Chapter08 Protecting Against Attacks and Vulnerabilities Part 2
The two most common password attacks are the dictionary attack and the brute force attack; let's look at these in turn:
Dictionary attack: For a dictionary attack, we could start by using all of the words in the Oxford English Dictionary and use that list to try and crack passwords, but it cannot crack misspelled names or passwords with special characters such as $ or % as they don't appear in a dictionary.
Which of the following passwords will a dictionary attack crack?
elasticity
el@ST1city
fred123
blueberry
It will crack elasticity and blueberry, but el@STcity is not spelt properly and has numbers and characters not in a dictionary, therefore it will fail. It was also not crack fred123 as it ends in numbers; a dictionary contains only letters.
Brute force attack: Brute force will run through all of the different combinations of letters and characters and eventually will crack the password. the length of the password may slow down brute force but it will eventually be cracked. This is the fastest type of password cracker that will crack all different combinations. Salting a password with randomized characters will only slow brute force down. Brute force comes in two different modes:
Online mode: The attacker must use the same login interface as the user application.
Offline mode: This attack requires the attacker to steal the password file first, and then it will give them unlimited attempts at guessing the password.
Which of the following passwords will a brute force attack crack?
elasticity@abc123
el@ST1city
fred12redrafg
blueberryicecream12345
It will crack them all—eventually.
Hybrid attack: A hybrid attack is a combination of both dictionary and brute force.
Account lockout: Account Lockout is the number of attempts a user can make to insert their password before being locked out of the system. If I set account lockout at three attempts, it will stop both a dictionary and brute force attacks.
Minimum number of characters: Should account lockout not be an option, the best way to slow down a password is salting or key stretching, where randomized characters are inserted into the password. This will prevent a dictionary attack, but will only slow down the brute force attack.
Account lockout with a low value will prevent a brute force attack.
Login errors: Inserting the incorrect password because you have rushed inserting it or have the caps lock on or off will create password errors. If we look at certificates, smart cards, TOTP, and passwords, the password is the most likely to be inserted incorrectly.
Weak implementations: Weak implementations of passwords are as follows:
Using the most common passwords
A low number of characters (less than seven characters)
Simple passwords such as 123456 or abcdef
Default passwords for devices
These make it very easy to guess them using a password cracker. Password is the most common password to be used. The following list shows the most common passwords over the years:
123456
Password
123456789
qwerty
letmein
iloveyou
abc123
football
Over the past few years, the use of wireless in our daily lives and in the office has increased to an extent that if I am booking a hotel room and there is no wireless, then I look for another hotel. As you travel on the railways to and from work, the rail company provides complimentary Wi-Fi. Let's look at the types of wireless attacks:
Evil twin: An evil twin is a wireless access point with no security that is made to look like a legitimate wireless access point; when the user connects to it, all of his traffic is being scanned and he is unaware of this:

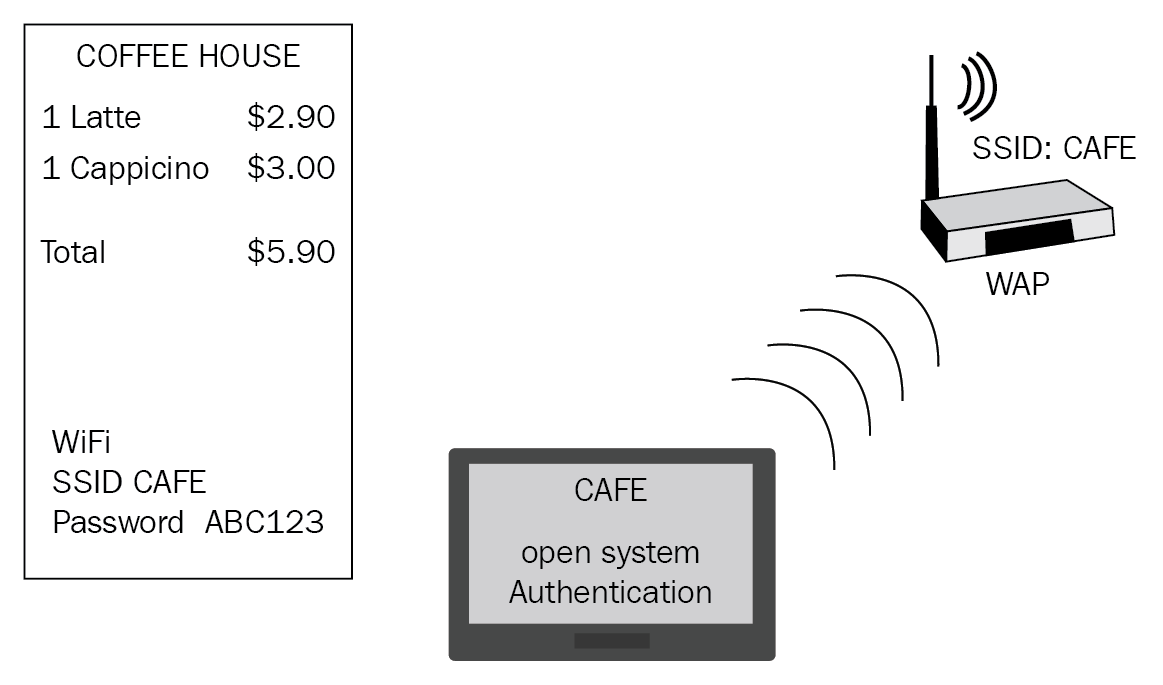
Figure 9: Evil twin
The diagram in Figure 9 will help explain an evil twin wireless access point. The victim has gone to a coffee shop to purchase some coffee; the shop is providing Wi-Fi free of charge, the SSID is hidden, and the WAP password is included on the receipt. However, when the customer sits down at the table to hook up his tablet, he finds an SSID also called CAFÉ; he then thinks that this is the Wi-Fi that he has the details for and he clicks to join the network, but instead of requiring him to put in a Wi-Fi password, it is set to open system authentication, so it connects him immediately. He then thinks to himself what was the purpose of printing the Wi-Fi details on the receipt? He can connect automatically and he is unaware he has just joined an evil twin network where all of his data will be intercepted by a wireless packet sniffer. The legitimate WAP will not appear as the SSID is hidden.
Rogue access point: A rogue AP is where someone comes into your network and connects their own Open System Authentication wireless access point. Users think that it is great as they connect and get good speed Wi-Fi. The way to prevent a rogue WAP is to use an 802.1x managed switch as it authenticates the device before it can be functional, therefore, the rogue AP will be blocked.
Implementing a 802.1x managed switch prevents rogue WAPs from accessing your network as the AP needs to be authenticated first.
Jamming: Anyone with a transceiver can eavesdrop on ongoing transmissions, inject spurious messages, or block the transmission of legitimate ones. The simplest form of jamming is where the attacker corrupts transmitted messages by causing electromagnetic interference in the network's operational frequencies close to the targeted receivers.
WPS attack: WPS is where a password is already stored and to connect to the wireless network you simply push the button.
WEP IV attack: An initialization vector (IV) is an arbitrary number that can be used along with a secret key for data encryption. The use of an IV prevents repetition in data encryption, making it more difficult for a hacker using a dictionary attack to find patterns and break a cipher. It is very common with WEP. Once an attacker learns the plain text of one packet, the attacker can compute the RC4 key stream generated by the IV used.
Disassociation: A wireless disassociation attack is when you are using your Wi-Fi network and then all of a sudden you are disconnected and you can no longer see the WAP. This is similar to a DDoS attack where every time you connect you are disconnected. The only way to prevent this is to put a cable straight into the WAP.
Exam tip:
A wireless jamming attack uses interference to make the attack.
RFID: RFID systems, like most electronics and networks, are susceptible to both physical and electronic attacks. Like most products, RFID tags (https://www.atlasrfidstore.com/rfid-tags/) and readers (https://www.atlasrfidstore.com/rfid-readers/) can be reverse engineered; however, it would take a lot of knowledge about the protocols (https://blog.atlasrfidstore.com/uhf-rfid-tag-communications-protocols-standards) and features to be successful. Hackers would take apart the chip in order to find out how it works in order to receive the data from the integrated circuit.
Near Field Communication (NFC): NFC is used to make a wireless payment, but the card needs to be within 4 cm of the reader. NFC is built into most ban cards, and if someone with a skimmer is close to you they could steal your details to make a fraudulent transaction. You can prevent this by placing your card into an aluminum pouch or wallet. Remember when you take your card out to ensure that nobody is too close to you.
A penetration test is an intrusive test where a third party has been authorized to carry out an attack on a company's network. Rules have been agreed on, so they just need to identify the weaknesses, should it be exploited as far as it can go.
Penetration testing is commonly known as a pen test. The pen testers are given different amounts of information:
Black box: Black box pen testers are given no information on the company
Gray box: A gray box pen tester is given some information
White box: A white box pen tester knows everything about the system
For example, a pen tester is about to carry out a pen test but has not been given any information on the system. As he arrives at the company, the IT manager offers him a cup of coffee and then give him the local admin account of Server 1. What type of pen test is this? It is a gray box as he has been give some information, even if it is late.
Let's now look at the type of techniques that a pen tester may adopt:
Initial exploitation: This is where the pen tester will assess the information that he already knows and devises a plan so that he can exploit the company. He will look for the weakest point in the company's security at the initial point of exploitation.
Active reconnaissance: Active reconnaissance is where someone actively tries to gain information about the system. This could be running a port scan to see what ports are open and then trying to exploit that port. For example, an attacker finds the username left on one of the corporate desktops; he then rings up the active directory team pretending to be that person and asks for a password reset. This is active reconnaissance as he has carried out an action.
Passive reconnaissance: Passive reconnaissance is where an attacker is constantly gathering information, with the victim knowing that it is being done. For example, an attacker is sitting in a coffee shop where he realizes that two members of Company A's security team are having lunch. The attacker is listening to every word that is said, and the security team is not aware of the eavesdropping—this is passive reconnaissance.
Listening is passive reconnaissance. Password reset is active reconnaissance.
Pivot: A pivot is when an attacker gains access to a desktop computer inside a company that he then uses to attack another computer or server.
Persistence; An advanced persistent threat is an attack in which an unauthorized user gains access to a system or network and remains there for an extended period of time without being detected.
Escalation of privilege; Escalation of privilege is where an attacker exploits a weakness in the system so that they can gain a higher level of privileges on the system.
A vulnerability scanner is a passive scanner that identifies vulnerabilities or weaknesses on the system. For example, there could be missing updates for the operating system, anti-virus solutions, or there could be only one administrator account on the system. Microsoft has a vulnerability scanning tool called the Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer (MBSA). A zero day exploit cannot be traced by a vulnerability scanner; it has not yet been identified and has no updates or patches available.
Let's look at the type of output a vulnerability scanner could produce:
False positive: A false positive is where the scan believes that there is a vulnerability but when you physically check it is not there.
False negative: A false negative on the other hand is more dangerous as there is a vulnerability but the scanner does not detect it. An example of a false negative is a zero day exploit that is attacking the system without there being a way of detecting it.
A pivot is gaining access to one computer so that an attack can be launched on another computer.
Identify common misconfigurations: A vulnerability scanner looks at the architecture and design of the flow of data—is it flowing as it should be? Have services been enabled that should be disabled? Are the firewall rules as they should be? Have the correct permissions been set or are the default usernames and passwords being used, or has someone given themselves a higher level of permissions that they should have?
Security controls: A vulnerability scanner will passively test security controls such as:
Code review: A vulnerability scanner can passively test the source code for programs and applications to find vulnerabilities before the applications are put into production.
Attack surface: A vulnerability scanner can identify services that should not be running, applications that should not be installed, and missing patches, so that the attack surface is as secured as it can be at that time.
Permissions: Have permissions been set correctly, or has a user or application been granted a much higher level that they need? Have short, weak, or simple passwords been allowed when they should not have been?
Baselines: The computer baseline can be checked to ensure that unauthorized applications have not been installed on any IT system.
There are two types of scans, credentialed and non-credentialed. Let's look at these in turn:
Non-credentialed: A non-credentialed scan will monitor the network and see any vulnerabilities that the attacker would easily find; we should fix the vulnerabilities found with a non-credentialed scan first as this is what the hacker will see when he or she enters your network. For example, an administrator runs a non-credentialed scan on the network and he finds that there are three missing patches. The scan does not provide many details on these missing patches. The administrator installs the missing patches to keep the systems up to date as he can only operate on the information produced for him.
Credentialed scan: A credentialed scan is a much safer version of the vulnerability scanner. It will provide more detailed information than a non credentialed scan. You can also set up the auditing of files and user permissions.
Exam tip:A credentialed scan can produce more information and can audit.
A non—credentialed scan is primitive and can only find missing patches or updates.
The penetration test is more intrusive as it is trying to fully exploit the vulnerabilities that it finds; it could cause damage to the IT systems, whereas the vulnerability scanner is non-intrusive as it scans for vulnerabilities. Even the credentialed scan is only scanning the registry/permissions and finding missing matches—it is informational and does not exploit the system, and therefore, is less likely to cause damage to the systems.
In this exercise, we are going to download the Microsoft Baseline Analyzer Tool and run it against your local computer to look for vulnerabilities:
Go to Google and search for and download Microsoft's Baseline Analyzer tool. You can also just enter MBSA and it will find it.
Click on MBSASetup-x64-EN. The MBSA Setup wizard appears. Press Next:
Figure 10
Click on I accept the license agreement, then press Next:
Figure 11
On the destination folder page, press Next.
On the start installation page, press Install, then the installation progress page will appear:
Figure 12: Installation progress
Then, the setup will finish:
Figure 13: Installation complete
A shortcut is placed on the desktop. Double-click it. The UAC prompt appears; press Yes:

Figure 14: MBSA shortcut
The MBSA Management console appears; press Scan a Computer, and then at the bottom right, press Start Scan:
Figure 15: MBSA management console
The scan starts and it downloads security update information from Microsoft. As it is going to compare the computer updates against the latest updates for Windows 10, this will take about 10-15 minutes:
Figure 16: Obtaining security updates from Microsoft
The scan results page comes up; you will notice that the default is Score (worst first). Scroll down:
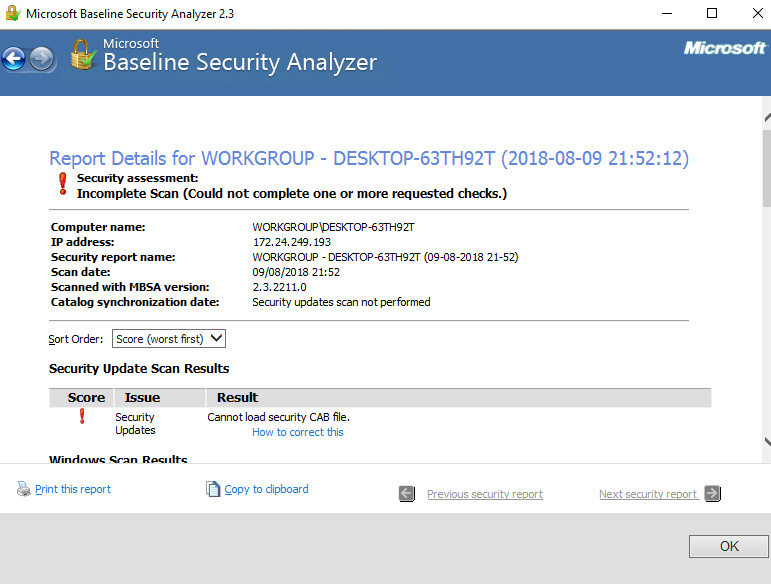
Figure 17
You can see that the MBSA is a vulnerability scanner that would be used as a credentialed scan and that it produces some good results, but it is passive and informational, and did not try to exploit the computer at all:
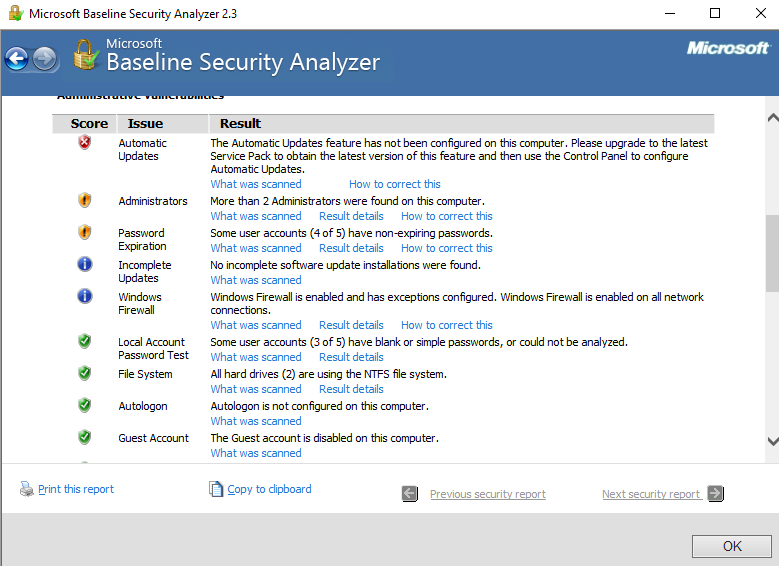
Figure 18: Credentialed vulnerability scan
You will now notice if you have any vulnerabilities on your computer. There are hyperlinks below each item listed, giving you information on how to update your vulnerabilities. Look at each of these in turn and take the appropriate actions.
If I install a freeware program that analyses my computer and then it finds 40,000 exploits and asks me to purchase the full version, what type of attack is this?
What is crypto-malware?
What type of virus replicates itself and uses either ports 4444 or 5000?
What type of virus inserts a .dll into either the SysWOW64 or System 32 folder?
What is a RAT?
What type of virus attacks the windows/system 32 folder on Windows, or the bin/ and /usr/bin/ on Linux
How does a logic bomb virus work?
What is the purpose of a keylogger?
What is a botnet?
Explain a phishing attack.
How does spear phishing differ from a phishing attack?
What is a whaling attack?
What type of attack it is if I leave a voicemail?
What is social engineering tailgating?
What is social engineering?
What type of attack is it if I dress as a policeman?
What type of attack is it if a fireman arrives and you let him into the server room to put out a fire?
What type of attack is it if I am in an ATM queue and someone has his phone to one side so that he can film the transaction?
What type of attack is distributing fake software?
What is a watering hole attack?
What type of attack is it if I receive an email from the CEO telling me to complete the form below by clicking on a link in the email?
One of the bosses asks me to give him the information of one of my peers gave him last week. I am not too sure, but I give him the information; what type of attack is this?
What type of attack is a multiple Syn flood attack on a well-known website that takes it down?
Explain a man-in-the middle attack.
How does a replay attack differ from a man-in-the-middle?
What type of attack is a man-in-the-middle attack using a SSL3.0 browser that uses a Chain Block Cipher (CBC)?
What type of attack is a man-in-the-browser attack?
How can I prevent a replay attack in a Microsoft environment?
How can I prevent a pass the hash attack?
What type of attack uses HTML tags with JavaScript?
What type of exploit has no patches and cannot be detected by the NIDS or NIPS?
What is domain hijacking?
What is blue jacking?
What is Bluesnarfing?
What type of attack does the attacker need to be local and how can I prevent that attack?
For what type of attack do I use the tool strcpy for?
What is an integer overflow attack?
What type of attack uses the phrase 1=1?
Name two methods to prevent the attack in question 36.
What type of attack is session hijacking?
If I misspell a website but still get there, what type of attack is this?
What type of attack would I use shimming or refactoring for?
What type of attack is susceptible to a birthday attack?
What are rainbow tables?
How can I store passwords to prevent a dictionary attack?
Name two tools that can be used for key stretching.
What is the fast password attack that can crack any password?
What is the only way to prevent a brute force attack?
What can we do to slow down a brute force attack?
What type of authentication is the most prone to errors?
What is an evil twin?
How can I prevent an attack by a rogue WAP?
I am trying to use the internet but my wireless session keeps crashing—what type of attack is this?
How close does an attacker need to be for an NFC attack?
If I have no information on the system but at the last minute the IT manager gives me the local admin account, what type of penetration test is this?
How much information does a black box pen tester have?
How much information does a white box pen tester have?
Which type of vulnerability scan can I use for auditing?
If I carry out a non-credentialed vulnerability scan, what will I find?
What type of reconnaissance is it if I try and obtain a password reset?
What type of reconnaissance is it if I actively listen?
What is a pivot?
Because you have parted with money, this is a subtle form of ransomware.
An example of crypto-malware is ransomware where the victim's hard drive is encrypted and held to ransom.
A worm replicates itself and can use either ports 4444 or 5000.
A Trojan inserts a .dll into either the SysWOW64 or System 32 folder.
A remote access Trojan is a Trojan that sends the user's username and password to an external source so that they can create a remote session.
A rootkit virus attacks the root in windows it is the /system 32 folder or in Linux it is the /usr/bin/ directory.
A logic bomb virus is triggered off by an event; for example, the Fourth of July logic bomb would activate when the date on the computer was July 4.
A keylogger is a piece of software that could run from a USB flash drive plugged into the back of a computer it then records all of the keystrokes being used. It can capture sensitive data that is being typed in such as bank account details and passwords.
A botnet is a group of computers that have been infected so that they can be used to carry out malicious acts with the real attacker being identified. They could be used for a DDoS attack.
A phishing attack is when a user receives an email asking him to fill in a form requesting his bank details.
Spear phishing is a phishing attack that has been sent to a group of users.
A whaling attack targets the CEO or a high-level executive in a company.
A vishing attack can use a telephone or leave a voicemail.
Social engineering tailgating is where someone has used a smart card or entered a pin to access a door then someone behind them enters the door before it closes and they enter no credentials.
Social engineering exploits an individual's character in a situation that they are not used to.
If I dress as a policeman it could be an impersonation attack.
If I let fireman into the server room to put out a fire that is a social engineering urgency attack.
I am using an ATM queue and someone films the transaction this is a subtle shoulder surfing attack.
Fake software that will not install is a hoax. An email alert telling you to delete a system file as it is a virus is also a hoax.
A watering hole attack infects a website that a certain group of people visit regularly.
An email that looks like it has come from the CEO telling you to carry out an action is a social engineering authority attack.
This is a social engineering consensus attack where the person being attacked wants to be accepted by their peers.
An attack with multiple Syn flood attacks is a DDoS attack.
A man-in-the middle attack is where a connection between hosts has been intercepted, replaying and changing the conversation, but the people still believe that they are talking directly to each other.
A reply attack is similar to a man-in-the-middle attack, except the intercepted packet is replayed at a later date.
A POODLE attack is a man-in-the-middle attack using an SSL3.0 browser that uses Chain Block Cipher (CBC).
A man-in-the-browser attack is a Trojan that intercepts your session between your browser and the internet; it aims at obtaining financial transactions.
Kerberos authentication uses USN and time stamps and can prevent a replay attack, as the USN packets need to be sequential and the time stamps need to be in order.
Disabling NTLM will prevent a pass the hash attack.
XSS uses HTML tags with JavaScript.
A zero day virus has no patches and cannot be detected by the NIDS or NIPS as it may take the anti-virus vendor up to five days to release a patch.
Domain hijacking is where someone tries to register your domain, access your hosted control panel, and set up a website that is similar to yours.
Bluejacking is hijacking someone's Bluetooth phone so that you can take control of it and send text messages.
Bluesnarfing is where you steal someone's contacts from their Bluetooth phone.
An ARP attack is a local attack that can be prevented by using IP Sec.
Strcpy can be used for a buffer overflow attack.
An integer overflow inserts a number larger than what is allowed.
An attack that uses the phrase 1=1 is an SQL injection attack.
Input Validation and Stored Procedures can prevent an SQL injection attack.
Session hijacking is where your cookies are stolen so someone can pretend to be you.
Typosquatting is where an attack launches a website with a similar name to the legitimate website in the hope that victims misspell the URL.
Shimming or refactoring are used for a driver manipulation attack.
Digital signatures are susceptible to a birthday attack.
Rainbow tables are a pre-computed list of passwords with the relevant hash in either MD5 or SHA1.
If I salt passwords it will insert a random value and prevent dictionary attacks as a dictionary does not contain random characters.
Two tools that can be used for key stretching are bcrypt and PBKDF2.
Brute forces is the fastest password attack that crack any password as it uses all combinations of characters, letters, and symbols.
An account locked with a low value is the only way to prevent a brute force attack.
If account lockout is not available the best way to slow down a brute force attack is making the password length longer or to salt the passwords.
Using passwords for authentication is more likely prone to errors as certificates and smart cards don't tend to have many errors.
An evil twin is a WAP that is made to look like a legitimate WAP.
Using an 802.1x authentication switch can prevent an attack by a rogue WAP as the device needs to authenticate itself to attach to the switch.
A wireless disassociation attack is where the attacker prevents the victim from connecting to the WAP.
An attacker need to be within 4 cm of my card to launch an NFC attack.
This is a gray box pen test; although it says he has no information that would make it black box, at the last minute he is given a password, making it gray box. He is given some information.
A black box pen tester has no information.
A white box pen tester has all of the information.
A credentialed vulnerability scan can be used for auditing.
A non-credentialed vulnerability scan can only see missing patches of the systems on your network
Active reconnaissance is where I try to obtain a password reset.
Listening is a passive reconnaissance technique; active listening means that you are concentrating on what is being said, and you are not taking any action.
A pivot is where you gain access to a network so that you can launch an attack on a secondary system.