What is $scope in AngularJS?
The scope is a JavaScript object which basically binds the "controller" and the "view". One can define member variables in the scope within the controller which can then be accessed by the view.
Consider example below:
angular.module('app',[]).controller(
function($scope)
{
$scope.message = "Hello World"
});
Code Explanation:
From the above code snippet you can see that we can define multiple member variables like tutorial name, name, topic, etc. and assign them the relevant values.
In our div tag, we can the display these values accordingly. Hence as we mentioned before the scope object is the main object which is used to pass information from the controller to the view.
Setting up or adding Behavior
In order to react to events or execute some sort of computation/processing in the View, we must provide behavior to the scope.
Behaviors are added to scope objects to respond to specific events that may be triggered by the View. Once the behavior is defined in the controller, it can be accessed by the view.
Let's look at an example of how we can achieve this.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta chrset="UTF 8">
<title>Guru99</title>
</head>
<body ng-app="DemoApp">
<h1> Guru99 Global Event</h1>
<script src="https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular.js"></script>
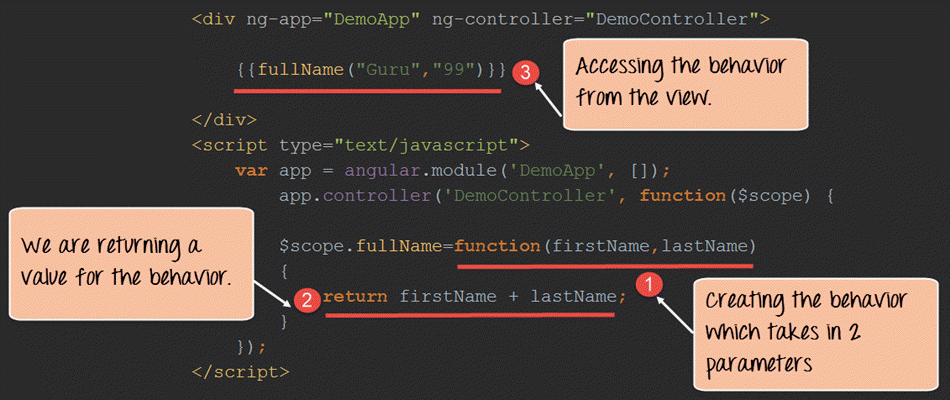
<div ng-controller="DemoController">
{{fullName("Guru","99")}}
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var app = angular.module("DemoApp", []);
app.controller("DemoController", function($scope) {
$scope.fullName=function(firstName,lastname){
return firstName + lastname;
}
} );
</script>
</body>
</html>
Code Explanation:
- We are creating a behavior called "fullName". This behavior is a function which accepts 2 parameters (firstName,lastname).
- The behavior then returns the concatenation of these 2 parameters.
- In the view we are calling the behavior and passing in 2 values of "Guru" and "99" which gets passed as parameters to the behavior.
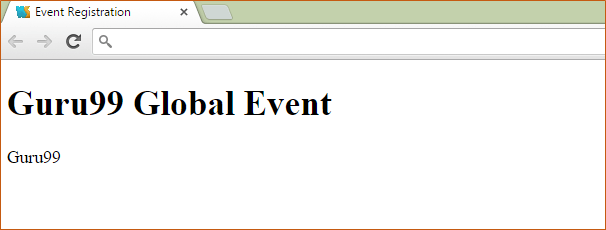
If the command is executed successfully, the following Output will be shown when you run your code in the browser.
Output:
In the browser you will see a concatenation of both the values of Guru & 99 which were passed to the behavior in the controller.
Summary
- Various member variables can be added to the scope object which can then be referenced in the view.
- Behavior can be added to work with events which are generated for actions performed by the user.