Non-Generic Stack Collection Class in C# with Examples
Posted by Superadmin on November 15 2023 14:33:50
Non-Generic Stack Collection Class in C# with Examples
In this article, I am going to discuss the Non-Generic Stack Collection Class in C# with Examples. Please read our previous article before proceeding to this article where we discussed the Hashtable Collection Class in C# with Examples. The Stack Collection Class in C# represents a Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) collection of objects. That means it is used when we need Last-In, First-Out access to the items of a collection. The Non-Generic Stack Collection Class in C# belongs to the System.Collections namespace. At the end of this article, you will understand the following pointers.
- What is Stack in C# and how does it work?
- Methods, Properties, and Constructor of Stack Class in C#
- How to create a Stack Collection in C#?
- How to Add Elements into a Stack in C#?
- How to Remove Elements from a Stack in C#?
- How to get the topmost element of a Stack in C#?
- How to check whether an element exists or not in the stack in C#?
- How to Clone the Non-Generic Stack Collection in C#?
- How to copy a stack to an existing array in C#?
- When to use Stack Collection in Real-time Applications in C#?
What is Stack in C# and how does it work?
The Stack in C# is a Non-Generic collection class that works in the LIFO (Last in First out) principle. So, we need to use the Stack Collection Class in C#, when we want Last-In-First-Out access to the items of a collection. That means the item which is added last to the collection will be the first item to be removed from the collection.
When we add an item to a stack collection, then it is called pushing an item. Similarly, when we remove an item from the stack then it is called popping an item.
In order to understand stack collection, first, we need to understand the LIFO Principle as Stack works on the LIFO Principle. Let us try to understand the LIFO principle with an example. Imagine we have a stack of books where each book is added on top of the other. The last book which is added to the stack will be the first one to be removed from the stack. It is not possible to remove a book from the middle of the stack. For a better understanding, please have a look at the following image.

In C#, the Non-Generic Stack Collection also works in the same way. Elements are added to the stack, on top of each other. When we add an item to the stack, then it is called pushing an item. The process of adding an element to the stack is called a Push operation. Similarly, when we remove an item from the stack then it is called popping an item. This operation is known as Pop. For a better understanding, please have a look at the below image.

Note: Stack is Defined as both generic and non-generic types of collection. The Generic Stack is defined in System.Collections.Generic namespace whereas Non-Generic Stack is defined under System.Collections namespace. Here in this article, we will be discussing the Non-Generic Stack Collection Class in C# with Examples.
Methods, Properties, and Constructor of Stack Class in C#:
If you go to the definition of the Non-Generic Stack Collection Class in C#, then you will see the following signature. As you can see the Non-Generic Stack class implements the IEnumerable, ICollection, and ICloneable interfaces.

How to create a Non-Generic Stack Collection in C#?
The non-generic collection Stack class in C# has three constructors which we can use to create a stack. The constructors are as follows:
- Stack(): It is used to initialize a new instance of the Stack class that is empty and has the default initial capacity.
- Stack(ICollection col): It is used to initialize a new instance of the non-generic Stack class that contains elements copied from the specified collection and has the same initial capacity as the number of elements copied. Here, the parameters col specifies the System.Collections.ICollection to copy elements from.
- Stack(int initialCapacity): It is used to initialize a new instance of the System.Collections.Stack class that is empty and has the specified initial capacity or the default initial capacity, whichever is greater. Here, the parameter initialCapacity specifies the initial number of elements that the Stack can contain.
Let’s see how to create a stack using the Stack() constructor:
Step1:
As the Stack class belongs to System.Collections namespace, so first, we need to include System.Collections namespace in our program with the help of the “using” keyword as follows:
using System.Collections;
Step2:
Next, we need to create an instance of the Stack Collection class using the Stack() constructor as follows:
Stack stack = new Stack();
How to Add Elements into a Stack Collection in C#?
If you want to add elements to a stack, then you need to use the Push() method of the Stack class.
Push(object obj): The push() method is used to insert an object on top of the Stack. Here, the parameter obj specifies the Object to push onto the Stack. The value can be null.
Example to Understand How to Create a Stack and Add Elements in C#:
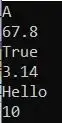
For a better understanding of how to create a Stack and how to add elements to a stack in C#, please have a look at the below example.
using System.Collections;
namespace StackCollectionDemo
static void Main(string[] args)
// Creating a stack collection
Stack stack = new Stack();
//Adding item to the stack using the push method
//Printing the stack items using foreach loop
foreach (object item in stack)
Output:
How to Remove Elements from a Non-Generic Stack Collection in C#?
In Stack, you are allowed to remove elements from the top of the stack. The Stack class in C# provides two different methods to remove elements. They are as follows:
- Pop(): This method is used to remove and return the object at the top of the Stack. It returns the Object (element) removed from the top of the Stack.
- Clear(): This method is used to remove all objects from the Stack.
Let us see an example to understand the Pop and Clear method of Stack in C#. Please have a look at the below example.
using System.Collections;
namespace StackCollectionDemo
static void Main(string[] args)
// Creating a stack collection
Stack stack = new Stack();
//Adding item to the stack using the push method
//Printing the stack items using foreach loop
Console.WriteLine($"All Stack Elements: Count {stack.Count}");
foreach (var item in stack)
Console.Write($"{item} ");
//Removing and Returning an item from the stack using the pop method
Console.WriteLine($"\n\nDeleted Element: {stack.Pop()}");
//Printing item after removing the last added item
Console.WriteLine($"\nAll Stack Elements After Deletion: Count {stack.Count}");
foreach (var item in stack)
Console.Write($"{item} ");
Output:

How to get the topmost element of a Stack in C#?
The Stack class in C# provides the following two methods to get the topmost element of the Stack.
- Pop(): This method is used to remove and return the object at the top of the Stack. It returns the Object (element) removed from the top of the Stack. If there is no object (or element) present in the stack and if you are trying to remove an item or object from the stack using the pop() method then it will throw an exception i.e. System.InvalidOperationException
- Peek(): The peek() method is used to return the object from the top of the Stack without removing it. If there is no object (or element) present in the stack and if you are trying to return an item (object) from the stack using the peek() method then it will throw an exception i.e. System.InvalidOperationException
For a better understanding, please have a look at the below example which shows how to get the topmost element from the stack.
using System.Collections;
namespace StackCollectionDemo
static void Main(string[] args)
// Creating a stack collection
Stack stack = new Stack();
//Adding item to the stack using the push method
Console.WriteLine($"Total elements present in stack : {stack.Count}");
// Fetch the topmost element of stack Using Pop method
Console.WriteLine($"Topmost element of stack is {stack.Pop()}");
Console.WriteLine($"Total elements present in stack : {stack.Count}");
// Fetch the topmost element from Stacj Using Peek method
Console.WriteLine($"Topmost element of Stack is {stack.Peek()}");
Console.WriteLine($"Total elements present in stack : {stack.Count}");
Output:

Note: If you want to remove and return the top element from the stack, then use the Pop method and if you only want to return the top element from the stack without removing it, then you need to use the Peek method and this is the only difference between these two methods of Stack class in C#.
How to check whether an element exists or not in the stack in C#?
If you want to check whether an element exists or not in the stack, then you need to use the following Contains() method of the Stack class. You can also use this method to search for an element in the given stack.
- Contains(object obj): This method is used to determine whether an element is in the Stack. Here, the parameter obj specifies the object or element to locate in the Stack. The value can be null. It returns true if obj is found in the Stack; otherwise, false.
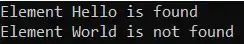
Let us understand this with an example. The following example shows how to use the Contains() method of the non-generic collection Stack class in C#.
using System.Collections;
namespace StackCollectionDemo
static void Main(string[] args)
// Creating a stack collection
Stack stack = new Stack();
//Adding item to the stack using the push method
// Checking if the element Hello is present in the Stack or not
if (stack.Contains("Hello"))
Console.WriteLine("Element Hello is found");
Console.WriteLine("Element Hello is not found");
// Checking if the element Hello is present in the Stack or not
if (stack.Contains("World"))
Console.WriteLine("Element World is found");
Console.WriteLine("Element World is not found");
Output:
Note: The Contains(object obj) method of Stack Class takes O(n) time to check if the element exists in the stack. This should be taken into consideration while using this method.
How to Clone the Non-Generic Stack Collection in C#?
If you want to clone the Non-Generic Stack collection in C#, then you need to use the following Clone() method provided by the Stack Collection Class.
- Clone(): This method is used to create and return a shallow copy of a stack object.
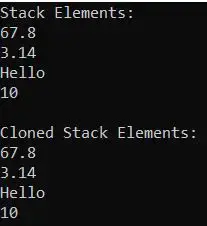
For a better understanding, please have a look at the below example.
using System.Collections;
namespace StackCollectionDemo
static void Main(string[] args)
// Creating a stack collection
Stack stack = new Stack();
//Adding item to the stack using the push method
//Printing All Stack Elements using For Each Loop
Console.WriteLine("Stack Elements:");
foreach (var item in stack)
//Creating a clone queue using Clone method
Stack cloneStack = (Stack)stack.Clone();
Console.WriteLine("\nCloned Stack Elements:");
foreach (var item in cloneStack)
Output:
How to copy a stack to an existing array in C#?
In order to copy a stack to an existing array in C#, we need to use the following CopyTo method of the Non-Generic Stack Collection Class.
- CopyTo(Array array, int index): This method is used to copy the Stack elements to an existing one-dimensional Array, starting at the specified array index. Here, the parameter array specifies the one-dimensional array that is the destination of the elements copied from the stack. The Array must have zero-based indexing. The index parameter specifies the zero-based index in the array at which copying begins. If the parameter array is null, then it will throw ArgumentNullException. If the parameter index is less than zero, then it will throw ArgumentOutOfRangeException.
This method works on one-dimensional arrays and does not change the state of the stack. The elements are ordered in the array in the same way as the order of the elements from the start of the stack to the end. Let us see an example for a better understanding.
using System.Collections;
namespace StackCollectionDemo
static void Main(string[] args)
// Creating a stack collection
Stack stack = new Stack();
//Adding item to the stack using the push method
//Printing All Queue Elements using For Each Loop
Console.WriteLine("Stack Elements:");
foreach (var item in stack)
//Copying the queue to an object array
object[] stackCopy = new object[5];
stack.CopyTo(stackCopy, 0);
Console.WriteLine("\nStack Copy Array Elements:");
foreach (var item in stackCopy)
Output:

Properties of Non-Generic Stack Collection Class in C#
- Count: It returns the number of elements contained in the Stack.
- IsSynchronized: Gets a value indicating whether access to the Stack is synchronized (thread-safe). It returns true if access to the Stack is synchronized (thread-safe); otherwise, false. The default is false.
- SyncRoot: Gets an object that can be used to synchronize access to the Stack. It returns an object that can be used to synchronize access to the Stack.
Characteristics of Non-Generic Stack Collection Class in C#:
- The capacity of a Stack is the number of elements the Stack can hold. As we add elements to a Stack, the capacity of the stack is automatically increased.
- If Count is less than the capacity of the stack, Push is an O(1) operation. If the capacity needs to be increased to accommodate the new element, Push becomes an O(n) operation, where n is Count. Pop is an O(1) operation.
- The Stack Collection in C# allows both null and duplicate values.
Summary
The following are important points that you need to remember while working with Stack in C#.
- In C#, stacks are used to store a collection of objects in a LIFO (Last in, First out) style, i.e., the element which added last will come out first.
- By using the Push() method, we can add elements to a stack.
- The Pop() method will remove and return the topmost element from the stack.
- The Peek() method will return the last (top-most) inserted element of the stack, and it won’t delete the element from the stack.
In the next article, I am going to discuss the Non-Generic Queue Collection Class in C# with Examples. Here, In this article, I try to explain the Non-Generic Stack Collection Class in C# with Examples. I hope this Non-Generic Stack Collection Class in C# article will help you with your needs.







![]()

