
Introduction to Javascript Date Function
The following article provides an outline on the JavaScript Date Function. In javascript, we can manage and use the dates using the object named Date.
The default format in which date is displayed is as follows:
Thu Dec 26 2019 14:09:42 GMT+0530 (India Standard Time)
We can create a Date object using four ways::
- new Date()
- new Date(year, month, day, hours, minutes, seconds, milliseconds)
- new Date(milliseconds)
- new Date(date string)
Points to be Remembered in JavaScript Date Function
- These objects created are Even though the system clock is ticking. The objects created using any of the above methods will not change its value.
- Months are counted from 0 to 11 which means 0 stands for January while 11 for December.
- In the second method of date object creation, the parameters specified can be reduced. If 7 arguments are passed above format will be In the case of 6 parameters year, month, day, hour, minute, second will be considered, for 5 parameters year, month, day, hour, and minute will be considered and so on.
- However, is only one parameter is passed to Date() function it will not be considered as a year. Instead, it is treated as the milliseconds.
- In case if the year is mentioned in 2 digits then 19xx will be, For example, new Date(96,00,26) will give- Fri Jan 26, 1996, 00:00:00 GMT+0530 (India Standard Time)
- Javascript stores the date in the milliseconds’ This millisecond is considered from January 01, 1970, 00:00:00 UTC (Universal Time Coordinated).
- The zero time i.e new Date(0) is January 01, 1970, 00:00:00
Let’s see an example of the above declaration ways of date:
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript Date() Function</h2>
<p id="currentDate"></p>
<p id="timestampInMilliseconds"></p>
<p id="dateString"></p>
<p id="dateAndTime"></p>
<p id="zeroDate"></p>
<script>
// Current Date
var d = new Date()
document.getElementById("currentDate").innerHTML = d;
// Timestamp method
d = new Date(-1000000000000);
document.getElementById("timestampInMilliseconds").innerHTML = d;
// Date string method
d = new Date("January 31 1980 12:30"); document.getElementById("dateString").innerHTML = d
// Date and time method
d = new Date(1885, 6, 4, 12, 30, 20, 10);
document.getElementById("dateAndTime").innerHTML = d;
// Date and time method with six parameters d = new Date(1885, 6, 4, 12, 30, 50);
document.getElementById("dateAndTime").innerHTML = d;
// Date and time method with five parameters d = new Date(1885, 6, 4, 12, 20);
document.getElementById("dateAndTime").innerHTML = d;
//Default Date
d = new Date(0); document.getElementById("zeroDate").innerHTML = d;
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
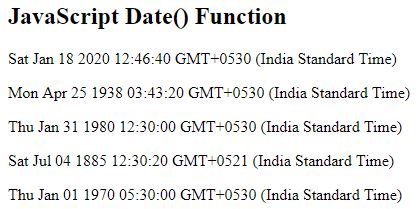
Date Methods
Javascript provides us with numerous methods to operate on the date object. We can get and set milliseconds, seconds, minutes, hour, day, month or year of date using either local time or Universal(UTC or GMT) time.
By default output of date object in javascript is in string format which is as follows:
- Thu Dec 26 2019 14:09:42 GMT+0530 (India Standard Time)
- However, it can be further modified by using different methods like toUTCString(), toDateString().
toString() method will not have any effect as the output is already in the string format.
Example of converting date output
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript Date()</h2>
<b>Default Output</b>
<p id="TodaysDateId"></p>
<b>Output when converted to string</b>
<p id="toStringId"></p>
<b>Output when converted to date string</b>
<p id="toDateStringId"></p>
<b>Output when converted to UTC string</b>
<p id="toUTCStringId"></p>
<script>
var d = new Date();
document.getElementById("TodaysDateId").innerHTML = d; document.getElementById("toStringId").innerHTML = d.toString(); document.getElementById("toDateStringId").innerHTML = d.toDateString(); document.getElementById("toUTCStringId").innerHTML = d.toUTCString();
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
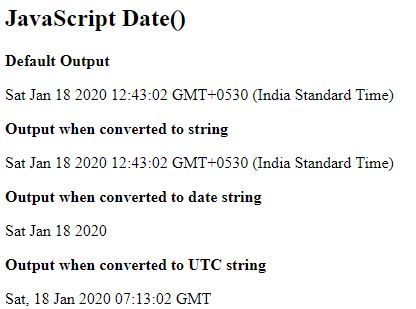
Three Date Formats in Javascript
- ISO Date – “2019-09-20” (The International Standard)
- Short Date – “09/20/2019”
- Long Date – “Oct 20 2019” or “20 Oct 2019”
In javascript, ISO format is strictly followed. However, other formats are browser-specific. The international standard for the representation of dates and times is ISO 8601 and it’s preferred format is (YYYY-MM-DD). It can also be specified without a day in YYYY-MM format or even with the only year in YYYY format. For example,
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript ISO Dates</h2>
<p id="demo"></p>
<p id="demo1"></p>
<p id="demo2"></p>
<script>
var d = new Date("2015-03-25"); document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = d;
d = new Date("2015-03"); document.getElementById("demo1").innerHTML = d;
d = new Date("2015"); document.getElementById("demo2").innerHTML = d;
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

As javascript is mostly used for web-based projects, here are some of the points that you need to remember while coding with dates.
- Date and time are separated with T and while declaring dates in UTC (Universal Time Coordinated)/GMT(Greenwich Mean Time). it is specified by Z. If we do not specify T or Z then different results can be expected on different browsers.
- If we are setting a date or getting it and we do not mention time zone then JavaScript will consider the browser’s time zone.
- For example, if you are browsing from India then date and time will be converted and displayed with IST(India Standard Time).
- Short dates specified in “MM/DD/YYYY” or “YYYY/MM/DD” can return undefined as Some browsers will guess the format correctly while some won’t.
- If we do not specify leading zeroes then some browsers may give an undefined date if they are not able to guess it.
- Month and day can be specified in any order and month can be written in full or abbreviated format like December/Dec. And names are case insensitive.
- Commas are not considered and are ignored by the parser in case if they occur in date string.
Dates can be parsed to obtain it in milliseconds format provided only if valid dates are passed to parse() method.
Javascript Date Get and Set Methods
There are various methods provided for getting and setting the year, month, day, hour, minutes and seconds in javascript which are as follows:
Date Get Methods
| Method |
Details |
| getFullYear() | Year as a four-digit number (yyyy) can be |
| getMonth() | Month as a number (0-11) can be retrieved |
| getDate() | Day as a number (1-31) can be retrieved |
| getHours() | Hour (0-23) can be retrieved |
| getMinutes() | Minute (0-59) can be retrieved |
| getSeconds() | Second (0-59) can be retrieved |
| getMilliseconds() | Millisecond (0-999) can be retrieved |
| getTime() | Time (milliseconds since January 1, 1970) |
| getDay() | Weekday as a number (0-6) can be retrieved |
| Date.now() | Time. ECMAScript 5. |
Date Set Methods
|
Method |
Details |
| setDate() | Day as a number (1-31) can be set |
| setFullYear() | Year (optionally month and day) can be set |
| setHours() | Hour (0-23) can be set |
| setMilliseconds() | Milliseconds (0-999) can be set |
| setMinutes() | Minutes (0-59) can be set |
| setMonth() | Month (0-11) can be set |
| setSeconds() | Seconds (0-59) can be set |
| setTime() | Time (milliseconds since January 1, 1970) |
Let’s see some of this method with the help of an example:
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function getTime() {
var today = new Date();
var hours = today.getHours();
var minutes = today.getMinutes();
var seconds = today.getSeconds();
minutes = checkTime(minutes);
seconds = checkTime(seconds);
document.getElementById('clock').innerHTML =
hours + ":" + minutes + ":" + seconds;
var t = setTimeout(getTime, 1000);
}
function checkTime(counter) {
if (counter < 10) {counter = "0" + counter};// add zero in front of numbers < 10
return counter;
}
</script>
</head>
<body onload="getTime()">
<div id="clock"></div>
</body>
</html>Output:
![]()