VB.Net - Database Access
Posted by Superadmin on October 31 2015 15:58:11
ADO.Net Object Model
ADO.Net object model is nothing but the structured process flow through various components. The object model can be pictorially described as:
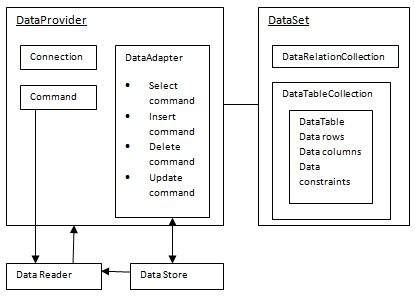
ADO.Net objects
The data residing in a data store or database is retrieved through the data provider. Various components of the data provider retrieve data for the application and update data.
An application accesses data either through a dataset or a data reader.
- Datasets store data in a disconnected cache and the application retrieves data from it.
- Data readers provide data to the application in a read-only and forward-only mode.
Data Provider
A data provider is used for connecting to a database, executing commands and retrieving data, storing it in a dataset, reading the retrieved data and updating the database.
The data provider in ADO.Net consists of the following four objects:
S.N |
Objects & Description |
|---|
1 |
Connection
This component is used to set up a connection with a data source.
|
2 |
Command
A command is a SQL statement or a stored procedure used to retrieve, insert, delete or modify data in a data source.
|
3 |
DataReader
Data reader is used to retrieve data from a data source in a read-only and forward-only mode.
|
4 |
DataAdapter
This is integral to the working of ADO.Net since data is transferred to and from a database through a data adapter. It retrieves data from a database into a dataset and updates the database. When changes are made to the dataset, the changes in the database are actually done by the data adapter.
|
Connecting to a Database
The .Net Framework provides two types of Connection classes:
SqlConnection - designed for connecting to Microsoft SQL Server.
OleDbConnection - designed for connecting to a wide range of databases, like Microsoft Access and Oracle.
Example 1
We have a table stored in Microsoft SQL Server, named Customers, in a database named testDB. Please consult 'SQL Server' tutorial for creating databases and database tables in SQL Server.
Let us connect to this database. Take the following steps:
Select TOOLS -> Connect to Database
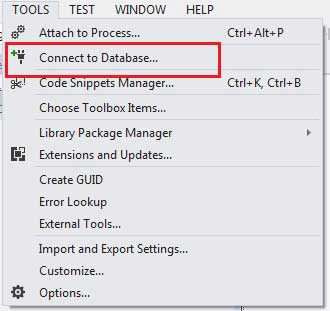
Select a server name and the database name in the Add Connection dialog box.
Click on the Test Connection button to check if the connection succeeded.
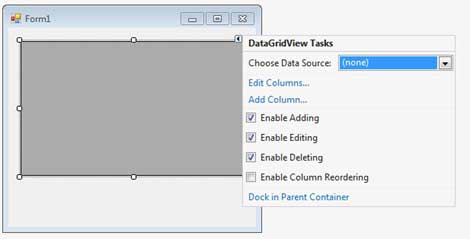
Add a DataGridView on the form.
Click on the Choose Data Source combo box.
Click on the Add Project Data Source link.
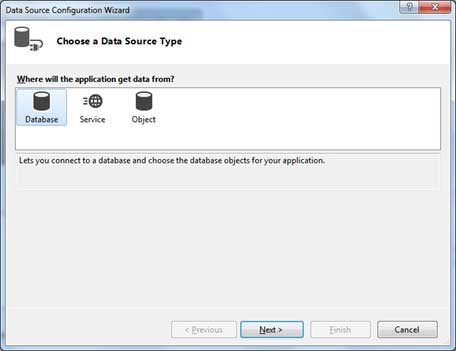
This opens the Data Source Configuration Wizard.
Select Database as the data source type
Choose DataSet as the database model.
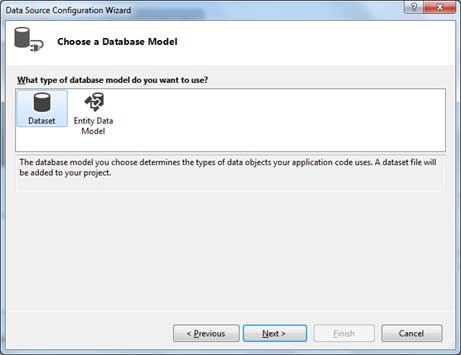
Choose the connection already set up.
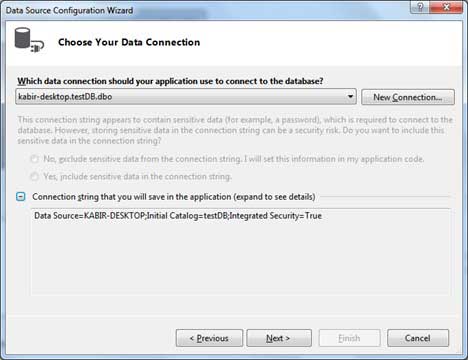
Save the connection string.
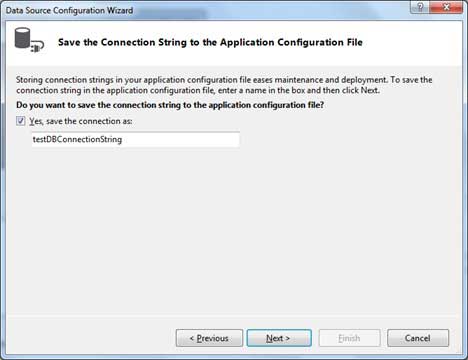
Choose the database object, Customers table in our example, and click the Finish button.
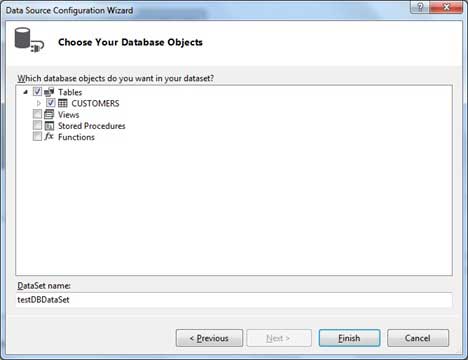
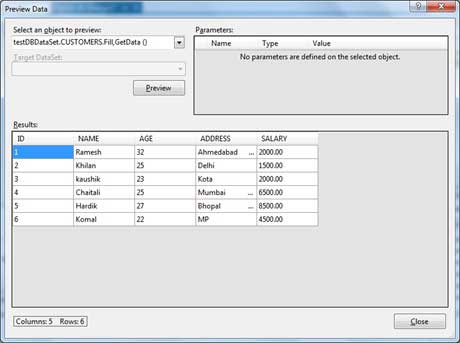
Select the Preview Data link to see the data in the Results grid:
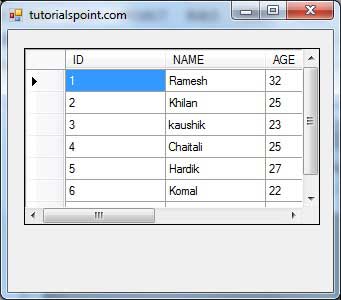
When the application is run using Start button available at the Microsoft Visual Studio tool bar, it will show the following window:
Example 2
In this example, let us access data in a DataGridView control using code. Take the following steps:
Add a DataGridView control and a button in the form.
Change the text of the button control to 'Fill'.
Double click the button control to add the required code for the Click event of the button, as shown below:
Imports System.Data.SqlClient
Public Class Form1
Private Sub Form1_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) _
Handles MyBase.Load
'TODO: This line of code loads data into the 'TestDBDataSet.CUSTOMERS' table. You can move, or remove it, as needed.
Me.CUSTOMERSTableAdapter.Fill(Me.TestDBDataSet.CUSTOMERS)
' Set the caption bar text of the form.
Me.Text = "tutorialspoint.com"
End Sub
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
Dim connection As SqlConnection = New sqlconnection()
connection.ConnectionString = "Data Source=KABIR-DESKTOP; _
Initial Catalog=testDB;Integrated Security=True"
connection.Open()
Dim adp As SqlDataAdapter = New SqlDataAdapter _
("select * from Customers", connection)
Dim ds As DataSet = New DataSet()
adp.Fill(ds)
DataGridView1.DataSource = ds.Tables(0)
End Sub
End Class
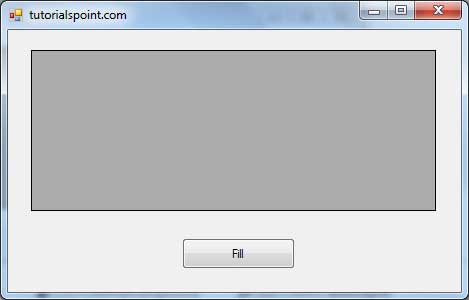
When the above code is executed and run using Start button available at the Microsoft Visual Studio tool bar, it will show the following window:
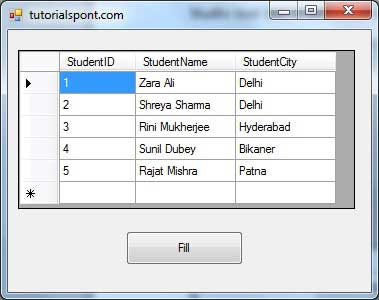
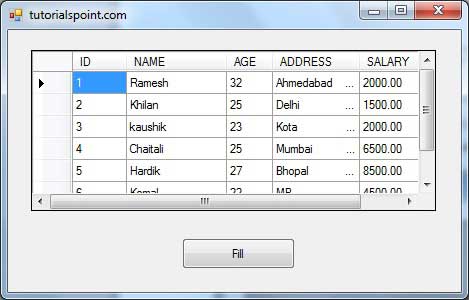
Clicking the Fill button displays the table on the data grid view control:
Creating Table, Columns and Rows
We have discussed that the DataSet components like DataTable, DataColumn and DataRow allow us to create tables, columns and rows, respectively.
The following example demonstrates the concept:
Example 3
So far, we have used tables and databases already existing in our computer. In this example, we will create a table, add columns, rows and data into it and display the table using a DataGridView object.
Take the following steps:
Add a DataGridView control and a button in the form.
Change the text of the button control to 'Fill'.
Add the following code in the code editor.
Public Class Form1
Private Sub Form1_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
' Set the caption bar text of the form.
Me.Text = "tutorialspont.com"
End Sub
Private Function CreateDataSet() As DataSet
'creating a DataSet object for tables
Dim dataset As DataSet = New DataSet()
' creating the student table
Dim Students As DataTable = CreateStudentTable()
dataset.Tables.Add(Students)
Return dataset
End Function
Private Function CreateStudentTable() As DataTable
Dim Students As DataTable
Students = New DataTable("Student")
' adding columns
AddNewColumn(Students, "System.Int32", "StudentID")
AddNewColumn(Students, "System.String", "StudentName")
AddNewColumn(Students, "System.String", "StudentCity")
' adding rows
AddNewRow(Students, 1, "Zara Ali", "Kolkata")
AddNewRow(Students, 2, "Shreya Sharma", "Delhi")
AddNewRow(Students, 3, "Rini Mukherjee", "Hyderabad")
AddNewRow(Students, 4, "Sunil Dubey", "Bikaner")
AddNewRow(Students, 5, "Rajat Mishra", "Patna")
Return Students
End Function
Private Sub AddNewColumn(ByRef table As DataTable, _
ByVal columnType As String, ByVal columnName As String)
Dim column As DataColumn = _
table.Columns.Add(columnName, Type.GetType(columnType))
End Sub
'adding data into the table
Private Sub AddNewRow(ByRef table As DataTable, ByRef id As Integer,_
ByRef name As String, ByRef city As String)
Dim newrow As DataRow = table.NewRow()
newrow("StudentID") = id
newrow("StudentName") = name
newrow("StudentCity") = city
table.Rows.Add(newrow)
End Sub
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
Dim ds As New DataSet
ds = CreateDataSet()
DataGridView1.DataSource = ds.Tables("Student")
End Sub
End Class
When the above code is executed and run using Start button available at the Microsoft Visual Studio tool bar, it will show the following window:
Clicking the Fill button displays the table on the data grid view control: