Updated April 1, 2023

Introduction to Bitwise Operators in C
Bitwise operators are used to perform operations at the bit level and help to manipulate data at bit level which we can call bit-level programming. Bit-level programming contains 0 and 1. These can be done by first converting a decimal value to its binary form. This binary form is nothing but a sequence of bits. Bitwise operators perform operations on these bits. In this topic, we are going to learn about Bitwise Operators in C.
Six bitwise operators of C are as follows:
- & Bitwise AND
- | Bitwise OR
- ~ Bitwise NOT
- ^ Bitwise XOR
- << Left shift
- >> Right Shift
Syntax with Explanation
- The syntax for bitwise AND operator is as follows:
int c = a & b;In the above statement, int is the data type for variable ‘c’. Variables ‘a’ and ‘b’ are two operands of type integer on which the bitwise AND (&) operator has been applied. The result of this operation will be stored in ‘c’.
- Syntax for bitwise OR operator is as follows:
int c = a | b;Here, ‘c’ is a variable of type int, which stores the result of bitwise OR operation performed on variables ‘a’ and ‘b’. Variables ‘a’ and ‘b’ are of type int.
- Syntax for bitwise NOT operator is as follows:
int c = ~a;Here, ‘c’ is an integer variable that stores the result of bitwise NOT operation performed on integer variable ‘a’.
- Syntax for bitwise XOR operator is as follows:
int c = a ^ b;Here, ‘c’ is an integer variable that stores the result of bitwise XOR operation performed on integer variables ‘a’ and ‘b’.
- Syntax for left-shift operator is as follows:
int c = a << 1;Here, ‘c’ is an integer variable that stores the result of left shift operation performed on integer variable ‘a’. The numeric value (i.e. 1 in this case) after the left shift operator can be any valid integer number.
- Syntax for right shift operator is as follows:
int c = a >> 1;Here, ‘c’ is an integer variable that stores the result of right shift operation performed on integer variable ‘a’. The numeric value (i.e. 1 in this case) after the right shift operator can be any valid integer number.
In all the above syntaxes, variable names are user-defined names.
How Bitwise Operators work in C?
Let us now understand the working of each of the six bitwise operators in C with the help of some examples. Let us consider two numbers to work on these examples i.e. a = 20 and b = 40. The binary value of ‘a’ is 10100 and that of ‘b’ is 101000.
1. Bitwise AND operator
This operator is a binary operator which means it works on two operands. It is represented by an ampersand sign (&). This operator results in 1 when the values of both the bits are 1.
Example:
a = 0 0 1 0 1 0 0
b = 0 1 0 1 0 0 0
————————–
a&b 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
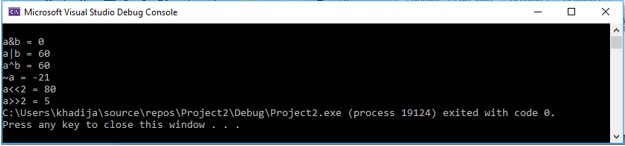
Thus, the value of ‘a & b’ is 0.
2. Bitwise OR operator
This operator is a binary operator. It is represented by a vertical bar sign (|). This operator results in 1 when the value of at least one bit is 1.
Example:
a = 0 0 1 0 1 0 0
b = 0 1 0 1 0 0 0
————————–
a|b 0 1 1 1 1 0 0
Thus, the value of ‘a|b’ in binary is 0111100 and in decimal, it is 60.
3. Bitwise NOT operator
This operator is a unary operator which means it requires only one operand. It is also known as a bitwise complement or one’s complement operator. This operator is represented by the tilde sign (~). When applied on bits, this operator converts all zeroes (0’s) to ones (1’s) and vice versa.
Example:
a = 1 0 1 0 0
————————
~a 0 1 0 1 1
Thus, the value of ‘~a’ in binary is 01011 and in decimal, it is 11. But the bitwise complement of 20 will be -21. The calculation is done with the help of expression – (n+1). In our case, n = 20 thus – (n+1) will be -21.
4. Bitwise XOR operator
This operator is a binary operator. It is known as XOR i.e. exclusive OR operator. This operator is represented by ‘^’ sign. For opposite bits it results in 1 and for the same bits it results in 0.
Example:
a = 0 0 1 0 1 0 0
b = 0 1 0 1 0 0 0
————————–
a^b 0 1 1 1 1 0 0
Thus, the value of ‘a^b’ in binary is 0111100 and in decimal, it is 60.
5. Left shift operator
It is represented by the ‘<<’ sign. It is used to shift all the bits to the left by a specified number of bits.
Example:
a = 1 0 1 0 0
———————————-
a<<2 1 0 1 0 0 0 0
Thus, the value of ‘a<<2’ in binary is 1010000 and in decimal, it is 80.
6. Right shift operator
It is represented by ‘>>’ sign. It is used to shift all the bits to the right by a specified number of bits.
Example:
a = 1 0 1 0 0
———————————-
a>>2 0 0 1 0 1
Thus, the value of ‘a>>2’ in binary is 00101 and in decimal, it is 5.
Example of Bitwise Operators in C
Here are the following example mention below
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
int a = 20, b = 40;
//Binary: a=10100 and b=101000
printf("\na&b = %d", a&b);
printf("\na|b = %d", a|b);
printf("\na^b = %d", a^b);
printf("\n~a = %d", ~a);
printf("\na<<2 = %d", a<<2);
printf("\na>>2 = %d", a>>2);
}Output:
Conclusion
- Bitwise operators are the operators which operate on bits.
- C supports six bitwise operators.
- When we apply a bitwise operator on a decimal value, then internally it is first converted to a binary value i.e. in form of bits. Then the operator works on this binary value.