can recover our data and systems. We need to ensure if it is far enough away and if one region suffers power failure or is hit by a hurricane, can we get it back up and running? This is why the cloud would be a good choice.
Off-site backups: When we back up our data, we should be storing backup tapes in a fire-proof safe and keeping our latest copy off-site, in case we suffer from a natural disaster such as a flood, fire, or hurricane.
Data sovereignty: Data that has been created and turned into digital data is subject to the laws and regulations of the company that created it. It cannot be moved to another region – even for a backup reason. This affects both cloud providers and multinational corporations, as they cannot just simply move data where they want to.
Legal implications: Digital data is subject to the laws and regulations of the company in which it is created. The company creating the data must be compliant, for example, they may need to hold medical data for 25 years, financial data for 5 years, and normal data for 2 years.
Continuity of operations planning: Companies need to look at each type of disaster and put processes in-place for the company to keep running as quickly as possible. For example, your hot site could be in the cloud or you may have two different sites, and when the disaster happens, you would failover to the other site, keeping the business running.
Disaster recovery exercises: There are two types of exercises that you can carry out to ensure that your company is ready for any disaster; these are structured walkthrough and tabletop exercises. Let's look at both of these:
Tabletop exercise: A tabletop exercise is paper-based, where all parties meet around a table and discuss how they would deal with a disaster scenario.
Structured walkthrough: A structured walkthrough is where a disaster is carried out physically with all parties involved. The military would call this a mission where they would go to a training area and carry out manoeuvres.
After-action reports: Once a company has suffered a disaster, the management of the company needs to review all of the information so that they can reduce the impact or prevent the disaster from re-occurring – this is known as lessons learned.
Failover: Failover can be measured in two different ways. You may set up servers in a cluster where the passive server will take over when the active server fails. Another method of failover is where the company has two or more different sites so that when one site fails, the other site takes over and keeps the business functioning.
Alternate processing sites: There are two main alternate processing sites that you could use following a disaster. You could use a mobile site or you could use a cloud provider to provide the infrastructure that you need.
Alternate business practices: You may adopt an alternate business practice to ensure that you can keep the business going, or you may need to purchase services from another company.
Exam tip:If we don't hold a post-incident meeting, then we will not prevent the incident from re-occurring. This is known as lessons learned.
What type of BIOS needs to be implemented if we want an operating system to be able to secure boot?
When a Windows 10 operating systems secure boots, what checks does it carry out relating to drivers?
What type of trust model is being used if we use Full Disk Encryption?
If my laptop is going to use Full Disk Encryption, what type of chip do I need to have installed on the motherboard?
Why would you need to vet your supply chain?
Where does EMI come from and how can it affect your computer systems?
What is the difference between EMI and EMP?
What can a company install to reduce the threat of EMP?
What is the purpose of a Kiosk?
Describe a trusted operating system.
Name two mobile operating systems and where they are used.
When we receive a new IT system or IoT device, what is the first step we need to carry out?
Why would you disable unnecessary ports and services?
What is the purpose of using STIG?
How can I protect an external storage device against data theft?
What should I do to reduce the attack surface on a digital camera?
What is the best way to test a bespoke application before moving it into production?
What are the four stages when designing a new application?
What is an example of access violation?
If I purchase a new X509 certificate and it does not work, what two actions should I carry out?
How can I tell if someone is stealing data using steganography?
What can we do to prevent someone stealing PII or sensitive data?
What is the most common authentication method that can be incorrectly configured?
How can we prevent someone from stealing a laptop and a tablet?
If a remote user is accessing the company's network externally and decides not to use a VPN, what is he guilty of?
What information should I not post on social media, such as Twitter or Facebook?
What are two symptoms that someone is downloading unauthorized software?
Give an example of license compliance violation.
What is the fastest site to implement during disaster recovery?
If my company is a multinational corporation, can I store New York data in London, in case the New York site falls over?
If my hot site is over 200 miles away, what should I consider to make recovery much faster?
What is a theory-based or paper-based disaster recovery exercise?
What is the purpose of an after-action report?
What is the cheapest disaster recovery site but the slowest to get back up and running?
What is the difference between geotracking and geotagging?
You would implement the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) as it is more secure and has the ability to secure boot an operating system.
When a Windows 10 operating system secure boots, it checks that all of the drivers are digitally signed.
A hardware root of trust is used by FDE.
Full Disk Encryption needs a TPM chip on the motherboard or a portable HSM.
You need to vet people working for companies in your supply chain and also ensure that they are large enough to supply goods and services.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) coming from motors, fluorescent lights, and radio frequencies interference affects a systems performance and could cause jamming to prevent IT system's working.
EMI interferes with IT systems, but EMP destroys them.
A company installs a UPS or a surge protector to reduce the threat of EMP.
A Kiosk is a computer in a reception area or foyer that needs to be tied down so that only the displayed information about the building is available.
A trusted operating system is a secure system normally used by the military where it has multiple layers of security as it is used to access classified data. It is tied down tightly and changes to the operating system are controlled.
Apple iOS is an operating system for mobile devices such as the iPhone and the iPad, and Android is used by all other mobile telephones, such as Samsung.
The first stage when we receive a new IT system or IoT device is to change the default administrator account and password.
You disable unnecessary ports and services to harden the operating system and reduce the attack surface.
A Security Technical Implementation Guides (STIG) is used by the military to ensure that operating systems are tied down tightly.
You should use FDE to protect an external storage device against data theft.
You should remove the memory card to reduce the attack surface on a digital camera.
You should use sandboxing to test a bespoke application before moving it into production.
The four stages when designing a new application are developing, testing, staging, and then production.
Access violation is where a user is accessing data that they should not be able to see.
You would first of all check that the certificate is valid and then check if it has been added to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities.
A file would be larger and an image would be lighter in color.
We can use DLP to prevent someone stealing PII or sensitive data.
The most common authentication method that can be incorrectly configured is a username and password.
We can use cable locks to prevent someone from stealing a laptop and a tablet.
They are guilty of policy violation.
Company information should never be posted on social media, such as Twitter or Facebook.
Your internet bandwidth has increased and your local disk space has been reduced.
License compliance violation is where you steal the license to an application and then install it on your desktop without consent.
The fastest disaster recovery site is the hot site.
No data can only be stored regionally; you would need a backup site in the USA.
You should consider moving your hot site to the cloud.
A tabletop exercise is a theory-based or paper-based disaster recovery exercise.
An after-action report looks at how an incident happened and put measures in place to prevent re-occurrence, sometimes called lessons learned.
The cheapest disaster recovery site is the cold site; it is the slowest to get back up and running as it has power and water and nothing else.
Geotracking can tell you the location of a mobile device and geotagging puts the location on a picture and when it was taken.