03 Project Executing Forms
Posted by Superadmin on December 20 2015 13:08:18
3.0 EXECUTING PROCESS GROUP
The purpose of the Executing Process Group is to carry out the work necessary to meet the project objectives.
There are eight processes in the Executing Process Group.
Direct and Manage Project Work
Perform Quality Assurance
Acquire Project Team
Develop Project Team
Manage Project Team
Manage Communications
Conduct Procurements
Manage Stakeholder Engagement
The intent of the Executing Process Group is to at least:
Create the deliverables
Manage project quality
Manage the project team
Carry out project communications
Report progress
Manage changes
Manage stakeholders
Bid and award contracts
In these processes, the main work of the project is carried out and the majority of the funds are expended. To
be effective, the project manager must coordinate project resources, manage changes, report progress, and manage stakeholders, while completing the project deliverables.
The forms used to document project execution include:
Team Member Status Report
Change Request
Change Log
Decision Log
Quality Audit
Team Directory
Team Operating Agreement
Team Performance Assessment
Team Member Performance Appraisal
Issue Log
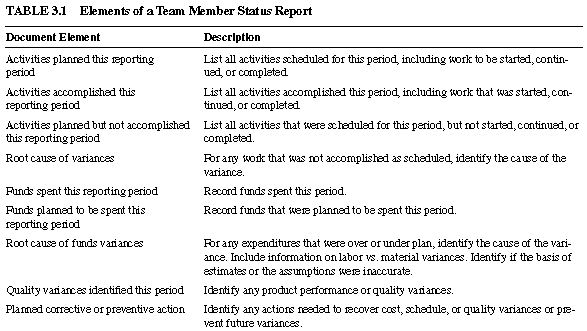
3.1 TEAM MEMBER STATUS REPORT
The Team Member Status Report is fi lled out by team members and submitted to the project manager on a regular basis. It tracks schedule and cost status for the current reporting period and provides planned information for the next reporting period. Status reports also identify new risks and issues that have arisen in the current reporting period. Typical information includes:
Activities planned for the current reporting period
Activities completed in the current reporting period
Activities planned but not completed in the current reporting period
Root causes of activities variances
Funds spent in the current reporting period
Funds planned to be spent for the current reporting period
Root causes of funds variances
Root causes of quality variances identifi ed in the current reporting period
Planned corrective or preventive action
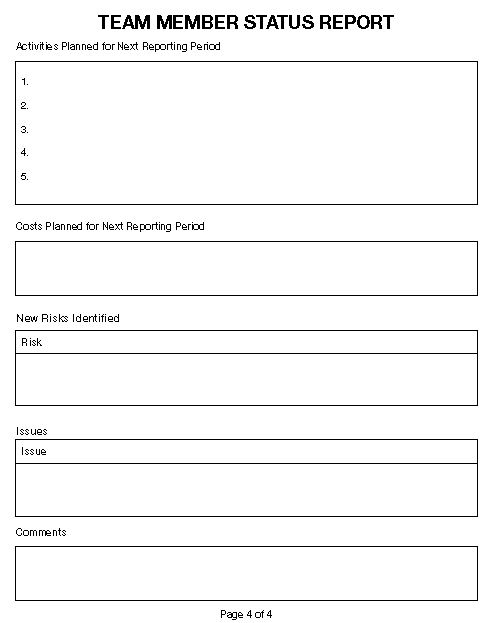
Activities planned for the next reporting period
Costs planned for the next reporting period
New risks identifi ed
Issues
Comments
This information is generally compiled by the project manager into a Project Performance Report. The Team Member Status Report and the Project Performance Report are examples of work performance reports, an output of 9.4 Manage Project Team in the PMBOKฎ GuideFifth Edition.
You can use the element descriptions in Table 3.1 to assist you in developing a Team Member Status Report.




3.2 CHANGE REQUEST
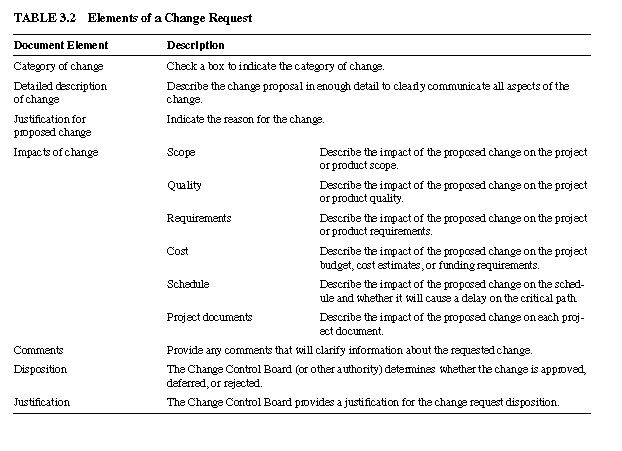
A Change Request is used to change any aspect of the project. It can pertain to project, product, documents,
requirements, or any other aspect of the project. Upon completion, it is submitted to the Change Control Board or other similar body for review. Typical information includes:
Person requesting the change
An identifi er, such as the change number
Category of change
Detailed description of the proposed change
Justifi cation for the proposed change
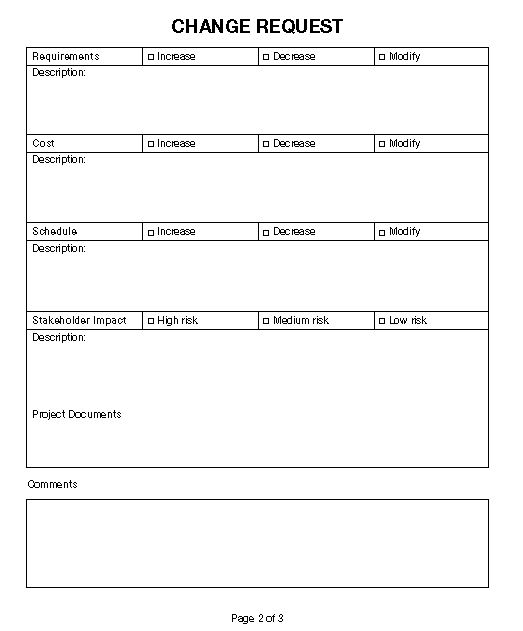
Impacts of the proposed change
Scope
Quality
Requirements
Cost
Schedule
Project documents
Disposition of change
Justifi cation
Signatures of Change Control Board
The Change Request form can result from these processes:
Direct and Manage Project Work Monitor and Control Project Work
Validate Scope Control Scope
Control Schedule Control Costs
Perform Quality Assurance Control Quality
Manage Project Team Control Communications
Control Risks Plan Procurement Management
Conduct Procurements Control Procurements
Control Stakeholder Engagement
The Change Request form is related to:
Change Log
Change Management Plan
It provides information to the following process:
Perform Integrated Change Control
You can use the element descriptions in Table 3.2 to assist you in developing a Change Request.


3.3 CHANGE LOG
The Change Log is a dynamic document that is kept throughout the project. It is used to track changes from
request through fi nal disposition. Typical information includes:
Change ID
Category
Description of change
Submitter
Submission date
Status
Disposition
The Change Log is related to the:
Change Request
Change Management Plan
You can use the element descriptions in Table 3.3 to assist you in developing a Change Log.


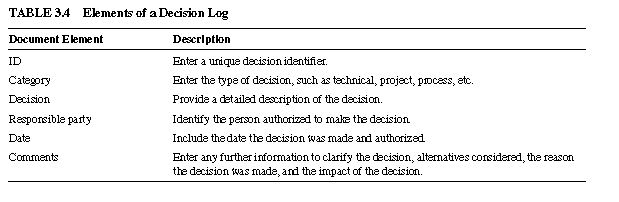
3.4 DECISION LOG
The Decision Log is a dynamic document that is kept throughout the project. Frequently there are alternatives in developing a product or managing a project. Using a Decision Log can help keep track of the decisions that were made, who made them, and when they were made. A Decision Log can include:
Identifier
Category
Decision
Responsible party
Date
Comments
Use the information from your project to tailor the form to best meet your needs. You can use the element
descriptions in Table 3.4 to assist you in developing a Decision Log.
3.5 QUALITY AUDIT
A Quality Audit is a technique that employs a structured, independent review to project and/or product elements.
Any aspect of the project or product can be audited. Common areas for audit include:
Project processes
Project documents
Product requirements
Product documents
Implementation of approved changes
Implementation of corrective or preventive action
Defect or defi ciency repair
Compliance with organizational policies and procedures
Compliance with the quality plan
Additional audit information can include:
Good practices to share
Areas for improvement
Description of defi ciencies or defects
Defects or defi ciencies should include action items, a responsible party, and be assigned a due date for compliance.
Audits should be tailored to best meet the needs of the project.
A Quality Audit is a technique from process 8.2, Perform Quality Assurance, in the PMBOKฎ GuideFifth
Edition. Audits should be tailored to best meet the needs of the project. Results from the audit may necessitate a Change Request, including preventive or corrective action, and defect repair.
You can use the element descriptions in Table 3.5 to assist you in developing a document to support a quality
audit.













