
Introduction to JavaScript Constants
Today, we shall look into JavaScript Constant. To start with any programming logic, we need to first have some constants and variables in hand, which would be useful for the logic. These JavaScript Constants are read-only and declared with const keyword, which gets assigned at the time of declaration. Constants can be either global or local to function where it’s being declared. We have two new JavaScript keywords, i.e., let and const. Variables that are defined with const behave as let variables cannot be reassigned or redeclared. JavaScript Constants being blocked scoped similar to variables being declared using the let keyword.
Syntax
Below is the syntax mentioned:
const <name of the variable> = value;Naming a constant in JavaScript has some rules for naming a variable, keeping intact the const keyword, and global constants. If in case the keyword ‘const’ is removed, the identifier is represented as a variable.
Hence to declare a constant variable, need to use the keyword ‘const’ instead of ‘let.’
E.g.,
const employeeName = "Karthick";Here variable employeeName is a constant with vale ‘Karthick”.
If in case you try to change the value of employeeName to ‘Anusha,’ you will face an error as you cant reassign a constant
Only when the programmer is sure that the variable will not face any changes, then it can be declared using const to guarantee the fact that the variable is a constant
JavaScript value that cannot be altered by programming during execution is a Constant, simple to work on, right? Yes, but we have something called Naming Convention for these Constants. JavaScript being an interpreted language, previously we used to store values in variables even though they are constant value. To differentiate among variables and constants, ECMAScript 6 follows some guidelines for naming constants.
- One main thing is capitalization, which we surely help to know which are the constant values and the variables in the program.
var EMPLOYEE_AGE = 24;- ES6 has helped people in declaring the const, which is a constant, and added new keywords ‘const’ and ‘let.’
- So you might doubt why we should capitalize when we have the keyword ‘const’ or do we need to capitalize on anything that is declared using the const keyword.
- Const creates a constant which has a read-only reference; there is no meaning that the value the variable is holding is immutable.
- Some of the constant references can change depending upon the programming logic.
- So const here only prevents users from trying to reassign the name of the variable, but the object property can be passed as objects are Pass By Reference.
- Overall, constants can be declared whether using an upper case or lower case, the most used and common convention is to all upper case letters.
Examples of Javascript constants
Given below are the examples of Javascript constants:
Example #1
Use of const keyword. Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript const</h2>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
const EMPLOYEE_NAME = "Karthick";
document.write('Best Employee of the month: ' + EMPLOYEE_NAME);
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

Example #2
Assigning or changing the value of constant EMPLOYEE_NAME in the above code.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript const, assigning different value to the constant</h2>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
const EMPLOYEE_NAME = "Karthick";
EMPLOYEE_NAME = "Saideep";
document.write('Best Employee of the month: ' + EMPLOYEE_NAME);
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
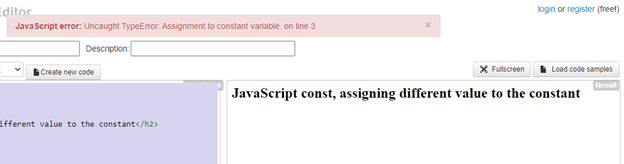
You can see the error on the screenshot as ‘Assignment to the constant variable online 3.’
Example #3
Redeclaring the constant and reassigning the value.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript const, redeclaring the constant variable and reassigning</h2>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
const EMPLOYEE_NAME = "Karthick";
document.write('Best Employee of the month: ' + EMPLOYEE_NAME);
const EMPLOYEE_NAME = "Anusha";
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
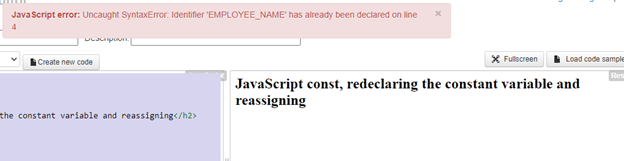
Constant EMPLOYEE_NAME has already been declared, which is a Syntax error
Example #4
Not initializing the constant.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript const, not initializing the constant</h2>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
const EMPLOYEE_AGE;
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
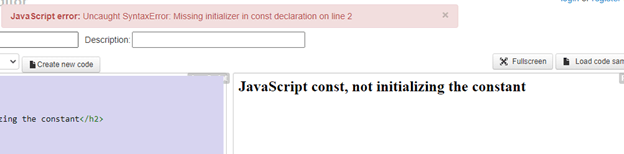
We are just declaring the constant EMPLOYEE_AGE and not initializing it with a value. Hence the Missing Initializer Syntax error.
Example #5
JavaScript const in Arrays and Objects
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript const in objects and arrays</h2>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
const COMPANY = {'key': 'value'};
// COMPANY = {'SAMPLE': 'value'};
COMPANY.key = '1204';
document.write(COMPANY.key + "<br/>");
const COMPANY_ARRAY = [];
COMPANY_ARRAY.push('INFOSYS');
// COMPANY_ARRAY = ['Capgemini'];
document.write(COMPANY_ARRAY);
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

Commented lines, you people can just try out by uncommenting it. It will give an error as ‘error: Uncaught TypeError: Assignment to constant variable.’
One of the interesting parts of using constants is to know about the Object.freeze() method.
If you want any of the objects to be immutable, we need to use Object.freeze() method, so by freezing the object properties of the object are frozen but not the Object references by the properties. Let us take an example,
Example #6
Using Object.freeze() method for const.
Code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript const, using Object.freeze() method</h2>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
const SCHOOL = Object.freeze({
studentName: 'Jasmine',
studentAddress: {
street: 'Totavari Street',
city: 'Visakhapatnam',
state: 'Andhra Pradesh',
zipcode: 520070,
country: 'India',
}
});
SCHOOL.studentAddress.phNumber = 9876544310;
SCHOOL.studentAddress.flatNumber = 'B1-104';
document.write('Updated address details of student Jasmine: ', SCHOOL.studentAddress.phNumber + '<br/>' + SCHOOL.studentAddress.flatNumber);
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

SCHOOL Object is const and frozen; no other details will be mutable, but the SCHOOL.studentAddress Object can be mutable, new properties can be added.
Conclusion
With this, we conclude the topic ‘JavaScript constant’. We have seen what JavaScript Constant and its syntax is. Illustrated a few simple examples which you people can try your hands on. Const keyword denoting that the variable is a constant which cannot be reassigned or redeclared. New Method Object.freeze(), which will help you to add properties to an object for which we have seen an example illustrating the same.