SAP for Beginners
Posted by Superadmin on January 03 2019 14:52:55
SAP for Beginners
SAP has the largest market share of all ERP systems & commands unparalleled premium in the ERP & IT market. These basic tutorials will introduce the SAP ERP, Business suite, SAP Modules, GUI and process to become a SAP consultant.
What should I know?
Nothing! This course assumes you to be an absolute beginner to SAP.
Syllabus
| Tutorial |
Introduction to SAP Introduction to SAP and Why it is required ? |
| Tutorial |
SAP Business Suite |
| Tutorial |
SAP Modules Introductions |
| Tutorial |
How to choose Best SAP Module for your career |
| Tutorial |
How to become SAP consultant |
| Tutorial |
How to get a SAP Certification |
| Tutorial |
SAP GUI & Navigation Tutorial |
| Tutorial |
How to install SAP IDES for Practice |
| Tutorial |
What is mySAP? |
| Tutorial |
What is Netweaver? |
| Tutorial |
How to Display Technical Names in SAP |
| Tutorial |
SAP Molga List for ALL Countries |
| Tutorial |
How to Execute SAP Reports |
| Tutorial |
How to use SAP variant |
| Tutorial |
Top 50 SAP Interview Questions |
| Tutorial |
What is SAP Business Blueprint? |
| Tutorial |
What is the Full Form and Meaning of ERP? |
| Tutorial |
What is Full form of SAP? |
| Tutorial |
Top 18 SAP Testing Interview Questions & Answers |
What is SAP?
SAP stands for Systems Applications and Products in Data Processing.
SAP by definition is also named of the ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software as well the name of the company.
SAP Software was Founded in 1972 by Wellenreuther, Hopp, Hector, Plattner and Tschira.
SAP system consists of a number of fully integrated modules, which covers virtually every aspect of the business management.
SAP is #1 in the ERP market. As of 2010, SAP has more than 140,000 installations worldwide, over 25 industry-specific business solutions and more than 75,000 customers in 120 countries
Other Competitive products of SAP Software in the market are Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics etc.
What is SAP ERP? Why it is Required?
Following Video will explain the need of an ERP software like SAP in an enterprise
Please be patient. The Video will load in some time. If you still face issue viewing video click
here
The very basic question to any beginners is why Enterprise Resource Planning also called ERP is required? To answer this, let’s examine this typical business scenario.
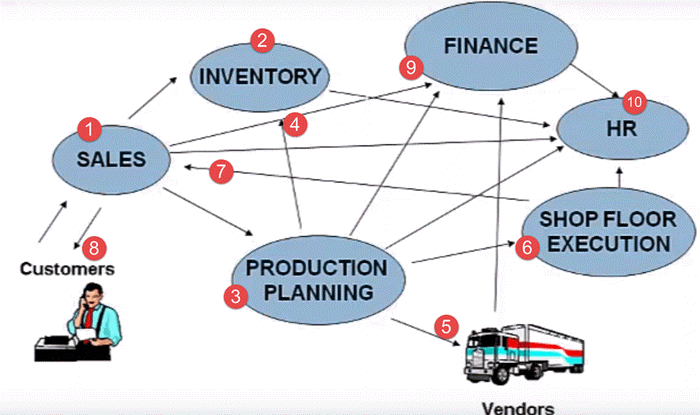
Suppose a client approaches sales team asking for a particular product. The sales team contacts to inventory department to check the availability of the product. To their surprise, sales team found out that the product is out of stock. So next time this don’t happen, they have to introduce a SAP ERP tool.
Before we actually see in detail, what ERP is and how ERP can help in your business process, we will understand how different departments are involved in the whole business process, right from the ordering of the raw material – to manufacturing goods – to delivering final goods to the customer.
Here is the whole process that is followed by any business unit.
- Client contacts the sales team to check the availability of the product
- Sales team approaches the Inventory department to check for the availability of the product
- In case the product is out of stock, the sales team approaches the Production Planning Department to manufacture the product
- The production planning team checks with inventory department for availability of raw material
- If raw material is not available with inventory, the Production Planning team buys the raw material from the Vendors
- Then Production Planning forwards the raw materials to the Shop Floor Execution for actual production
- Once ready, the Shop Floor Team forwards the goods to the Sales Team
- Sales Team who in turn deliver it to the client
- The sales team updates the finance with revenue generated by the sale of the product. Production planning team update the finance with payments to be made to different vendors for raw materials.
- All departments approach the HR for any Human Resource related issue.
That is a typical business process for any manufacturing company. Some key inferences one could derive from the scenario would be.
- It has many departments or business units
- These departments or business units continuously communicate and exchange data with each other
- The success of any organization lies in effective communication, and data exchange, within these departments, as well as associated third party such as vendors, outsourcers, and customers.
Based on the manner in which communication and data exchanged is managed. Enterprise systems can be broadly classified as
1) Decentralized System
2) Centralized System which are also called as ERP.
Decentralized System
Let's look at Decentralized system first, in a company with Decentralized System of Data Management, there are two major problems –
- Data is maintained locally at the individual departments
- Departments do not have access to information or data of other departments
To identify problems arising due to decentralized Enterprise management system lets look at the same business process again. The customer approaches the sales team for a product, but this time around he needs the product, on an urgent basis.
Since it is a decentralized process, the Sales Team do not have any real-time information access to the products availability. So they approach the Inventory department to check the availability of the product. This process takes time and customer chooses another vendor leading to loss of revenue and customer dissatisfaction.
Now, suppose the product is out of stock and the Sales Team approaches the Production Planning team to manufacture the product for future use. Production Planning Team checks the availability of the raw materials required.
In a decentralized system, raw material information is separately stored by Production Planning as well as Inventory Department. Thus, data maintenance cost (in this case Raw Material) goes up.
The raw material information is available in two different departments Inventory as well as Production Planning. When sales team check a particular raw material required to manufacture the product, it shows the raw material is available as per the inventory, but as per the database of the production planning team, the raw material is out of stock.
So, they go ahead and buy the raw material. Thus, material as well inventory cost goes up.
Once the raw material is available, the shop floor department suddenly realizes they are short of workers they approach the HR, who in turn hire temporary employees at higher than market rates. Thus LABOR Cost Increases.
The production planning department fails to update the finance department on the materials they have purchased. The finance department defaults the payment deadline set by the vendor causing the company loss of its reputation and even inviting a possible legal action.
These are just a few of many problems with decentralized systems.
Some Major problems with the decentralized system are –
- Numerous disparate information system generates individually over time which are difficult to maintain
- Integrating the data is time and money consuming
- Inconsistencies and duplication of data
- Lack of timely information leads to customer dissatisfaction , loss of revenue and reputation
- High Inventory, material, and human resource cost.
These are some major drawbacks for which we need a solution. Well the Solution lies in Centralized Systems i.e. ERP.
Centralized System
In a company, with Centralized System of Information and Data Management.
1) Data is maintained at a central location and is shared with various Departments
2) Departments have access to information or data of other Departments
Let’s look at the same business process again to understand how a Centralized Enterprise System helps to overcome problems posed by a Decentralized Enterprise System.
In this Case, all departments update a Central Information System.
- When Customer approaches the sales team to buy a product on an urgent basis. The Sales Team has real-time information access to the products in inventory which is updated by the Inventory Department in the Centralized System
- Sales Team respond to customer request on time leading to Increased Revenue and Customer Delight.
- In case, manufacturing is required the Sales Team update the Centralized Database, so that all the department remain informed about the product status.
- Production Planning Department is auto updated by the Centralized Database for requirements. Production Planning Team checks the availability of the raw materials required via Central Database, which is updated by the Inventory Department.
- Thus, Data Duplication is avoided, and accurate data is made available. The Shop Floor Team update their Man Power Status regularly in the Central Database, which can be accessed by the HR department.
- In case of shortage of workforce, HR team starts recruitment process with considerable lead time to hire a suitable candidate at market price.Thus labor cost goes down.
- While vendors can directly submit their invoices to the Central Enterprise System, which can be accessed by the finance department. Thus, payments are made on time, and possible legal actions are avoided
- SAP software is a type of Centralized System. SAP System is most popularly used ERP software.
Key benefits of the centralized system are:
- It Eliminates the duplication, discontinuity and redundancy in data
- Provides information across departments in real time.
- SAP System is Provides control over various business processes
- Increases productivity, better inventory management , promotes quality , reduced material cost, effective human resources management, reduced overheads boosts profits
- Better customer interaction and increased throughput. It also improves customer service
- Hence, a centralized enterprise management system is required.
- SAP Software is a centralized enterprise management system also known as Enterprise Resource Planning.
What is SAP Business Suite?
SAP Business Suite is collection of fully integrated applications such as SAP customer relationship management (CRM), SAP Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), SAP product lifecycle management (PLM), SAP supplier relationship management (SRM), and SAP supply chain management (SCM) modules.
Most people relate SAP with its ERP offering. But SAP now offers variety of products to address varied needs of an organization. Lets have a look at them -
- SAP HANA:- High Performance Analytic Appliance uses in-memory computing, a breakthrough technology that enables analysis of very large, non-aggregated data at unprecedented speed in local memory (vs. disk-based database) enabling complex analyses, plans and simulations on real-time data.
- SAP Convergent Charging :- SAP Convergent Charging provides a rating and charging solution for high-volume processing in service industries. It delivers pricing design capabilities, high performance rating and convergent balance management.
- Customer Relationship Management:- Unlike other CRM software, the SAP Customer Relationship Management (SAP CRM) application, part of the SAP Business Suite, not only helps you address your short-term imperatives – to reduce cost and increase your decision-making ability – but can also help your company achieve differentiated capabilities in order to compete effectively over the long term.
- Enterprise Resource Planning:- A sound foundation is necessary to compete and win in the global marketplace. The SAP ERP application supports the essential functions of your business processes and operations efficiently and are tailored to specific needs of your industry like SAP ERP Financials, SAP ERP Human capital management,SAP ERP Operations,SAP ERP corporate services.
- SAP Environment, Health, and Safety Management :- It supports environmental, occupational and product safety processes, regulatory compliance, and corporate responsibility. This is accomplished by embedding corporate policies, compliance, and environmental, health and safety capabilities with global business processes for human resources, logistics, production and finance.
- SAP Global Batch Traceability :- It allows you to completely trace tracked objects, for example, a batch, across both SAP systems and non-SAP systems. In the event of a recall or withdrawal, SAP GBT ensures the timely compliance with legal reporting timelines. Furthermore, it helps you to minimize cost and corporate risk exposure. You can also analyze multiple objects, for example, batches, in one run.
- SAP Product Life Cycle Management:- To survive in an ever-changing global environment, creating and delivering innovative and market differentiating products and services is what distinguishes your company from the competition. The SAP Product Lifecycle Management (SAP PLM) application provides you with a 360-degree-support for all product-related processes – from the first product idea, through manufacturing to product service
- SAP Supplier Life Cycle Management:- SAP Supplier Lifecycle Management is a holistic approach to managing supplier relationships. It deals with the supply base as a whole to constantly determine the right mix of suppliers. It covers the lifecycle of individual suppliers ? from onboarding to a continuous development.
- Supply Chain Management :- You face enormous pressure to reduce costs while increasing innovation and improving customer service and responsiveness. SAP Supply Chain Management (SAP SCM) enables collaboration, planning, execution, and coordination of the entire supply network, empowering you to adapt your supply chain processes to an ever-changing competitive environment.
- Supplier Relationship Management:- With SAP SRM you can examine and forecast purchasing behavior, shorten procurement cycles, and work with your partners in real time. This allows you to develop long-term relationships with all those suppliers that have proven themselves to be reliable partners.
- Governance, Risk and Compliance:- Risk is unavoidable, but it can be managed. With governance, risk, and compliance (GRC), businesses can strategically balance risk and opportunity.
- Sales and operations planning:- SAP Sales and Operations Planning enables you to optimally and profitably meet long-term future demand. Typically, this process repeats every month and involves many participants including Sales, Marketing, Finance, Demand Planning, and Supply Chain Planning.
- SAP Transportation Management :- It supports you in all activities connected with the physical transportation of goods from one location to another.
- Extended Warehouse Management:- SAP Extended Warehouse Management gives you the option of mapping your entire warehouse complex in detail in the system, down to the storage bin level. Not only does this give you an overview of the total quantity of a product in the warehouse, but you can also always see exactly where a specific product is, at any time, in your warehouse complex. With EWM, you can optimize the use of various storage bins and stock movements, and can combine the storage of stocks from several plants in randomly-managed warehouses.
- Mobile Apps:- Mobile devices can also access SAP system.
SAP Modules can be categorized into
- Functional Modules
- Technical Modules
These functional and technical modules are tightly coupled. Below is a list of key SAP Modules
- SAP FI Module - FI stands for Financial Accounting
SAP FI module is very robust and covers almost all financial business process encountered in various industries. It is one of the widely implemented modules in SAP. Learn more about SAP FI
- SAP CO Module - CO stands for Controlling
Cost Accounting (CO) module of SAP provides information to managers decision makers to understand where the company's money is being spent. CO helps them to optimize business costs.
- SAP HCM Module - HR stands for Human Resources
SAP Human Capital Management (HCM) is also called SAP-HR. SAP HCM consists of sub-modules like Personnel Administration (PA), Organizational Management (OM), Time, Payroll that help in employee management. Learn more about SAP HCM
- SAP MM Module - MM is Materials Management
Materials Management module in SAP consists of several components and sub-components including Master Data, Purchasing, and Inventory. Learn more about SAP MM
- SAP QM Module - QM stands for Quality Management
SAP QM (Quality Management) is an integral part of several key business processes of SAP like production, sales, procurement, material management, etc. Learn more about SAP QM
- SAP PP Module - PP is Production Planning
SAP PP ( Production Planning) is a SAP module, specially designed for integrating different department involved in production and manufacturing. It has various components like Data Center, BOM, Work Center, CRP etc. Learn more about SAP PP
- SAP SD Module - SD is Sales and Distribution
SAP Sales and Distribution (SD) is an important module of SAP ERP consisting of business processes required in selling, shipping, billing of a product. The module is tightly integrated with SAP MM & SAP PP. Key sub-modules of SAP SD are Customer and Vendor Master Data, Sales, Delivery, Billing, Pricing and Credit Management. Learn more about SAP SD
- SAP BW Module - where BW stands for Business (Data) Warehouse
SAP BI (Business Intelligence) or SAP BW is a leading data warehousing and reporting tool. It helps convert raw data into information and insights that help improve business margins. Learn more about SAP BW
- SAP Basis -
SAP Basis is a set of programs and tools that act as an interface with Database, Operating system, communication protocols and other SAP modules like FI,HCM, SD etc. Learn more about SAP Basis
- SAP ABAP -
ABAP (Advanced Business Application Programming) is the default programming language for SAP applications. You can also use Java to code in SAP. Learn more about SAP ABAP
- SAP CRM - where CRM stands for Customer Relationship Management
SAP CRM is the Market Leader in Customer Relationship Management Software. SAP CRM plays a pivotal role in strengthening customer relationships. Learn more about SAP CRM
- SAP HANA - where Hana stands for High-performance Analytic Appliance.
SAP HANA is an in-memory computing platform that allows real-time data analysis. Its currently the market leader in BI.Learn more about SAP HANA
- SAP EC Module - where EC stands for Enterprise Controlling
- SAP TR Module - where TR stands for Treasury
- SAP IM Module - where IM stands for Investment Management
- SAP IS -where IS stands for Industries Specific Solution
- SAP PS Module- and PS is Project Systems
- SAP CAC - Cross Application Components
- SAP SCM- where SCM stands for Supply Chain Management
- SAP PLM- where PLM stands for Product LifeCycle Management
- SAP SRM- where SRM stands for Supplier Relationship Management
- SAP CS- where CS stands for Customer Service
- SAP SEM - where SEM stands for STRATEGIC ENTERPRISE MANAGEMENT
- SAP RE - where RE stands for Real Estate
- SAP PM Module- where Plant Maintenance is the PM
- SAP Security Learn more about SAP Security
- SAP FSCM - where FSCM stands for Financial Supply Chain Management
- SAP NetWeaver
- SAP IS - where IS stands for Industry Specific Solution
- SAP XI - where XI stands for Exchange Infrastructure
- SAP Solution Manager – Learn more about Solution Manager
- SAP LE - where LE stands for Logistics Execution
- SAP APO- where APO stands for Advanced Planning and Optimization
- SAP AFS - where AFS stands for Apparel and Footwear Solution
- SAP CC - where CC stands for Convergent Charging
- SAP ITS - where ITS stands for Internet Transaction Server
- SAP ICM - where ICM stands for Incentive and Commission Management
- SAP KW - where KW stands for Knowledge Warehouse
- SAP MDM - where MDM stands for Master Data Management
We often emails along the line ... "I have done XYZ degree and have ABC work experience. Could you recommend a SAP module for me? "
It is difficult to answer all your emails, so, we decided to bring out a guide that will help you in choosing the "right" module for you.
You need to consider three factors in choosing a SAP module
- Job Opportunities in the chosen Module
- You academic background and work experience
- Your Career / Life Goals
Let's look at them one by one.
Job Opportunities
SAP has 25 modules and adding. Refer this list of all SAP Modules
But not all the 25 SAP modules are implemented in every company. The most implemented modules are the ones with most job opportunities.
We recommend you narrow down your choice of SAP Modules to following which are in demand
- SAP FI
- SAP MM
- SAP SD
- SAP PP
- SAP HCM
- SAP Basis/ ABAP - for people with a technical bent
Apart from above modules, you can also consider making a career in many SAP add-on modules like which are HOT in market
- SAP CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
- SAP BI also known as SAP BW (Business Warehouse)
Academic Background and work experience
Once you have narrowed your choices to above modules, you need to factor in your education and work experience (if any) to trim the choices even further.
For instance, if you are a MBA in HR it makes no sense choosing SAP FI module. SAP HCM is a more apt module for you. Working in HCM module will give you a competitive advantage as compared to SAP FI where you will work as a fresher.
Your career and life goals.
This is often the most overlooked although the most important factor. Before selecting a SAP module , you need to think hard whether you want to work on SAP in first place ?
You need to factor in your inclination , passion , aptitude and career goals into your decision.
You need to ask yourself, whether you are looking for a "career" in SAP or just a job ?
Following tool will help you choose the best sap module for yourself. Good Luck :)
SAP Career Suggestion Tool
Plan to make a career as a SAP Consultant? If Yes, this guide is a MUST READ!
What is a SAP Consultant?
SAP Consultant is a Subject Matter Expert (SME) either on the
- Business/ sales
- Functional
- Development or
- Basis
domains of SAP. The consultant provides advisory, recommendations, guidance, implementation help in their respective SAP domains.
Why SAP?
SAP (Systems Applications and Products) is the world's leading provider of business software which specializes in industry specific Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solutions.
SAP is implemented in 9 out of every 10 Fortune 500 company.
SAP consultants enjoy a premium remuneration over their IT counterparts working in other technologies like Java, .net etc.
Types of SAP Consultant
1) Business/Sales Consultant - They try to win projects at customer end - without knowing much about SAP :-)
2) SAP Functional Consultant - They are responsible for customizing SAP as per customer demand. They talk with developers to code custom ABAP programs as per client requirements.
3) Developer Consultant - They are responsible for coding ABAP/Java Programs
4) SAP Basis Consultant - They help in installing, maintenance and performance tuning of SAP servers and databases
Above are the major consulting roles found in almost all SAP projects. Depending on the nature and size of the project there may be other consulting roles as well such as SAP security consultant, SAP Techno-functional consultants, etc.
Skills required in becoming a SAP Functional Consultant
The skills expected of a SAP Functional consultant vary with experience. But a fresher SAP consultant must have following skills that almost all employers look for -
- Extensive SAP (module specific) knowledge.
- Good Domain (Banking, Telecommunication, etc. ) knowledge
- Good Communication and presentation skills. SAP consultants are often required to interface with the client and understand client's requirements. A SAP consultant should be good in explaining technical information to non-technical people
- Ability to work in Teams and good interpersonal skills.
Academic Background
SAP Consultant Salary
The salary of a fresher SAP consultant in the USA is from $48,000 to $60,000 and the bonuses are from $1,000 to $2,000.
The salary of a fresher SAP consultant in India is from RS 247,000 to RS 4,50,000 and the bonuses are from RS 10,000 to RS 15,000.
How to become a SAP consultant
From time to time we get emails asking "How do I become a SAP consultant." Obviously, there is no one answer. There are many ways to enter the SAP market. Here are a few we can conjure ... Obtain SAP Training & Certification. Choose a SAP module and get a certification from an authorized SAP training partner. SAP training is expensive, but it's worth the investment
Join a consulting companyIf you have good business/domain knowledge (and want to learn SAP ?), you could consider joining an IT consultancy company like IBM, Deloitte, Infosys. etc as a junior consultant.
Join as a Trainee or in SAP supportYou can consider joining a company which has SAP implemented and work as a Trainee or support personnel. The company may later sponsor your SAP certification and training. The trick here is to find such a company and convince them to hire you
Join SAP Project as a non-SAP person.Many SAP projects require skills outside of SAP. For instance, lots of projects require a data conversion individual. If you are good in database and SQL, you might consider joining the project and later teach yourself SAP
Any other ways to enter the SAP market? ... Leave a comment
SAP offers various certification for different modules.
Certifications can be found based on the
- SAP Solution (Like SAP Business One, Business Objects, ERP, Netweaver, PLM etc)
- Your Role ( Development, Application, Technology)
As of today there are 220+ different certifications on offer
Each certificate has 2 levels
- Associate
- Professional – (Please be aware that the professional-level certifications also require several years of practical on-the-job experience and address real-life scenarios)
| Types of SAP certification |
Types of questions |
Requirement |
Exam Duration |
| Associate certification |
80 multiple choice, multiple response and matching questions and answers |
_______ |
3 hours |
| NEW- Speciality Certification |
40 multiple choice, multiple response and matching question and answers |
Comes along in addition to associate exams |
90 minutes |
| Professional certification |
of 80 multiple choice, multiple response, scenario based and matching questions and answers |
Requires project experience, business process knowledge and understanding of SAP solutions |
3 hours |
Eligibility Criteria
For SAP there are no specific criteria if you are enrolling for basic modules of SAP; any graduate can pursue their career in SAP. However, some SAP modules require relevant work experience in field like engineer graduate with relevant work experience of minimum two years can take a course in SAP MM, PP, and PM module while a commerce graduate or MBA can choose SAP FICO.
Registration for SAP certification
Since 2014 SAP certification vouchers are only available for purchased directly from SAP education. Pearson Vue is no longer accepting payment for SAP certification.
Registration for SAP Certification exams taken at Pearson VUE
- Contact your local SAP education department to register to your S-user number
- Purchase a voucher from SAP education. You have to pay $500
- Create a new web account if you don't already have an account with Pearson Vue
- Sign in to your Pearson Vue account and schedule your exam appointment. At the checkout screen, enter your voucher number in the space marked "Voucher/Promotion Code"
- For few countries, online certification service is not provided and you have to call SAP where a representative will guide you through the process.
- To register for SAP certification online, you have to visit the website http://www.sap.com/training-education/certification/about.html
Tips to prepare for SAP certification exam
- Find the right level of certification ( Associate or Professional certification exam)
- Start your search for your module directly in the certification web shop (https://training.sap.com/shop/certification/). Select the country and language to get all information for your location
- If you are new to SAP, use the options training and certification shop (https://training.sap.com/shop/catalogue/by-delivery-method) it offers a wide variety of training options to meet your learning needs, it includes e-learning courses as well
- In order to get a better idea about which topics are important for your certification, you have to review the syllabus. On the certification site, you can find an overview of the related topics
- SAP education also provides some sample questions on its site; these are actual questions asked during past exams. You will find these questions under certification details for each exam
- Learning with SAP books is a good alternative
- SAP learning hub general user guide allows to interact with SAP solution experts through a forum. It also offers multiple courses in various languages
- In SAP exam be careful in using English words especially words like can, only, always, except
What is SAP Logon?
SAP Logon is used initiate a user session in a desired SAP Server. The same SAP Logon pad can be used to login into different SAP ERP environments. SAP Logon is a client side software usually used by Consultants, developers and end-users
Following Video will take you through the various screen elements observed in the SAP - Graphical User Interface (GUI)
Please be patient. The Video will load in some time. If you still face issue viewing video click
here
-
To access SAP, double click in the SAP logon PAD.
-
You are shown a list of servers that you could log into right now there is only one server
-
But you see multiple servers like one for production, one for Testing one for development.
-
Select the server and click the Log On Button. In the next screen, enter your user id and password. You are taken to Sap's easy access menu
-
At the top, you will see the menu bar. Next you will see the standard tool bar where you options to Print , Save Find , Scroll etc
-
To view or maintain any data in SAP or access different business process you need to know the corresponding transaction. Every transaction has a unique code.
-
For example, transaction number to maintain a PA data is PA30
- To access the transaction, in the command prompt enter PA30 and hit enter.
- If you notice the title bar changes in accordance with the transaction, you are currently in.
- To go back to the initial screen click the back button
- Alternatively, if you do not remember the transaction code, a tree is provided with all the transaction available.
- Navigate in the tree. Double click in the corresponding transaction. Suppose you do not want to navigate so much to access a transaction, right click on it and select Add to favorites
- The transaction is added to your favorites. At the bottom of a screen you will notice Message Bar. This Bar has three colors
- Red - for errors
- Yellow - for warnings
- Green - for success
- If you double click on the bar, detailed information of the message is reflected
- At the bottom, you will see various system related information like the client or the program you are currently in.
- To get help in SAP, select on the corresponding screen element and press F1
- Suppose, I want help on command prompt, pressing F1 gives me a very detailed help document.
- That's it to the SAP GUI
SAP GUI Navigation
When you logon to SAP or you open a new session- you will see the following screen
Lets look into the various screen elements-
SAP User Menu
The SAP User Menu is tailored to the user's specific needs. It includes all transactions relevant to a user, grouped under relevant folders
SAP Easy Access Menu
The SAP Easy Access Menu includes all transactions offered by SAP, grouped in folders according to SAP modules (FI/CO, MM, etc.). It is not tailored to the user's specific needs
SAP Menu Bar
The SAP Menu Bar CHANGES from one screen to another. You follow a menu path to access a function or a transaction.
SAP Standard Tool Bar
The SAP Standard Toolbar does NOT change from one transaction to another. You can use the SAP Standard Toolbar to execute various functions.
- Buttons available are enabled
- Buttons not available are disabled
- In the "Transaction Box", you can directly access a transaction, without using the SAP Menu, by entering the transaction code
General Icons and their Description
Hint: You open a maximum of 6 different SAP session at a time
SAP Application Toolbar
The SAP Application Toolbar CHANGES from one screen to another.
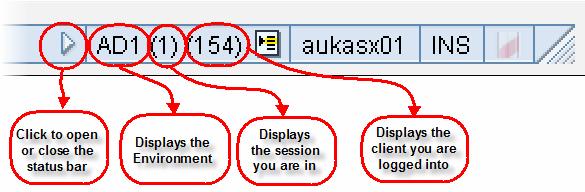
SAP Status Bar
The SAP Status Bar does NOT change from one screen to another. It tells you WHERE you are in SAP:
- Which environment you are using (Production , Development , Quality).
- In which session you are in (as you can open up to 6 sessions).
- What client you are using.
Clicking on button gives more information -
SAP Function Keys
Functions keys are just another way of navigating around SAP. The availability of function keys CHANGES from one screen to another While in a transaction , right click on your mouse , you will see a list of function keys available
How to get HELP in SAP
More often than not while using SAP you will need HELP. You can access in-built SAP Help functionality for ANY screen element(like text fields , buttons ,labels etc ) for ANY SAP Screen In this training , we will assume you need help for the following field -
You can access help in three different ways
- Clicking on the "Help" button.
- Right-clicking on your mouse and selecting "Help".
- Pressing the F1 button on your keyboard.
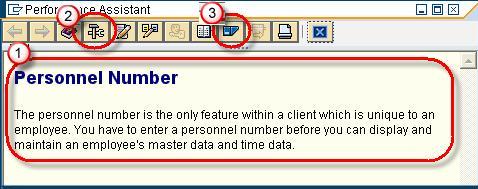
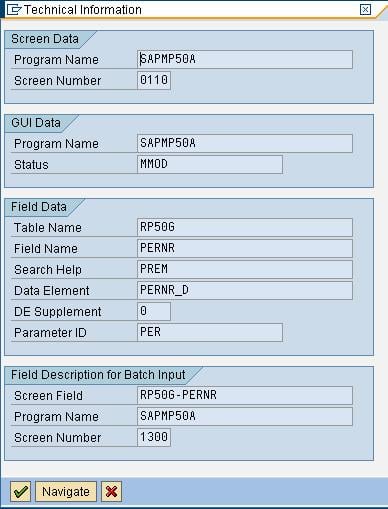
A Performance Assistance Screen Opens-
1. It gives you information on how to fill the specific field on screen
2. Clicking on Technical Information Button gives you information like program name , table name and other technical details which comes in very handy at times
3. Clicking on portal button gives you access to the online SAP Library available via the internet.
What is SAP IDES?
IDES is a demo SAP system developed by SAP AG used for learning and training and purpose. IDES stand for Internet Demonstration and Evaluation System.
SAP IDES is an easy way for end users or consultants to get acquainted with SAP or gain mastery over the SAP ERP.
This document will explain you the installation of IDES server for learning and practice purpose. There are some prerequisites before installation of IDES EHP6 server. We required installation media, list of media is shown below:
- j2sdk-1_4_2_17-windows-amd64.exe
- IDES EHP6 Installation Master
- IDES EHP6 Installation Export
- NW703 Kernel 720_Ext
- SL Controller 720
- MS SQL RDBMS
- SAPCRYPTOGRAPHIC Library
- JCE (Java Cryptography Extension) Policy
The above media is available on SAP Marketplace. Download and store it on your local hard disk. What we have gone through was software requirement, now let us focus on hardware requirement. For the installation we require server with
- RAM of 4 GB and above
- HDD of 600 GB
- Intel i3 processor 64-bit and above
- Windows server 2006 R2 operating system.
Note: You can install SAP on Linux , AIX and Sun Solaris as well Below we have explained road map and each step for SAP IDES installation.
Many learners need a video of the installation steps or do not have access to the SAP Marketplace to download the necessary files.
For such students we recommend you follow this course to get step by step process to install SAP in your laptop.
Fig. Roadmap of SAP Installation
Installation steps:
- Hostname of the server where you want to install IDES should not be more than 13 characters otherwise you will get an error during installation.
- Increase the virtual memory to thrice of physical memory of the server or ideally you can make it 20 GB.
- Install the Java - j2sdk-1_4_2_17-windows-amd64.exe and set the JAVA_HOME environment variable. Windows server 2008 R2 has the java component within operating system package.
- Before you start SAP IDES installation, you need to decide the System Identifier (SID) and Instance Number (00). Here we will use SID = IDS and instance number = 00.
-
Now go to the installation master media and follow the path as shown below:
SAPCD(F:)/INST_MAST/IM_WINDOWS_X86_64/sapinst and double click on "sapinst" as shown in below figures 1 & 2.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
- After double clicking on "sapinst" it will open sap installation GUI as shown in figure 3.
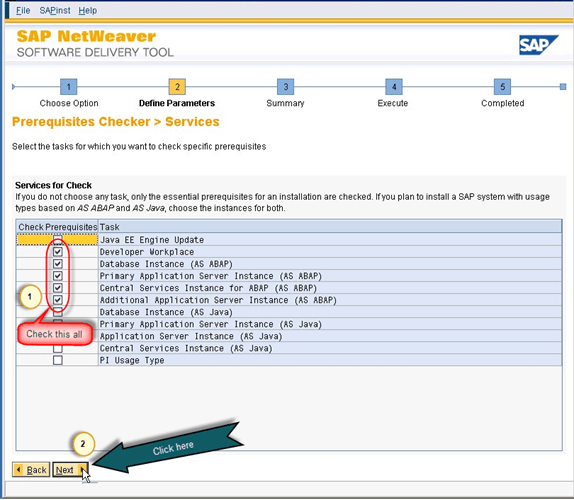
- Now follow the path as shown in figure 3 and select prerequisite check then click on the next.
Fig. 3
- Prerequisites check is needed because if there are any requisites missing then it will show you during this phase. Once you click on the next, it will take you to the next screen as shown in figure 4. There is a datafile to check the prerequisites on the installation master DVD. Once you will go to the next screen it will automatically detect the .xml file or you can browse the installation master DVD for "PREREQUISITE_CHECK_DATA.XML" and then click on the next.
Fig. 4
- As we are installing ABAP stack, we need to check the option shown in figure 5 and then click on next.
Fig. 5
- On the next screen figure 6, it will ask for the database for sap. Here we are going to install SAP on MS SQL database, so we have selected MS SQL server option. If you are planning to install another database then you can select it from the drop down option which is highlighted in figure 6.
Fig. 6
- On the next screen, you have to mention the JAVA_HOME path, where you have installed the java environment, and also we are installing Unicode so check all and then click on the next.
Fig. 7
- On the next screen figure 8, it will ask you to review the option which you selected. If you want to change the selection you can select the option "revise". Otherwise select next, and it will execute prerequisite check.
Fig. 8
- If there are any prerequisites missing then, it will show on the next screen, or it will complete execution successfully as shown in figure 9.
Fig. 9
- Now again repeat the step 5 and execute "sapinst" from installation master and select the "Operating System user and Groups" from drop down as shown in figure 10 and click on next.
Fig. 10
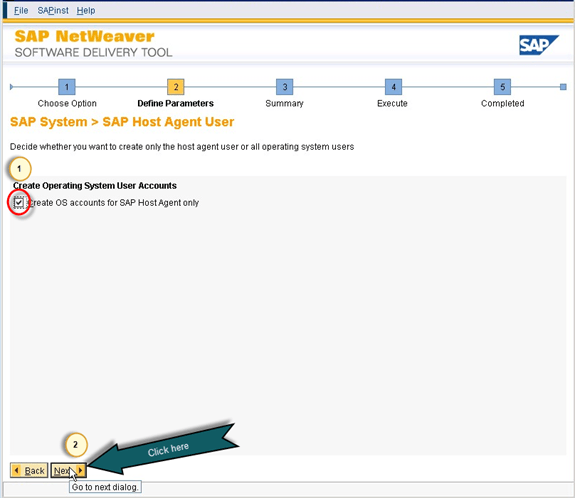
- On the next screen, it will ask you either you want to create OS accounts for sap host agent only or sap administrative user also. After selecting the option click on the next as shown in figure 11.
Fig. 11
- On the next screen, it provides the SAP system identifier "IDS". Select local domain installation or provide the domain of your host server as shown in figure 12 and then click next.
Fig. 12
- On the next screen, set the password. Password should be compatible with operating system password policy. After mentioning the password click on the next.
Fig. 13
- Next screen (figure 14), allows you to revise the option which you have selected. Otherwise you can continue with selected option and click on the next.
Fig. 14
- After successful execution of this step, following message is shown.
Fig. 15
- Once all the prerequisites and user creation is complete, we need to install the database before we start installation of central instance of IDES server. To start the DB installation we need to go to RDBMS DVD as shown in figure 16.Here we have MS SQL database and for that SAP provided the script "SQL4SAP", just double click on that script. If you have Oracle database then it will get install in between installation of SAP.
Fig. 16
- After you double click on the script, it will open a window and ask for the database instance SID. For sap installation always keeps it as default. So, it will create the DB SID same as SAP SID. Details are given in figure 17.
Fig. 17
- Once you click on the OK button, it will ask for the confirmation, so click on OK as shown in figure 18.
Fig. 18
- Once you confirm it will start the installation of MS SQL database in the background and installed on "C:/" drive.
Fig. 19
- Once the installation gets complete, it will show the message as shown in figure 20.
Fig. 20
- Now again repeat step 5 and start the "sapinst" and select the "Central Instance" and click on the next and start installation as shown in figure 21.
Fig. 21
- On the next screen, it will ask you for installation mode. If you select "Typical" mode then sapinst automatically selects some default settings, it will not allowe DB configuration and SAPDATA file selection. While if you select the "Custom" mode then it will ask for this expert settings. Ref. figure 22.
Fig. 22
- Next screen figure 23, provide the SAP system ID (SID) and installation drive where you want to install (where "\usr\sap" resides).
Fig. 23
- As shown in figure 24, it will ask for the server's Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN). If you are going for local server installation then uncheck the FQDN option otherwise check the FQDN option and provide your server's FQDN. Here we are going for local installation, so we have unchecked the option.
Fig. 24
- Now, enter master password for your sap system. This password will be used for all SAP accounts and users during installation. You can also use this password to log in to SAP system with DDIC and SAP* users.
Fig. 25
- As we have explained earlier, we are going to install as local installation. So, on the next screen (figure 26), select the local installation option and click on next.
Fig. 26
- On the next screen as shown in figure 27, it will ask the password for "<SID>adm" and SAPservice<SID>. As you have already provided the Master password, you can skip this step, or you can set a different password for each user. For Oracle database, there are "<SID>adm" and "ORA<SID>" users.
Fig. 27
- Now it will ask for the database instance. As you have previously installed the MS SQL database, so it will show default instance of the database, select that instance and click on the next.
Fig. 28
- On this screen, it will show the information message that DBSID and SAPSID is same. This is ok, just click on the next.
Fig. 29
- On the next screen it will ask you for the media path of Unicode Kernel NW 7.20. Please provide the path by browsing from "Browse" and click on the next.
Fig. 30
\
- Next it will show the installation drive where "\usr\sap\PRFCLOG" will get created.
Fig. 31
- Now it will ask for the domain detail for sap host agent. We are installing as local so select local Domain option and click on the next.
Fig. 32
- Now provide the password for sapadm user otherwise it will take the master password as default.
Fig. 33
- Now provide the path of installation export media and click on next.
Fig. 34
- Now it will ask for the password of database ABAP schema. By default it will take master password.
Fig. 35
- Now it will ask for the number of data file needs to be created for the database. As per the standard it will create 4 datafiles for small system, 8 datafiles for medium system and 16 datafiles for large system. Here we have selected 8 datafiles.
Fig. 36
- On the next screen, it will ask for the path where you want to store these datafiles. Also, you need to specify the initial size of datafiles.
Fig. 37
- Now it will ask for the location and size of tempdev and templog file.By default it will be on installation drive of a database. After providing the required details click on the next.
Fig. 38
- Here you need to provide the number of parallel jobs of ABAP import phase, default is 3, but its recommended to increase the number of parallel jobs as per server resources. We have increased the jobs from 3 to 10. SAP code page will be a default, do not change it.
Fig. 39
- Here it will ask for the central instance number, you can choose any number in between 00 to 99. Here we have chosen 00, which is a default.
Fig. 40
- Now provides the details of ABAP message server and Internal ABAP port. Default it will be 3600 and 3900 respectively. We also need to provide a host for transport directory, default it will be the same host where you are installing the server. Here you can change the host if there is common transport directory for single landscape.
Fig. 41
- Next screen will ask for the media path of sapcryptographic, provide the media path for the same. If you don't want to install then uncheck the option and click on the next.
Fig. 42
- In this step it will unpack the component of sapcryptographic library. Please select each package to unpack and click on the next.
Fig. 43
- Now it will ask for the SID of diagnostic agent system, default it will be DAA but you can provide as per you and also can change the destination drive.
Fig. 44
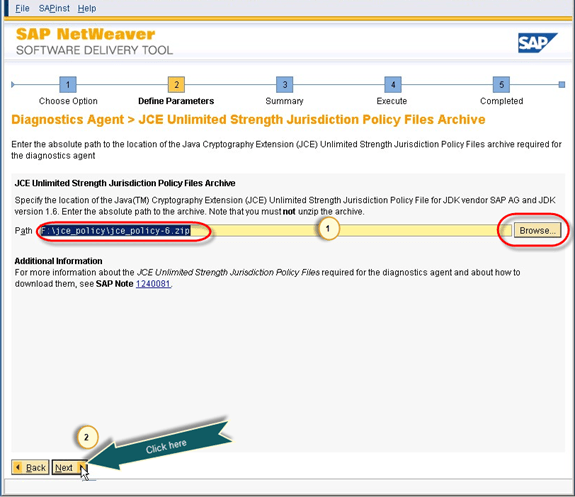
- Here we need to provide the media path of JAVA JCE policy.
Fig. 45
- Next it will ask for the diagnostic agent system domain detail. If you want to install as domain then provide the domain name and select the option "Domain of the current user" or " different domain" otherwise select local installation option, which we have selected here.
Fig. 46
- On this screen, it will ask for the password for diagnostic agent system. Default password will be master password which you have provided before.
Fig. 47
- Next it will ask for the instance number for the diagnostic agent system.
Fig. 48
- On the next screen, it will ask you to register your system in existing SLD if you want. SLD is the host where all server details are stored. If you choose to register in existing SLD then on the next screen, it will ask you the host details. Here we have selected "No SLD destination" option. You can find the details in figure 49 and figure 50.
Fig. 49
Fig. 50
- Now it will ask to unpack the archive for diagnostic agent system. Please check all and click on next.
Fig. 51
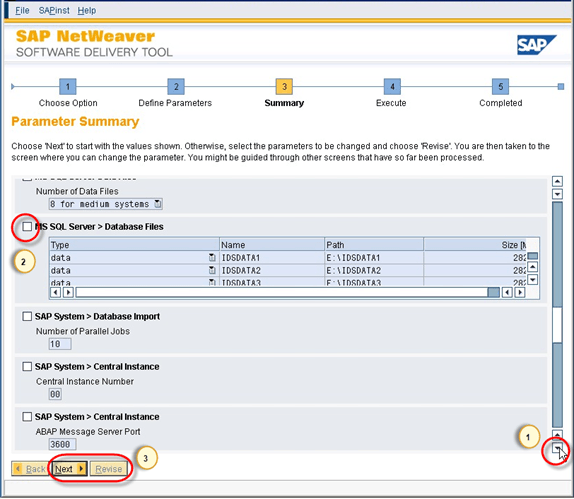
- Now on this screen it will show you all the parameter which you have selected during the "Define Parameters" phase. You can revise the input parameter if you want. Once you revise the parameter, you can click on the next.
Fig. 52
Fig. 53
- On this screen, it will ask for the solution manager key. You required unique key for your installation that you need to generate from SAP solution manager. After providing the solution manager key click on the next.
Fig. 54
- Once solution manager key provided, it will start the other installation phase. Longest phase will be "Import ABAP" phase. On the bottom of the screen, you can find the status of the installation.
Fig. 55
Fig. 56
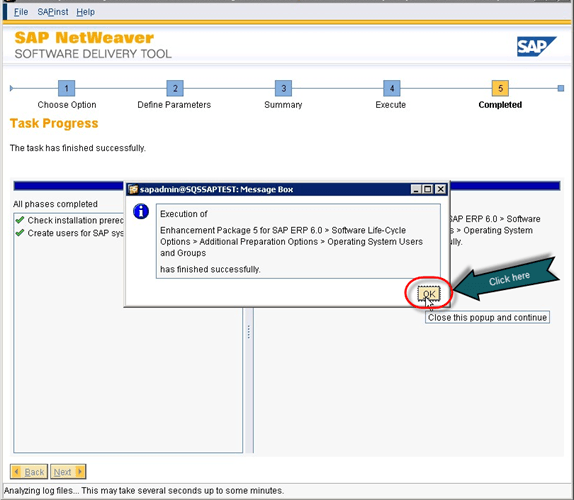
- Once all the phase completed successfully, it will pop-up new window which shows the message of successful installation.
Fig. 57
- Once the installation got complete, you can login to the system with DDIC and SAP* using SAP GUI with master password. SAP IDES server has default 000, 001, 066 and 800 client available.
mySAP is not a single product but is a suite of products from SAP including SAP R/3.
SAP R/3 was First launched in 1998 , is regularly updated ,and is market leader in ERP category till date.
SAP R/3 many modules such as HR , Finance , MM covering all enterprise Functions
"3" stands for three tier architecture - Presentation tier , Logic tier and Data tier.
Other products in the mySAP product suite includes SRM(Supplier Relationship Management), CRM(Customer Relationship Management), PLM(Product Lifecycle Management ) , SCM (Supply Chain Management)
Following Video will take you through the SAP product suite.