What is THIS Keyword in Java?
Keyword THIS is a reference variable in Java that refers to the current object.
The various usages of 'THIS' keyword in Java are as follows:
- It can be used to refer instance variable of current class
- It can be used to invoke or initiate current class constructor
- It can be passed as an argument in the method call
- It can be passed as argument in the constructor call
- It can be used to return the current class instance
Click here if the video is not accessible
Understand 'this' keyword with an example.
- Class: class Account
- Instance Variable: a and b
- Method Set data: To set the value for a and b.
- Method Show data: To display the values for a and b.
- Main method: where we create an object for Account class and call methods set data and show data.
Let's compile and run the code
Our expected output for A and B should be initialized to the values 2 and 3 respectively.
But the value is 0, Why? Let investigate.
In the method Set data, the arguments are declared as a and b, while the instance variables are also named as a and b.
During execution, the compiler is confused. Whether "a" on the left side of the assigned operator is the instance variable or the local variable. Hence, it does not set the value of 'a' when the method set data is called.
The solution is the "THIS" keyword
Append both 'a' and 'b' with the "this" keyword followed by a dot (.) operator.
During code execution when an object calls the method 'setdata'. The keyword 'this' is replaced by the object handler "obj." (See the image below).
So now the compiler knows,
- The 'a' on the left-hand side is an Instance variable.
- Whereas the 'a' on right-hand side is a local variable
The variables are initialized correctly, and the expected output is shown.
Suppose you are smart enough to choose different names for your instance variable and methods arguments.
But this time around, you create two objects of the class, each calling the set data method.
How the compiler will determine whether it is supposed to work on instance variable of object 1 or object 2.
Well, the compiler implicitly appends the instance variable with "THIS" keyword (image below).
Such that when object 1 is calling the set data method, an instance variable is appended by its reference variable.
While object 2 is calling the set data method, an instance variable of object 2 is modified.
This process is taken care by the compiler itself. You don't have to append 'this' keyword explicitly unless there is an exceptional situation as in our example.
Example: To learn the use "this" keyword
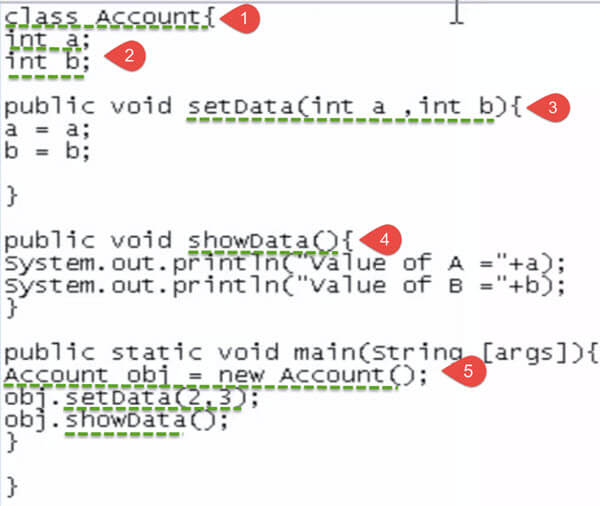
Step 1) Copy the following code into a notepad.
class Account{
int a;
int b;
public void setData(int a ,int b){
a = a;
b = b;
}
public void showData(){
System.out.println("Value of A ="+a);
System.out.println("Value of B ="+b);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Account obj = new Account();
obj.setData(2,3);
obj.showData();
}
}
Step 2) Save ,Compile & Run the code.
Step 3) Value of a & b is shown as zero? To correct the error append line # 6 & 7 with "this" keyword.
this.a =a; this.b =b;
Step 4) Save, Compile, and Run the code. This time around, values of a & b are set to 2 & 3 respectively.
Summary
- Keyword 'THIS' in Java is a reference variable that refers to the current object.
- It can be used to refer current class instance variable
- It can be used to invoke or initiate current class constructor
- It can be passed as an argument in the method call
- It can be passed as argument in the constructor call
- It can be used to return the current class instance
- "this" is a reference to the current object, whose method is being called upon.
- You can use "this" keyword to avoid naming conflicts in the method/constructor of your instance/object.