Clicking on a button, or entering some text in a text box, or clicking on a menu item, all are examples of events. An event is an action that calls a function or may cause another event.
Event handlers are functions that tell how to respond to an event.
VB.Net is an event-driven language. There are mainly two types of events:
Mouse events
Keyboard events
Mouse events occur with mouse movements in forms and controls. Following are the various mouse events related with a Control class:
MouseDown - it occurs when a mouse button is pressed
MouseEnter - it occurs when the mouse pointer enters the control
MouseHover - it occurs when the mouse pointer hovers over the control
MouseLeave - it occurs when the mouse pointer leaves the control
MouseMove - it occurs when the mouse pointer moves over the control
MouseUp - it occurs when the mouse pointer is over the control and the mouse button is released
MouseWheel - it occurs when the mouse wheel moves and the control has focus
The event handlers of the mouse events get an argument of type MouseEventArgs. The MouseEventArgs object is used for handling mouse events. It has the following properties:
Buttons - indicates the mouse button pressed
Clicks - indicates the number of clicks
Delta - indicates the number of detents the mouse wheel rotated
X - indicates the x-coordinate of mouse click
Y - indicates the y-coordinate of mouse click
Following is an example, which shows how to handle mouse events. Take the following steps:
Add three labels, three text boxes and a button control in the form.
Change the text properties of the labels to - Customer ID, Name and Address, respectively.
Change the name properties of the text boxes to txtID, txtName and txtAddress, respectively.
Change the text property of the button to 'Submit'.
Add the following code in the code editor window:
Public Class Form1
Private Sub Form1_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
' Set the caption bar text of the form.
Me.Text = "tutorialspont.com"
End Sub
Private Sub txtID_MouseEnter(sender As Object, e As EventArgs)_
Handles txtID.MouseEnter
'code for handling mouse enter on ID textbox
txtID.BackColor = Color.CornflowerBlue
txtID.ForeColor = Color.White
End Sub
Private Sub txtID_MouseLeave(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) _
Handles txtID.MouseLeave
'code for handling mouse leave on ID textbox
txtID.BackColor = Color.White
txtID.ForeColor = Color.Blue
End Sub
Private Sub txtName_MouseEnter(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) _
Handles txtName.MouseEnter
'code for handling mouse enter on Name textbox
txtName.BackColor = Color.CornflowerBlue
txtName.ForeColor = Color.White
End Sub
Private Sub txtName_MouseLeave(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) _
Handles txtName.MouseLeave
'code for handling mouse leave on Name textbox
txtName.BackColor = Color.White
txtName.ForeColor = Color.Blue
End Sub
Private Sub txtAddress_MouseEnter(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) _
Handles txtAddress.MouseEnter
'code for handling mouse enter on Address textbox
txtAddress.BackColor = Color.CornflowerBlue
txtAddress.ForeColor = Color.White
End Sub
Private Sub txtAddress_MouseLeave(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) _
Handles txtAddress.MouseLeave
'code for handling mouse leave on Address textbox
txtAddress.BackColor = Color.White
txtAddress.ForeColor = Color.Blue
End Sub
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) _
Handles Button1.Click
MsgBox("Thank you " & txtName.Text & ", for your kind cooperation")
End Sub
End Class
When the above code is executed and run using Start button available at the Microsoft Visual Studio tool bar, it will show the following window:
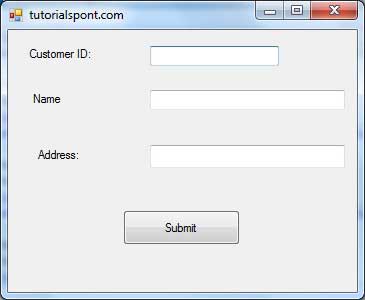
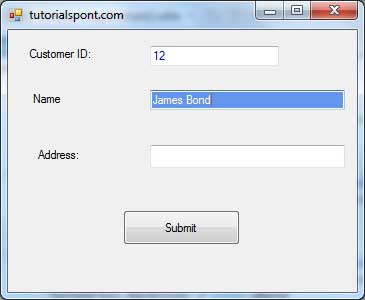
Try to enter text in the text boxes and check the mouse events:
Following are the various keyboard events related with a Control class:
KeyDown - occurs when a key is pressed down and the control has focus
KeyPress - occurs when a key is pressed and the control has focus
KeyUp - occurs when a key is released while the control has focus
The event handlers of the KeyDown and KeyUp events get an argument of type KeyEventArgs. This object has the following properties:
Alt - it indicates whether the ALT key is pressed/p>
Control - it indicates whether the CTRL key is pressed
Handled - it indicates whether the event is handled
KeyCode - stores the keyboard code for the event
KeyData - stores the keyboard data for the event
KeyValue - stores the keyboard value for the event
Modifiers - it indicates which modifier keys (Ctrl, Shift, and/or Alt) are pressed
Shift - it indicates if the Shift key is pressed
The event handlers of the KeyDown and KeyUp events get an argument of type KeyEventArgs. This object has the following properties:
Handled - indicates if the KeyPress event is handled
KeyChar - stores the character corresponding to the key pressed
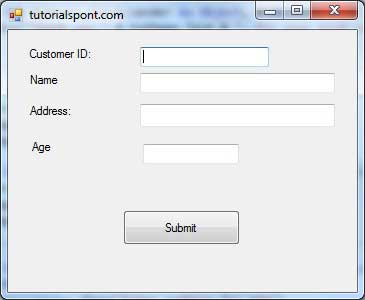
Let us continue with the previous example to show how to handle keyboard events. The code will verify that the user enters some numbers for his customer ID and age.
Add a label with text Property as 'Age' and add a corresponding text box named txtAge.
Add the following codes for handling the KeyUP events of the text box txtID.
Private Sub txtID_KeyUP(sender As Object, e As KeyEventArgs) _
Handles txtID.KeyUp
If (Not Char.IsNumber(ChrW(e.KeyCode))) Then
MessageBox.Show("Enter numbers for your Customer ID")
txtID.Text = " "
End If
End Sub
Add the following codes for handling the KeyUP events of the text box txtID.
Private Sub txtAge_KeyUP(sender As Object, e As KeyEventArgs) _
Handles txtAge.KeyUp
If (Not Char.IsNumber(ChrW(e.keyCode))) Then
MessageBox.Show("Enter numbers for age")
txtAge.Text = " "
End If
End Sub
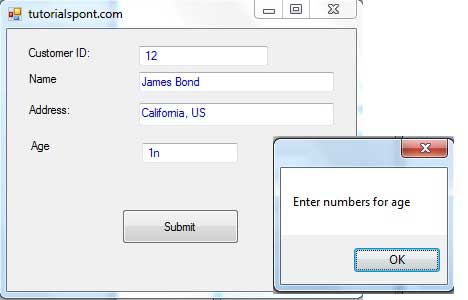
When the above code is executed and run using Start button available at the Microsoft Visual Studio tool bar, it will show the following window:
If you leave the text for age or ID as blank or enter some non-numeric data, it gives a warning message box and clears the respective text: