What Is Fuzzy Logic?
The term fuzzy mean things which are not very clear or vague. In real life, we may come across a situation where we can't decide whether the statement is true or false. At that time, fuzzy logic offers very valuable flexibility for reasoning. We can also consider the uncertainties of any situation.
Fuzzy logic helps to solve a problem after considering all available data. Then it takes the best possible decision for the given the input. The FL method imitates the way of decision making in a human which consider all the possibilities between digital values T and F.
History of Fuzzy Logic
Although, the concept of fuzzy logic had been studied since the 1920's. The term fuzzy logic was first used with 1965 by Lotfi Zadeh a professor of UC Berkeley in California. He observed that conventional computer logic was not capable of manipulating data representing subjective or unclear human ideas.
Fuzzy logic has been applied to various fields, from control theory to AI. It was designed to allow the computer to determine the distinctions among data which is neither true nor false. Something similar to the process of human reasoning. Like Little dark, Some brightness, etc.
Characteristics of Fuzzy Logic
Here, are some important characteristics of fuzzy logic:
- Flexible and easy to implement machine learning technique
- Helps you to mimic the logic of human thought
- Logic may have two values which represent two possible solutions
- Highly suitable method for uncertain or approximate reasoning
- Fuzzy logic views inference as a process of propagating elastic constraints
- Fuzzy logic allows you to build nonlinear functions of arbitrary complexity.
- Fuzzy logic should be built with the complete guidance of experts
When not to use fuzzy logic
However, fuzzy logic is never a cure for all. Therefore, it is equally important to understand that where we should not use fuzzy logic.
Here, are certain situations when you better not use Fuzzy Logic:
- If you don't find it convenient to map an input space to an output space
- Fuzzy logic should not be used when you can use common sense
- Many controllers can do the fine job without the use of fuzzy logic
Fuzzy Logic Architecture
Fuzzy Logic architecture has four main parts as shown in the diagram:
Rule Base:
It contains all the rules and the if-then conditions offered by the experts to control the decision-making system. The recent update in fuzzy theory provides various methods for the design and tuning of fuzzy controllers. This updates significantly reduce the number of the fuzzy set of rules.
Fuzzification:
Fuzzification step helps to convert inputs. It allows you to convert, crisp numbers into fuzzy sets. Crisp inputs measured by sensors and passed into the control system for further processing. Like Room temperature, pressure, etc.
Inference Engine:
It helps you to determines the degree of match between fuzzy input and the rules. Based on the % match, it determines which rules need implment according to the given input field. After this, the applied rules are combined to develop the control actions.
Defuzzification:
At last the Defuzzification process is performed to convert the fuzzy sets into a crisp value. There are many types of techniques available, so you need to select it which is best suited when it is used with an expert system.
Fuzzy Logic vs. Probability
| Fuzzy Logic | Probability |
| Fuzzy: Tom's degree of membership within the set of old people is 0.90. | Probability: There is a 90% chance that Tom is old. |
| Fuzzy logic takes truth degrees as a mathematical basis on the model of the vagueness phenomenon. | Probability is a mathematical model of ignorance. |
Crisp vs. Fuzzy
| Crisp | Fuzzy |
| It has strict boundary T or F | Fuzzy boundary with a degree of membership |
| Some crisp time set can be fuzzy | It can't be crisp |
| True/False {0,1} | Membership values on [0,1] |
| In Crisp logic law of Excluded Middle and Non- Contradiction may or may not hold | In the fuzzy logic law of Excluded Middle and Non- Contradiction hold |
Classical Set vs. Fuzzy set Theory
| Classical Set | Fuzzy Set Theory |
| Classes of objects with sharp boundaries. | Classes of objects do not have sharp boundaries. |
| A classical set is defined by crisp boundaries, i.e., there is clarity about the location of the set boundaries. | A fuzzy set always has ambiguous boundaries, i.e., there may be uncertainty about the location of the set boundaries. |
| Widely used in digital system design | Used only in fuzzy controllers. |
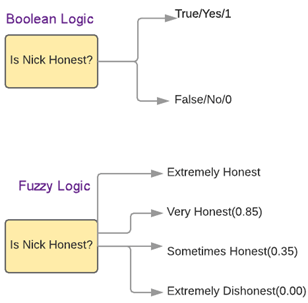
Fuzzy Logic Examples
See the below-given diagram. It shows that in fuzzy systems, the values are denoted by a 0 to 1 number. In this example, 1.0 means absolute truth and 0.0 means absolute falseness.
Application Areas of Fuzzy Logic
The Blow given table shows how famous companies using fuzzy logic in their products.
| Product | Company | Fuzzy Logic |
| Anti-lock brakes | Nissan | Use fuzzy logic to controls brakes in hazardous cases depend on car speed, acceleration, wheel speed, and acceleration |
| Auto transmission | NOK/Nissan | Fuzzy logic is used to control the fuel injection and ignition based on throttle setting, cooling water temperature, RPM, etc. |
| Auto engine | Honda, Nissan | Use to select geat based on engine load, driving style, and road conditions. |
| Copy machine | Canon | Using for adjusting drum voltage based on picture density, humidity, and temperature. |
| Cruise control | Nissan, Isuzu, Mitsubishi | Use it to adjusts throttle setting to set car speed and acceleration |
| Dishwasher | Matsushita | Use for adjusting the cleaning cycle, rinse and wash strategies based depend upon the number of dishes and the amount of food served on the dishes. |
| Elevator control | Fujitec, Mitsubishi Electric, Toshiba | Use it to reduce waiting for time-based on passenger traffic |
| Golf diagnostic system | Maruman Golf | Selects golf club based on golfer's swing and physique. |
| Fitness management | Omron | Fuzzy rules implied by them to check the fitness of their employees. |
| Kiln control | Nippon Steel | Mixes cement |
| Microwave oven | Mitsubishi Chemical | Sets lunes power and cooking strategy |
| Palmtop computer | Hitachi, Sharp, Sanyo, Toshiba | Recognizes handwritten Kanji characters |
| Plasma etching | Mitsubishi Electric | Sets etch time and strategy |
Advantages of Fuzzy Logic System
- The structure of Fuzzy Logic Systems is easy and understandable
- Fuzzy logic is widely used for commercial and practical purposes
- It helps you to control machines and consumer products
- It may not offer accurate reasoning, but the only acceptable reasoning
- It helps you to deal with the uncertainty in engineering
- Mostly robust as no precise inputs required
- It can be programmed to in the situation when feedback sensor stops working
- It can easily be modified to improve or alter system performance
- inexpensive sensors can be used which helps you to keep the overall system cost and complexity low
- It provides a most effective solution to complex issues
Disadvantages of Fuzzy Logic Systems
- Fuzzy logic is not always accurate, so The results are perceived based on assumption, so it may not be widely accepted.
- Fuzzy systems don't have the capability of machine learning as-well-as neural network type pattern recognition
- Validation and Verification of a fuzzy knowledge-based system needs extensive testing with hardware
- Setting exact, fuzzy rules and, membership functions is a difficult task
- Some fuzzy time logic is confused with probability theory and the terms
Summary
- The term fuzzy mean things which are not very clear or vague
- The term fuzzy logic was first used with 1965 by Lotfi Zadeh a professor of UC Berkeley in California
- Fuzzy logic is a flexible and easy to implement machine learning technique
- Fuzzy logic should not be used when you can use common sense
- Fuzzy Logic architecture has four main parts 1) Rule Basse 2) Fuzzification 3) Inference Engine 4) Defuzzification
- Fuzzy logic takes truth degrees as a mathematical basis on the model of the vagueness while probability is a mathematical model of ignorance
- Crisp set has strict boundary T or F while Fuzzy boundary with a degree of membership
- A classical set is widely used in digital system design while fuzzy set Used only in fuzzy controllers
- Auto transmission, Fitness management, Golf diagnostic system, Dishwasher, Copy machine are some applications areas of fuzzy logic
- Fuzzy logic helps you to control machines and consumer products