Chapter07 Managing Hosts and Applications Deployment Part 2
The Industrial Control System (ICS) is a general term that encompasses several types of control systems and instrumentation used for industrial process control. They are controlled by a SCADA system and are used for:
Electricity production and distribution
Water supply and treatment
Food production
Oil and gas production and supply
Chemical and pharmaceutical production
Telecommunications
Manufacturing of components and finished products
Paper and pulp production
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems are automated control systems that are crucial for industrial organizations since they help to maintain efficiency, process data for smarter decisions, and communicate system issues to help mitigate downtime.
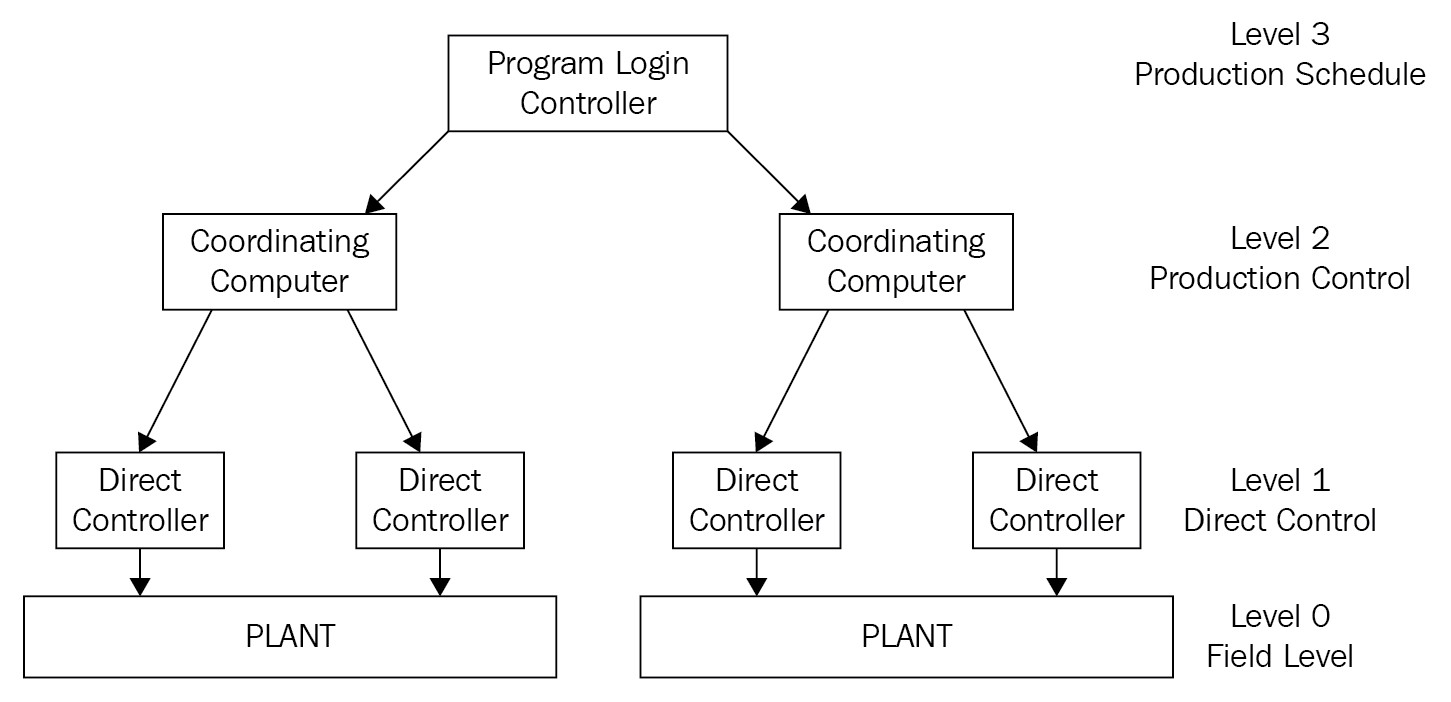
The SCADA system can be used for oil or gas refineries where there are multiple phases of production. Iran had a uranium enrichment facility that was a SCADA system, but it suffered an attack from the Stuxnet virus that attacked the centrifuges. The Stuxnet virus was discovered in 2007, but many believe it could have been there in 2005:

Figure 2: SCADA system
The security of the SCADA system is paramount. A network firewall prevents unauthorized access to the network, then they will use a NIPS as an additional layer. If further segmentation is required, they could use VLANs internally. This is no different from protecting a corporate network.
An embedded system is an electronic system that has software and is embedded in computer hardware. Some are programmable and some are not. Embedded systems are commonly found in consumer, cooking, industrial, automotive, medical, communications, commercial, and military applications.
Examples:
Household items: Microwave ovens, washing machines, dishwashers, refrigerators, baby monitors, printers, MP3 players, video game consoles and cameras, and audio/video surveillance to wireless devices that control lighting.
IT infrastructure: Telephone switches at the network end to cell phones at the consumer end. Dedicated routers and network bridges to route data. HVAC systems that use networked thermostats to control temperature and CCTV security systems.
Let's now look at each of these:
Smart devices/IoT: Smart devices, such as a smart TV, can connect to a home network and gain access to the internet. IoT comprises small devices, such as ATM cash machines, small robots, and wearable technologies, that can use an IP address and connect to internet-capable devices. We must ensure that we change the default usernames and passwords for these devices to prevent someone hacking them. From a security point of view, supporting IoT items is a nightmare because of the diversity of the devices:
Figure 3: IoT devices
Home automation: A home automation system will control lighting, climate, entertainment systems, alarm systems, and appliances.
Wearable technology: The use of wearable technology has increased in recent years from monitoring health and performance to sending texts and receiving calls on your watch.
System on a chip (SoC): An integrated circuit (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Integrated_circuit) that integrates all components of a computer or other electronic systems. Wearable technology and most embedded systems may include a SoC.
Real Time Operating System (RTOS): Intended to serve real-time applications that process data as it comes in, typically without buffer delays. Processing time requirements are measured in tenths of seconds or shorter increments of time. If a task or process does not complete within a certain time, the process will fail. This could be employed when robots are being used in production to ensure that the processes are being completed in a timely fashion.
Multifunctional Devices (MFD): Consists of at least two of the following: printer, scanner, fax, or photocopier in an all-in-one device. The weakness of each of these is that they all have a network interface and could be attacked through that interface. Any default setting or passwords must be changed.
Camera systems: Camera systems now tend to be networked and used for home automation or for security systems to protect premises.
Example: The police are dealing with a riot. As well as the police dressed in riot gear, there are vans with camera systems installed that are being used to tape the event in real time. The footage can be sent back to an incident control room where the police can see whether any of the rioters are on their internal police systems. This footage may be used in court.
Exam tip:
Multifunctional devices can be attacked through their network interfaces.
Heating Ventilation Air Conditioning (HVAC): Can be networked and centrally controlled by a security team. They can set the temperature in every room and can ensure that the data center is kept at a regulated temperature. The controllers can also view the usage to see which offices are occupied and which are empty.
Special-purpose devices are more expensive bespoke devices that provide a unique purpose. For example, there are man overboard devices that detect someone falling into the water—we are going to look at a defibrillator.
Mobile medical devices can include infusion devices that measure fluids that are given to patients in hospital. (See the following picture). Ambulances will carry life-support systems, such as defibrillators, that are used to save a person's life if they have just suffered from cardiac arrest. The defibrillators will have an SoC installed as it gives out instructions on how to use it, but if it detects a pulse, it will not send a charge:
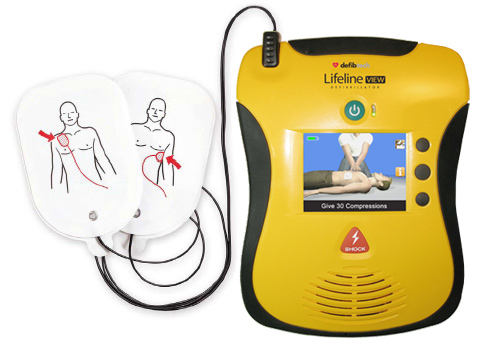
Figure 4: Defibrillator
Some luxury vehicles have embedded systems that produce a wireless hotspot in the car so that when you are driving along, your passengers can connect to the internet. Others have the ability to carry out automatic self-parking. There have been many trials recently of self-driving cars; vendors, such as Google, are still trying to perfect their systems.
For many years, people have been flying model aircrafts that also have embedded systems, but in the past 2-3 years, unmanned aerial vehicles called drones (aircraft/Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV)) have been making the headlines. The military can use these drones to carry out surveillance of areas where it is too dangerous to send manned aircrafts. Some drones can be as large as a mini-aircraft, and some can be as small as a model aircraft but can have a camera attached so that aerial photographs can be taken.
Some of the concepts used while securing an application during the development and deployment phases are as follows:
Baselining: Baselining is the process of recording all of the applications that are installed on a mobile device. At a later stage, you could run another baseline that would tell you which applications have been recently installed. If you have an up-to-date baseline, you can identify zero-day viruses. The baseline would show an addition of an unknown application and this would be the zero-day exploit.
Immutable systems: Immutable systems are composed of components so that every time a system is upgraded, the whole system is replaced as a clean install and never upgraded. This is best used in a cloud or virtual environment, but it would not work for on-premises and nonvirtual environments as it would take more time and labor.
Infrastructure as code: IaC is the process of managing and provisioning computer datacenters through machine-readable definition files, rather than physical hardware configuration or interactive configuration tools. An example of these would be to create a number of PowerShell scripts to automate processes that you wish to carry out.
Version control and change management: Change management normally occurs when software is getting either outdated or an audit has been carried out that highlights weak security with the software being used. Version control is used to identify the most up-to-date copy of software; for example, the first change would be version 1, the second would be version 2, and so on.
Provisioning and deprovisioning: Provisioning and deprovisioning have two different meanings. The first is when a new user arrives and we provision (create) their new account, then when they leave we deprovision (disable) their account. Software is very similar; if we create a new app that is designed for smartphones and tablets, when we provision it this means we roll it out, and when it is no longer useful, we deprovision it.
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a structure followed by a development team within the software organization. It consists of a detailed plan describing how to develop, maintain, and replace specific software. There are two main models that are adopted. One is the traditional method, which is called waterfall, and the more dynamic method is called agile.
The waterfall model is the traditional method used in the SDLC as it has a linear and sequential pattern to it. The development of the software moves from the top to the bottom, with each phase needing to be completed before the next phase can begin:
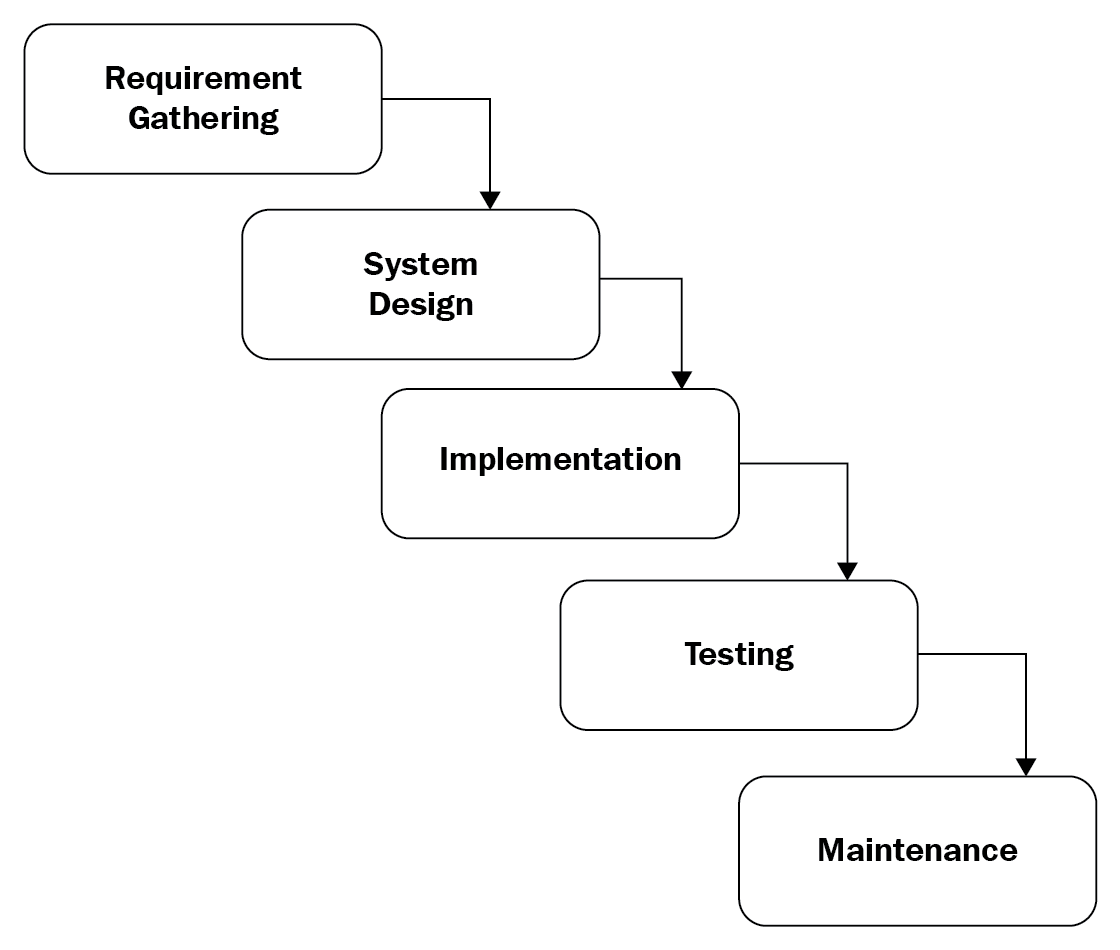
Figure 5: Waterfall model
It starts with gathering information about the requirement, then it is put into the design phase, and then it is implemented. The testing phase is carried out before it goes into production; any testing carried out will be rolled back prior to deployment. The maintenance phase is for patching and fixing any bugs.
The agile method anticipates change and breaks down each project into prioritized requirements, delivering each individually within an iterative cycle. Adaptability and customer satisfaction by rapid delivery are the key concepts of this model:
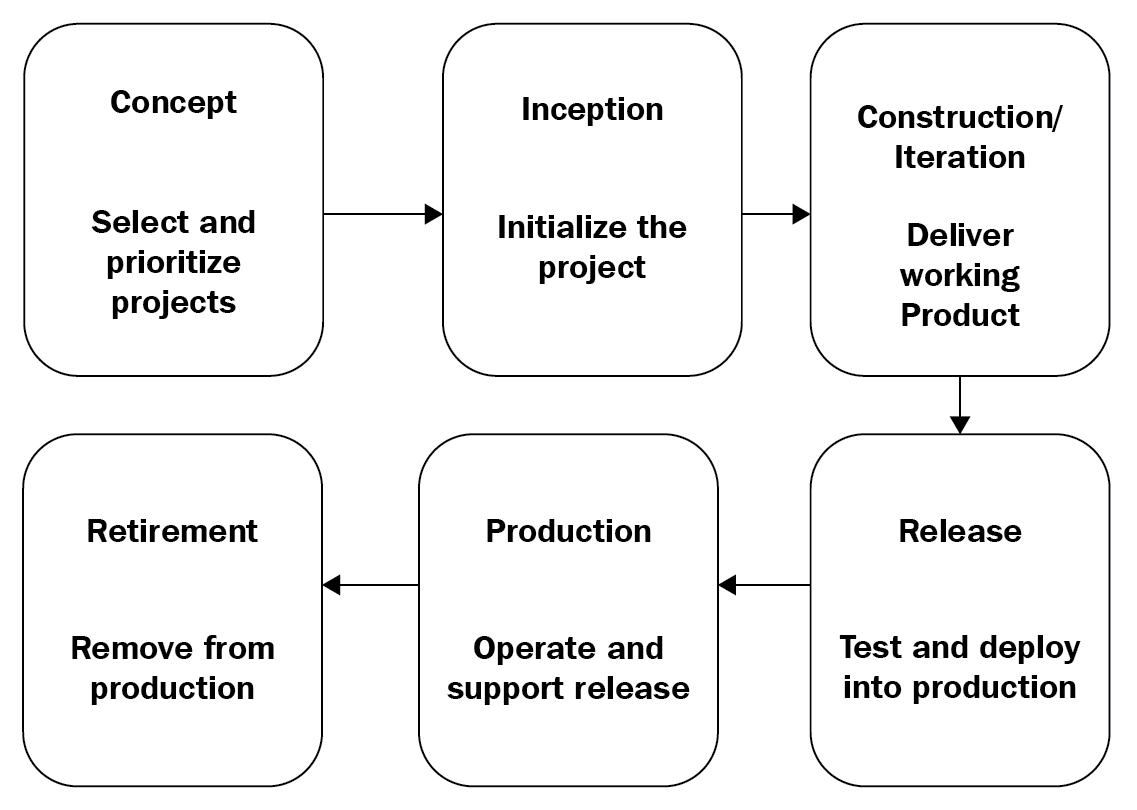
Figure 6: Agile model
Waterfall is a structured software development methodology, and can often be quite rigid, whereas the agile methodology is known for its flexibility. Waterfall must finish one process completely before it can begin another. Agile is dynamic and is geared for rapid deployment to ensure customer satisfaction.
Exam tip:Waterfall is an SDLC model that requires each step to be completed before starting the next step.
DevOps is where the IT operations and developers work together in the entire service life cycle, from design to rollout to production support. They use many of the same techniques as developers for their systems work.
Secure DevOps is where the security team, IT operations, and developers work together on software development; the focus is on reducing the time it takes for the software to get into production, which is why they adopt an agile SDLC. There are processes that help them and they are:
Security automation: This is the automatic handling of tasks by a computer rather than a security administrator. Orchestration is the connecting and integrating of various security applications and processes together.
Example: Security automation could be set up to scan for vulnerabilities at 6 pm without any human intervention.
Continuous integration (CI): CI requires developers to copy code into a shared repository several times a day. Each check-in is then verified by an automated build, allowing teams to detect problems early.
Although most people that work in networking or security are not application developers, CompTIA has introduced secure coding into the syllabus. This section needs to be understood so it is written in the simplest format we could think of:
A race condition is where two instructions from a different thread access the same data at the same time. When the developer wrote the application, the threads should have been programmed to access the data sequentially.
Example: Two guys buy tickets for the Super Bowl final, and when they arrive at the stadium they find that they have been allocated the same seat. That's a great profit for those selling the ticket, but a bad deal for those purchasing the ticket.
Proper error handling: When we develop IT systems, we want the errors that are sent back to users to be very short and generic so that an attacker has very little information to use and launch further attacks. However, we want the information logged on errors to be as detailed as possible so that the security administrators know why the error occurred.
Proper input validation: Input validation is controlled by either using wizards or web pages where the following are laid out:
Is it alphabetical?
Is it numerical?
Is it a certain format, such as a zip code or telephone number?
What are the minimum and maximum numbers of characters?
If the data is not input in the correct format, it will not be accepted. Input validation on web pages lists errors in red at the top of the page of the incorrect entries; this prevents SQL injection, integer overflow, and buffer overflow attacks.
Exam tip:System errors to the users should be generic, but the logging of errors for administrators should log the full details.
Normalization: Each database has a list of tables that are broken down into rows and columns. In a large relational database, data may be retained in multiple places. The goal of normalization is to reduce and eliminate the redundancy to make fewer indexes per table and make searching much faster.
Stored procedures: Transact SQL is used to query an SQL server database and can suffer from SQL injection attacks where attackers attack some code into the query. To avoid this, a developer may write an SQL query and then save it as a stored procedure, called Procedure 1. Instead of retyping all of the code, they just execute Procedure 1, which then executes the SQL query inside. Stored procedures are used to prevent SQL injection attacks.
Code signing: Code signing hashes the code so that you know it is the original code and it has not been tampered with.
Encryption: Encryption is the technique to protect the code from being stolen. To use the code, you must have the private key to decipher it.
Obfuscation/camouflage: Obfuscation or camouflage turns lines of code into an obscure format so that if the code is stolen, it cannot be understood.
Exam tip:
Stored procedures and input validation can prevent an SQL injection attack.
Code reuse/dead code: Developers like to keep code libraries where they store their source code. If they need to develop an application, they may start with old code then modify it for the new application. Dead procedures make up the most important part of dead code, it is code that is never executed. They inflate the executables, make systems harder to understand, and might even introduce new errors later in the life cycle of the program. They also consume resources and should be removed as they serve no purpose.
Memory management: It is important that when a developer writes an application, they control how much memory it can consume as it can create performance issues. Memory leaks occur when object references that are no longer needed are unnecessarily maintained, this causes the computer to gradually run out of memory.
Use of third-party libraries: The use of apps on mobile devices is a fierce marketplace, where as soon as you purchase a domain name, someone has emailed you offering you a good deal on mobile apps for your business. There are many third-party libraries that have many pieces of code, and although they not be perfect, it is a fast way to get your application to market. There are many third-party libraries for Android and for JavaScript that have grown in popularity.
Exam tip:Obfuscation makes code obscure so that if it is stolen, it cannot be understood.
Software-Developer Kits (SDKs): An SDK is a set of software development tools that allows the creation of applications for a certain software package, computer system, operating system, or similar development platform.
Example 1—Microsoft: There is a Windows 10 SDK from Microsoft that provides the latest headers, libraries, metadata, and tools for building Windows 10 apps.
Example 2—Oracle: There is a Java Standard Edition Development Kit. The JDK is a software development environment used for developing Java applications and applets. It includes the Java Runtime Environment (JRE), an interpreter/loader (java), a compiler (javac), an archiver (jar), a documentation generator (javadoc), and other tools needed in Java development.
Data exposure: Sensitive data is normally encrypted to prevent it from being stolen by attackers; this would include passwords and credit card details. We should limit the amount of data allocated to a user who is using an application; we should also use input validation and DLP to protect our data.
When an application developer writes an application, it needs to go through thorough testing before it is put into production. We need to ensure that the code does not have flaws or bugs that could be exploited by threat actors:
Pointer dereference: A pointer is an object in programming that stores the memory address of another value located in computer memory. When it retrieves the value, it is known as dereferencing the pointer. A failed pointer dereference means that the value has not been obtained.
Null pointer exception: A null pointer exception is thrown when an application attempts to use an object reference that has the null value. A developer may think that an object was created previously, but since it does not appear, the code will show a null value as there is no object to point to:
String s=null;
String s1="a";
String s2=s1+s;// null pointer exception
Static code analyzers: When developers use static code analyzers, the code is not executed locally. Instead, they launch the static code analyzer tool, then the source code is run inside the tool that reports any flaws or weaknesses.
Exam tip:A null pointer exception points to an object that is stored as a null value.
Dynamic code analysis: When developers use dynamic analysis, the code is run, and then they use a technique called fuzzing where a random input is inserted into the application to see what the output will be. White box pen testers use fuzzing to see the flaws and weaknesses in an application before it is rolled out to the production environment.
Stress testing: Stress testing is where a load is put through an application to see how its processors, memory, and disks can deal with the load.
Example: Microsoft has a tool called Jetstress that simulates a storage load on an Exchange email server. The administrator defines the number of users, and when Jetstress runs, it gives an output relating to the disk i/o and storage usage. The test results in a pass or fail.
Sandboxing: Sandboxing is where an application is run inside a virtual machine for testing purposes before it is put into production.
Model verification: Model verification and validation are the primary processes to ensure that an application has no bugs that need to be fixed and that it conforms to the specifications that were written.
Compiled versus runtime code: Code is written in either C, C++, Python, or JavaScript. Once it is written, turn on a compiler that identifies weaknesses in the code. When the code is runtime, it means that the developer is evaluating the code for errors as it runs. Compiled and runtime products are both used to find application errors.
Website scripts run in one of two places:
Server side—called the backend: Server-side validation is where the input by the user is being sent to the server and being validated with the response being sent back to the client. Programming languages such as C# and .NET are server-side.
Client side—called the frontend: Client-side validation does not require a round trip to the server, so the network traffic will help your server perform better. This type of validation is done on the browser side using script languages such as JavaScript, VBScript, or HTML5 attributes.
Client-side validation is much quicker, but an attacker can exploit the JavaScript and bypass the client side. Server-side validation takes much longer, and can use input validation to check that the input is valid and to stop the attacker who has just bypassed the client side. There is more control over server-side validation and it is more secure.
What is the purpose of MDM?
What is BYOD?
What two policies need to be agreed upon before BYOD is implemented?
How do BYOD and CYOD differ, and what are the benefits of CYOD to a company?
Name three types of mobile device connection methods.
What is used when we make a contactless payment using our debit card?
Which services allows your mobile device to be notified when an email message arrives in your inbox?
What two measures should I take to secure my mobile device?
What will prevent my laptop from being stolen when I am in a meeting with my boss?
What can I do to protect the data at rest on my mobile device?
What can I implement if I want to keep my personal data and pictures separate from my corporate data on my smartphone?
Once I have been authenticated by the VPN server, what method can be implemented to ensure that my mobile device is fully patched?
What is rooting and which operating system does it affect?
What is the purpose of jailbreaking and which operating system does it affect?
If my smartphone is with T-Mobile, what can be done at the end of my 2 year contract so that I can use Verizon as my provider?
What is the purpose of sideloading an application?
What is the benefit of USB OTG?
If I work in the R&D department, what are the two dangers when I take my cellphone to work?
When I go on holiday with friends from school, how can people on my social media know where the photograph was taken?
If I have been working in the sales department and have been using my cellphone to make work-related contactless payments, what does my company need to ensure happens during offboarding?
What two methods can I use to set up a wireless connection with another mobile device when using a WAP?
What is the purpose of tethering?
What is an embedded electronic system? Give two examples.
What is the purpose of a SCADA system?
What category of device are my smart TV and wearable technology?
What is home automation?
What is the purpose of SoC?
If a process is not carried out within a specified period of time, which causes the process to fail, what method am I using?
What is the most likely way an attacker would gain control of an MFD?
What is the purpose of the security team controlling the HVAC in a data center?
Someone at work has suffered from a cardiac arrest, the first aid delegate takes out a defibrillator that give instructions of the steps to take. What had been built into the device to give these instructions?
Give an example of embedded systems that can be used with vehicles.
What is an UAV? Give two examples.
What is the purpose of baselining?
What type of system am I using if I totally destroy the system and create a new system when an update takes place?
What software development life cycle is a traditional method that needs the previous stage to be complete before the next stage can start?
What software development life cycle is fast and customer-focused?
What is the purpose of secure automation in secure DevOps?
What is the benefit of using continuous integration in secure DevOps?
What is the main problem with a race condition when using an application?
What is the perfect way to set up error handling in an IT system?
Explain input validation and name three types of attacks that this could prevent.
How can I prevent an SQL injection attack other than with input validation?
What is the purpose of code signing?
What is the purpose of obfuscation?
What is dead code and how should it be treated?
If I am an Android developer, what can I obtain from the internet to help me make an application and get it to market quickly?
Explain how pointer dereference works.
What is a null pointer exception?
What is the technique used by developers to ensure that the application written conforms to the original specifications given by the customer?
MDM sets and enforces policies to protect the network from mobile devices.
BYOD is where you bring your personally owned device to use in the workplace.
The acceptable use policy and onboarding/offboarding policies need to be agreed upon before you can implement BYOD.
BYOD are personally owned devices, whereas CYOD are company-owned devices. Using CYOD allows the security administrators to remotely wipe the device if it is stolen and can make offboarding very easy as they own the device, so data ownership will never be an issue.
Mobile devices can connect through cellular, wireless, and Bluetooth connections.
Near field communication is used to make a contactless payment; the device must be within 4 cm of the card.
Push notification services notify your mobile device when an email message arrives at your inbox.
Screen locks and strong passwords are needed to secure a mobile device.
A cable lock will prevent my laptop from being stolen when I am in a meeting with my boss.
Full device encryption is used to protect the data at rest on my mobile device.
Storage segmentation will allow you to keep personal data separate from business data on a cellphone.
Network access control ensures that devices are fully patched before they enter the corporate network.
Rooting can be carried out on Android devices where custom firmware is downloaded that removes restrictions that the vendor puts on the mobile device. This then allows you to run unauthorized software on the device.
Jailbreaking is the same as rooting as it lifts the restriction on Apple's iOS devices. You can then install unauthorized software but can still access the Apple App Store.
Carrier unlocking will allow me to use my smartphone on another carrier's network.
Sideloading allows you to install third-party, unauthorized software on your mobile device.
USB On-The-Go (OTG) allows you to connect a USB device to your mobile device. Apple does not allow USB OTG.
If I work in a sensitive area, my cellphone will allow me to take pictures and post them on my social media. I could also make a video or record conversations of confidential meetings.
Most modern smartphones use GPS tracking to store the location where pictures were taken.
When they offboard people who use contactless payment on a smartphone, they need to ensure that the business credit card details have been removed from the wallet.
Wi-Fi direct and an ad-hoc network allow wireless connections with another mobile device by using a WAP.
Tethering allows you to use a cellphone on a laptop to provide internet.
Embedded electronic systems have software embedded into the hardware, some are using SoC. Examples are microwave ovens, gaming consoles, security cameras, wearable technology, smart TVs, medical devices such as defibrillators, or self-driving cars.
SCADA systems are industrial control systems used in the refining of uranium, oil, or gas.
Smart TVs and wearable technology are classified as IoT devices.
Home automation is where you can control temperature, lighting, entertainment systems, alarm systems, and many appliances.
An SoC is a low-power integrated chip that integrates all of the components of a computer or electronic system. An example would be the controller for a defibrillator. Think of it as an operating system stored on a small chip.
The Real-Time Operating System (RTOS) processes data as it comes in without any buffer delays. The process will fail if it is not carried out within a certain period of time.
An attacker would most likely gain control of an MFD through its network interface.
When a security team controls the HVAC in a data center, they can ensure that the temperature is regulated and the servers remain available. They also know which rooms are occupied based on the use of air-conditioning and electricity.
An SoC gives instructions of the steps to take when using a defibrillator, however, if it detects a pulse, it will not send a charge.
An example of embedded systems is vehicles that are either self-parking or self-driving.
Unmanned aerial vehicles are drones or small, model aircrafts that can be sent to areas where manned aircrafts cannot go. They can be fitted with a camera to record events or take Ariel photographs; an example of these would be to determine the spread of a forest fire.
Baselining is the process of recording all applications on a mobile device. You could then run the baseline at a later stage to find out what applications have been added since the last baseline.
An immutable system is totally destroyed when an update is made. This is ideal for the cloud or virtual environment.
Waterfall is a software development life cycle model that is traditional and needs each stage to be completed before the next stage can proceed.
Agile is a software development life cycle model that is fast and customer-focused.
Secure automation is where tasks, such as vulnerability scanning, are done by the computer and not the security administrator.
Continuous integration is where the developer will send code to a central repository two or three times a day so that it can be validated.
A race condition is when two threads of an application access the same data.
The perfect way to set up error handling is for the user to get generic information but for the log files to include a full description of the error.
Input validation is where data that is in the correct format is validated prior to being inserted into the system. SQL injection, buffer overflow, and integer overflow are prevented by using input validation.
Other than input validation, a stored procedure can prevent an SQL injection attack.
Code signing confirms that the code has not been tampered with.
Obfuscation is taking code and making it obscure so that if it is stolen it will not be understood.
Dead code is never used, but could introduce errors into the program life cycle, it should be removed.
Using a third-party library will help a developer obtain code from the internet to help make an application and get it to market quickly? There are many for Android and JavaScript.
When an object in programming has its value retrieved, this is known as a dereference.
A null pointer exception is a runtime exception where the application has tried to retrieve an object with a null value.
Model verification is a process used by developers to ensure that the application conforms to the original specifications.