
Introduction to Javascript Map Function
The Map is a standard built-in object that is used to hold elements in a key-value pair, and it also recollects the primordial insertion sequence of the keys. All types of values, such as objects, primitive values, functions, etc., can be used as either a key or a value. The Javascript Map Function object iterates in the original insertion sequence. If for each loop is used to iterate over the map, an array of key-value pairs will result in each iteration.
Syntax:
new Map( [itr] )Here it is an array or any other iterable which is in the form of key-value pair. (For example, an array named arr of 2 value like arr = [[‘a’, ‘value of a’], [‘b’, ‘value of b’]] ). Each of these key-value pair values will be added to the new map created.
Map Instances
All the Map instances are inherited from Map.prototype
Properties:
- prototype.size: This property will return the number of key-value pairs present at the instance in the map.
- prototype.constructor: This property will return the function which created the prototype for Map. It is the Map function by default.
Methods:
- prototype.get( key ): This method will return the associated value for the key or undefined if the key is not present in the Map.
- prototype.set( key, value ): This method will insert the key-value pair in the Map if the key is not present otherwise update the key with the value in the Map.
- prototype.clear( ): This method will delete all the key-value pairs from the Map object.
- prototype.enteries( ): This method will return a new iterable object which will have an array of all the key-value pairs in the same insertion order as that of Map.
- prototype.delete( key ): This method will return true if the key existed in the Map object and delete it from the Map otherwise it will return false when the key is absent in the Map.
- prototype.has( key ): This method will return a boolean result to tell whether a value is associated with the provided key in the Map or not.
- prototype.keys( ): This method will return an iterable object which will contain an array of all the keys in the Map object.
- prototype.values( ): This method will return an iterable object which will contain an array of all the values in the Map object.
Examples of Javascript Map Function
The examples of javascript map function are given below:
1. Using the Map Object
Code:
var mapObj= new Map()
var stringKey = 'Hello'
var objKey= {}
var funcKey = function () { }
// setting the values
mapObj.set(stringKey, "value for stringKey")
mapObj.set(objKey, "value for objKey")
mapObj.set(funcKey, "value for funcKey")
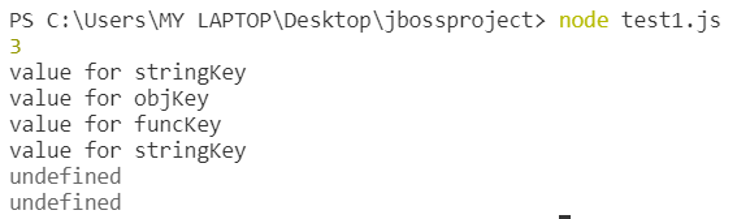
console.log(mapObj.size) // 3
// getting the values
console.log(mapObj.get(stringKey)) // "value for stringKey"
console.log(mapObj.get(objKey)) // "value for objKey"
console.log(mapObj.get(funcKey)) // "value for funcKey"
console.log(mapObj.get('Hello')) // "value for stringKey"
// because stringKey === 'Hello'
console.log(mapObj.get({})) // undefined, because objKey !== {}
console.log(mapObj.get(function () { })) // undefined, because funcKey !== function () {}Output:
2. Using NaN as a Map Key
Code:
var mapObj = new Map()
mapObj.set(NaN, 'not a number')
console.log(mapObj.get(NaN)) // "not a number"
var somethingelse = Number('abc')
console.log(mapObj.get(somethingelse)) // "not a number"Output:

3. Using forEach () loop to iterate over a Map
Code:
var mapObj = new Map()
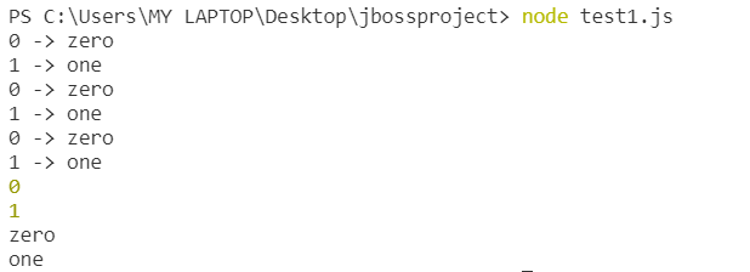
mapObj.set(0, 'zero')
mapObj.set(1, 'one')
mapObj.forEach(function (value, key) {
console.log(key + ' -> ' + value)
})
for (var [key, value] of mapObj.entries()) {
console.log(key + ' -> ' + value)
}
for (var [key, value] of mapObj) {
console.log(key + ' -> ' + value)
}
for (var key of mapObj.keys()) {
console.log(key)
}
for (var value of mapObj.values()) {
console.log(value)
}Output:
4. Merging two Maps
Code:
var fMap = new Map([
[1, 'one'],
[2, 'two'],
[3, 'three'],
])
var sMap = new Map([
[1, 'uno'],
[2, 'dos']
])
// Merge two maps. The last repeated key wins.
// Spread operator essentially converts a Map to an Array
var outputMap = new Map([...fMap, ...sMap])
console.log(outputMap.get(1)) // uno
console.log(outputMap.get(2)) // dos
console.log(outputMap.get(3)) // three
var mergeMap = new Map([... fMap, ...sMap, [1,'ek']])
console.log(mergeMap.get(1)) // ekOutput:

Maps and Objects Compared
Maps and Objects are usually similar in some aspects such as objects also have key-value pairs. They can also get values associated with a key, delete key-values, update them and also find out whether a particular key has an associated value. That is why Objects are more often used over Maps but there are significant differences as well let’s check them below:
- The keys of Objects can only be a String or Symbol whereas Maps can accept any value as the key such as functions, primitives, arrays, etc.
- The size of the Map can be determined by the size method whereas in Objects properties can be only manually calculated.
- The keys of a Map are always ordered in the sequence of their insertion whereas in Object the keys are not ordered.
- In order to iterate on an Object, we have to get the keys of it whereas a Map is directly iterable.
- A Map can perform better in cases where there are frequent addition and deletion of the key-value pairs.
Conclusion
Maps can become handy in a situation where data is in a key-value manner and is being regularly updated. Key equality in Maps is based on the sameValueZero algorithm. NaN is compared equal to NaN (whereas they are not equal) and all other values are being subjected to the === operator jurisdiction.
Setting the object properties for a Map also works. This condition should be taken care of as it can result in ambiguity.
var mapObj = new Map() mapObj['abc'] = 'abcd'; // Results in Ambigous Map MapObj.set('abc','abcd'); // Right way to set key-value pair