Before we start with routing, let's just have a quick overview on Single-Page Applications.
What is Single Page Applications?
Single page applications or (SPAs) are web applications that load a single HTML page and dynamically update the page based on the user interaction with the web application.
What is Routing in AngularJS?
In AngularJS, routing is what allows you to create Single Page Applications.
- AngularJS routes enable you to create different URLs for different content in your application.
- AngularJS routes allow one to show multiple contents depending on which route is chosen.
- A route is specified in the URL after the # sign.
Let's take an example of a site which is hosted via the URL http://example.com/index.html.
On this page, you would host the main page of your application. Suppose if the application was organizing an Event and one wanted to see what the various events on display are, or wanted to see the details of a particular event or delete an event. In a Single Page application, when routing is enabled, all of this functionality would be available via the following links
http://example.com/index.html#ShowEvent
http://example.com/index.html#DisplayEvent
http://example.com/index.html#DeleteEvent
The # symbol would be used along with the different routes (ShowEvent, DisplayEvent, and DeleteEvent).
- So if the user wanted to see all Events, they would be directed to the link (http://example.com/index.html#ShowEvent), else
- If they wanted to just see a particular event they would be re-directed to the link ( http://example.com/index.html#DisplayEvent) or
- If they wanted to delete an event, they would be directed to the link http://example.com/index.html#DeleteEvent.
Note that the main URL stays the same.
In this tutorial, you will learn-
- Adding Angular Route ($routeProvider)
- Creating a default route
- Accessing parameters from the route
- Using Angular $route service
- Enabling HTML5 Routing
Adding Angular Route ($routeProvider)
So as we discussed earlier, routes in AngularJS are used to route the user to a different view of your application. And this routing is done on the same HTML page so that the user has the experience that he has not left the page.
In order to implement routing the following main steps have to be implemented in your application in any specific order.
- Reference to angular-route.js. This is a JavaScript file developed by Google that has all the functionality of routing. This needs to be placed in your application so that it can reference all of the main modules which are required for routing.
-
The next important step is to add a dependency to the ngRoute module from within your application. This dependency is required so that routing functionality can be used within the application. If this dependency is not added, then one will not be able to use routing within the angular.JS application.
Below is the general syntax of this statement. This is just a normal declaration of a module with the inclusion of the ngRoute keyword.
var module = angular.module("sampleApp", ['ngRoute']);
- The next step would be to configure your $routeProvider. This is required for providing the various routes in your application.
Below is the general syntax of this statement which is very self-explanatory. It just states that when the relevant path is chosen, use the route to display the given view to the user.
when(path, route)
- Links to your route from within your HTML page. In your HTML page, you will add reference links to the various available routes in your application.
<a href="#/route1">Route 1</a><br/>
- Finally would be the inclusion of the ng-view directive, which would normally be in a div tag. This would be used to inject the content of the view when the relevant route is chosen.
Now, let's look at an example of routing using the above-mentioned steps.
In our example,
We will present 2 links to the user,
- One is to display the topics for an Angular JS course, and the other is for the Node.js course.
- When the user clicks either link, the topics for that course will be displayed.
Step 1) Include the angular-route file as a script reference.
This route file is necessary in order to make use of the functionalities of having multiple routes and views. This file can be downloaded from the angular.JS website.
Step 2) Add href tags which will represent links to "Angular JS Topics" and "Node JS Topics."
Step3) Add a div tag with the ng-view directive which will represent the view.
This will allow the corresponding view to be injected whenever the user clicks on either the "Angular JS Topics" or "Node JS Topics."
Step 4) In your script tag for AngularJS, add the "ngRoute module" and the "$routeProvider" service.
Code Explanation:
- The first step is to ensure to include the "ngRoute module." With this in place, Angular will automatically handle the routing in your application. The ngRoute module which is developed by Google has all of the functionality which allows for routing to be possible. By adding this module, the application will automatically understand all of the routing commands.
- The $routeprovider is a service that angular uses to listen in the background to the routes which are called. So when the user clicks a link, the routeprovider will detect this and then decide on which route to take.
- Create one route for the Angular link – This block means that when the Angular link is clicked, inject the file Angular.html and also use the Controller 'AngularController' to process any business logic.
- Create one route for the Node link – This block means that when the Node link is clicked, inject the file Node.html and also use the Controller 'NodeController' to process any business logic.
Step 5) Next is to add controllers to process the business logic for both the AngularController and NodeController.
In each controller, we are creating an array of key-values pairs to store the Topic names and descriptions for each course. The array variable 'tutorial' is added to the scope object for each controller.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta chrset="UTF 8">
</head>
<body ng-app="sampleApp">
<title>Event Registration</title>
<script src="https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular-route.js"></script>
<script src="https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular.js"></script>
<h1> Guru99 Global Event</h1>
<div class="container">
<ul>
<li><a href="#Angular">Angular JS Topics</a></li>
<li><a href="#Node.html">Node JS Topics</a></li>
</ul>
<div ng-view></div>
</div>
<script>
var sampleApp = angular.module('sampleApp',['ngRoute']);
sampleApp.config(['$routeProvider',
function($routeProvider){
$routeProvider.
when('/Angular',{
templateUrl : '/Angular.html',
controller: 'AngularController'
}).
when("/Node", {
templateUrl: '/Node.html',
controller: 'NodeController'
});
}]);
sampleApp.controller('AngularController',function($scope) {
$scope.tutorial = [
{Name:"Controllers",Description :"Controllers in action"},
{Name:"Models",Description :"Models and binding data"},
{Name:"Directives",Description :"Flexibility of Directives"}
]
});
sampleApp.controller('NodeController',function($scope){
$scope.tutorial = [
{Name:"Promises",Description :"Power of Promises"},
{Name:"Event",Description :"Event of Node.js"},
{Name:"Modules",Description :"Modules in Node.js"}
]
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Step 6) Create pages called Angular.html and Node.html. For each page we are carrying out the below steps.
These steps will ensure that all of the key-value pairs of the array are displayed on each page.
- Using the ng-repeat directive to go through each key-value pair defined in the tutorial variable.
- Displaying the name and description of each key-value pair.
- Angular.html
<h2>Anguler</h2>
<ul ng-repeat="ptutor in tutorial">
<li>Course : {{ptutor.Name}} - {{ptutor.Description}}</li>
</ul>
- Node.html
<h2>Node</h2>
<ul ng-repeat="ptutor in tutorial">
<li>Course : {{ptutor.Name}} - {{ptutor.Description}}</li>
</ul>
If the code is executed successfully, the following Output will be shown when you run your code in the browser.
Output:
If you click on the AngularJS Topics link the below output will be displayed.
The output clearly shows that,
- When the "Angular JS Topics" link is clicked, the routeProvider that we declared in our code decides that the Angular.html code should be injected.
- This code will be injected into the "div" tag, which contains the ng-view directive. Also, the content for the course description comes from the "tutorial variable" which was part of the scope object defined in the AngularController.
- When one clicks on the Node.js Topics, the same result will take place, and the view for Node.js topics will be manifested.
- Also, notice that the page URL stays the same, it's only the route after the # tag which changes. And this is the concept of single page applications. The #hash tag in the URL is a separator which separates the route ( which in our case is 'Angular' as shown in above image) and main HTML page(Sample.html)
Creating a default route
Routing in AngularJS also provides the facility to have a default route. This is the route which is chosen if there is no match for the existing route.
The default route is created by adding the following condition when defining the $routeProvider service.
The below syntax just simply means to redirect to a different page if any of the existing routes don't match.
otherwise ({
redirectTo: 'page'
});
Let's use the same example above and add a default route to our $routeProvider service.
function($routeProvider){
$routeProvider.
when('/Angular',{
templateUrl : 'Angular.html',
controller: 'AngularController'
}).
when("/Node", {
templateUrl: 'Node.html',
controller: 'NodeController'
}).
otherwise({
redirectTo:'/Angular'
});
}]);
Code Explanation:
- Here we are using the same code as above with the only difference is that we are using the otherwise statement and the "redirectTo" option to specify which view should be loaded if no route is specified. In our case we want the '/Angular' view to be shown.
If the code is executed successfully, the following Output will be shown when you run your code in the browser.
Output:
From the output,
- You can clearly see that the default view shown is the angular JS view.
- This is because when the page loads it goes to the 'otherwise' option in the $routeProvider function and loads the '/Angular' view.
Accessing parameters from the route
Angular also provides the functionality to provide parameters during routing. The parameters are added to the end of the route in the URL, for example, http://guru99/index.html#/Angular/1. In this example
- , http://guru99/index.html is our main application URL
- The # symbol is the separator between the main application URL and the route.
- Angular is our route
- And finally '1' is the parameter which is added to our route
The syntax of how parameters look in the URL is shown below:
HTMLPage#/route/parameter
Here you will notice that the parameter is passed after the route in the URL.
So in our example, above for the Angular JS topics, we can pass a parameter's as shown below
Sample.html#/Angular/1
Sample.html#/Angular/2
Sample.html#/Angular/3
Here the parameters of 1, 2 and 3 can actually represent the topicid.
Let's look in detail at how we can implement this.
Step 1) Add the following code to your view
-
Add a table to show all the topics for the Angular JS course to the user
-
Add a table row for showing the topic "Controllers." For this row, change the href tag to "Angular/1" which means that when the user clicks this topic, the parameter 1 will be passed in the URL along with the route.
-
Add a table row for showing the topic "Models." For this row, change the href tag to "Angular/2" which means that when the user clicks this topic, the parameter 2 will be passed in the URL along with the route.
-
Add a table row for showing the topic "Directives." For this row, change the href tag to "Angular/3" which means that when the user clicks this topic, the parameter 3 will be passed in the URL along with the route.
Step 2) In the routeprovider service function add the:topicId to denote that any parameter passed in the URL after the route should be assigned to the variable topicId.
Step 3) Add the necessary code to the controller
- Make sure to first add the "$routeParams" as a parameter when defining the controller function. This parameter will have access to all of the route parameters passed in the URL.
- The "routeParams" parameter has a reference to the topicId object, which is passed as a route parameter. Here we are attaching the '$routeParams.topicId' variable to our scope object as the variable '$scope.tutotialid'. This is being done so that it can be referenced in our view via the tutorialid variable.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta chrset="UTF 8">
<title>Event Registration</title>
</head>
<body ng-app="sampleApp">
<script src="https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular-route.js"></script>
<script src="https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="/lib/bootstrap.js"></script>
<script src="/lib/bootstrap.css"></script>
<h1> Guru99 Global Event</h1>
<table class="table table-striped">
<thead>
<tr> <th>#</th><th>Angular JS topic</th><th>Description</th><th></th> </tr> </thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>l</td><td>l</td><td>Controllers</td>
<td><a href="#Angular/l">Topic details</a></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>2</td><td>2</td><td>Models</td>
<td><a href="#Angular/2">Topic details</a></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>3</td><td>3</td><td>Directives</td>
<td><a href="#Angular/3">Topic details</a></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<script>
var sampleApp = angular.module('sampleApp',['ngRoute']);
sampleApp.config(
function($routeProvider){
$routeProvider.
when('/Angular/:topicId',{
templateUrl : 'Angular.html',
controller: 'AngularController'
})
});
sampleApp.controller('AngularController',function($scope,$routeParams) {
$scope.tutorialid=$routeParams.topicId
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Step 4) Add the expression to display the tutorialid variable in the Angular.html page.
<h2>Anguler</h2>
<br><br>{{tutorialid}}
If the code is executed successfully, the following Output will be shown when you run your code in the browser.
Output:
In the output screen,
- If you click on the Topic Details link for the first topic, the number 1 gets appended to the URL.
- This number will be then taken as a "routeparam" argument by the Angular.JS routeprovider service and can then be accessed by our controller.
Using Angular $route service
The $route service allows you to access the properties of the route. The $route service is available as a parameter when the function is defined in the controller. The general syntax of how the $route parameter is available from the controller is shown below;
myApp.controller('MyController',function($scope,$route)
- myApp is the angular.JS module defined for your applications
- MyController is the name of the controller defined for your application
- Just like the $scope variable is made available for your application, which is used to pass information from the controller to the view. The $route parameter is used to access the properties of the route.
Let's have a look on how we can use the $route service.
In this example,
- We are going to create a simple custom variable called "mytext," which will contain the string "This is angular."
- We are going to attach this variable to our route. And later we are going to access this string from our controller using the $route service and then subsequently use the scope object to display that in our view.
So, let's see the steps which we need to carry out to achieve this.
Step 1) Add a custom key-value pair to the route. Here, we are adding a key called 'mytext' and assigning it a value of "This is angular."
Step 2) Add the relevant code to the controller
- Add the $route parameter to the controller function. The $route parameter is a key parameter defined in angular, which allows one to access the properties of the route.
- The "mytext" variable which was defined in the route can be accessed via the $route.current reference. This is then assigned to the 'text' variable of the scope object. The text variable can then be accessed from the view accordingly.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta chrset="UTF 8">
<title>Event Registration</title>
</head>
<body ng-app="sampleApp">
<script src="https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular-route.js"></script>
<script src="https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="/lib/bootstrap.js"></script>
<script src="/lib/bootstrap.css"></script>
<h1> Guru99 Global Event</h1>
<table class="table table-striped">
<thead>
<tr> <th>#</th><th>Angular JS topic</th><th>Description</th><th></th> </tr> </thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>l</td><td>l</td><td>Controllers</td>
<td><a href="#Angular/l">Topic details</a></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>2</td><td>2</td><td>Models</td>
<td><a href="#Angular/2">Topic details</a></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>3</td><td>3</td><td>Directives</td>
<td><a href="#Angular/3">Topic details</a></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<script>
var sampleApp = angular.module('sampleApp',['ngRoute']);
sampleApp.config(['$routeProvider',
function($routeProvider){
$routeProvider.
when('/Angular/:topicId',{
mytext:"This is angular",
templateUrl : 'Angular.html',
controller: 'AngularController'
})
}]);
sampleApp.controller('AngularController',function($scope,$routeParams,$route) {
$scope.tutorialid=$routeParams.topicId;
$scope.text=$route.current.mytext;
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
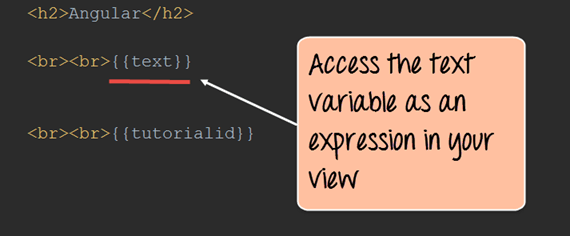
Step 3) Add a reference to the text variable from the scope object as an expression. This will be added to our Angular.html page as shown below.
This will cause the text "This is angular" to be injected into the view. The {{tutorialid}} expression is the same as that seen in the previous topic and this will display the number '1'.
<h2>Anguler</h2>
<br><br>{{text}}
<br><br>
If the code is executed successfully, the following Output will be shown when you run your code in the browser.
Output:
From the output,
- We can see that the text "This is angular" also gets displayed when we click on any of the links in the table. The topic id also gets displayed at the same time as the text.
Enabling HTML5 Routing
HTML5 routing is used basically to create clean URL. It means the removal of the hashtag from the URL. So the routing URLs, when HTML5 routing is used, would appear as shown below
Sample.html/Angular/1
Sample.html/Angular/2
Sample.html/Angular/3
This concept is normally known as presenting pretty URL to the user.
There are 2 main steps which need to be carried out for HTML5 routing.
- Configuring $locationProvider
- Setting our base for relative links
Let's look into the detail of how to carry out the above-mentioned steps in our example above
Step 1) Add the relevant code to the angular module
- Add a baseURL constant to the application – This is required for HTML5 routing so that the application knows what the base location of the application is.
- Add the $locationProvider services. This service allows you to define the html5Mode.
- Set the html5Mode of the $locationProvider service to true.
Step 2) Remove all the #tags for the links ('Angular/1', 'Angular/2', 'Angular/3') to create easy to read URL.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta chrset="UTF 8">
<title>Event Registration</title>
</head>
<body ng-app="sampleApp">
<script src="https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular-route.js"></script>
<script src="https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="/lib/bootstrap.js"></script>
<script src="/lib/bootstrap.css"></script>
<h1> Guru99 Global Event</h1>
<table class="table table-striped">
<thead>
<tr> <th>#</th><th>Angular JS topic</th><th>Description</th><th></th> </tr> </thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>l</td><td>l</td><td>Controllers</td>
<td><a href="/Angular/l">Topic details</a></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>2</td><td>2</td><td>Models</td>
<td><a href="/Angular/2">Topic details</a></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>3</td><td>3</td><td>Directives</td>
<td><a href="/Angular/3">Topic details</a></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<script>
var sampleApp = angular.module('sampleApp',['ngRoute']);
sampleApp.constant("baseUrl","http://localhost:63342/untitled/Sample.html/Angular");
sampleApp.config(
function($routeProvider,$locationProvider){
$routeProvider.
when('/Angular/:topicId',{
templateUrl : 'Angular.html',
controller: 'AngularController'
})
});
sampleApp.controller('AngularController',function($scope,$routeParams,$route) {
$scope.tutorialid=$routeParams.topicId
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
If the code is executed successfully, the following Output will be shown when you run your code in the browser.
Output:
From the output,
- You can see that the # tag is not there when accessing the application.
Summary
- Routing is used to present different views to the user on the same web page. This is basically the concept used in Single page applications which are implemented for almost all modern day web applications
- A default route can be set-up for angular.JS routing. It is used to determine what will be the default view to be shown to the user
- Parameters can be passed to the route via the URL as route parameters. These parameters are then subsequently accessed by using the $routeParams parameter in the controller
- The $route service can be used to define custom key-value pairs in the route which can then be subsequently accessed from within the view
- HTML5 routing is used to remove the #tag from routing URL in angular to form pretty URL