Initially, it was Google Big Table, afterwards it was re-named as HBase and is primarily written in Java.
HBase can store massive amounts of data from terabytes to petabytes.
A table for a popular web application may consist of billions of rows. If we want to search particular row from such huge amount of data, HBase is the ideal choice as query fetch time in less. Most of the online analytics applications uses HBase.
Traditional relational data models fail to meet performance requirements of very big databases. These performance and processing limitations can be overcomed by HBase.
In big data analytics, Hadoop plays a vital role in solving typical business problems by managing large data sets and gives best solutions in analytics domain.
In terms of storing unstructured, semi-structured data storage as well as retrieval of such data's, relational databases are less useful. Also, fetching results by applying query on huge data sets that are stored in Hadoop storage is a challenging task. NoSQL storage technologies provide the best solution for faster querying on huge data sets.
For example, MongoDB is a document-oriented database from NoSQL family tree. Compared to traditional databases it provides best features in terms of performance, availability and scalability. It is an open source document-oriented database, and it's written in C++.
Cassandra is also a distributed database from open source Apache software which is designed to handle a huge amount of data stored across commodity servers. Cassandra provides high availability with no single point of failure.
While, CouchDB is a document-oriented database in which each document fields are stored in key-value maps.
HBase storage model is different from other NoSQL models discussed above. This can be stated as follow
MongoDB, CouchDB, and Cassandra are of NoSQL type databases that are feature specific and used as per their business needs. Here, we have listed out different NoSQL database as per their use case.
HBase is used to store billions of rows of call detailed records. If 20TB of data is added per month to the existing RDBMS database, performance will deteriorate. To handle a large amount of data in this use case, HBase is the best solution. HBase performs fast querying and display records.
The Banking industry generates millions of records on a daily basis. In addition to this, banking industry also needs analytics solution that can detect Fraud in money transactions.
To store, process and update huge volumes of data and performing analytics, an ideal solution is - HBase integrated with several Hadoop eco system components.
HBase provides unique features and will solve typical industrial use cases. As a column-oriented storage, it provides fast querying, fetching of results and high amount of data storage.
HBase is an open-source, column-oriented distributed database system in Hadoop environment.Apache HBase is needed for real-time Big Data applications. The tables present in HBase consists of billions of rows having millions of columns.
Hbase is built for low latency operations, which is having some specific features compared to traditional relational models.
In this tutorial- you will learn,
Storage Mechanism in Hbase
HBase is a column-oriented database and data is stored in tables. The tables are sorted by RowId. As shown below, HBase has RowId, which is the collection of several column families that are present in the table.
The column families that are present in the schema are key-value pairs. If we observe in detail each column family having a multiple numbers of columns. The column values stored in to disk memory. Each cell of the table has its own Meta data like time stamp and other information.
Coming to HBase the following are the key terms representing table schema
-
Table: Collection of rows present.
-
Row: Collection of column families.
-
Column Family: Collection of columns.
-
Column: Collection of key-value pairs.
-
Namespace: Logical grouping of tables.
-
Cell: A {row, column, version} tuple exactly specifies a cell definition in HBase.
Column-oriented and Row oriented storages
Column and Row oriented storages differ in their storage mechanism. As we all know traditional relational models store data in terms of row-based format like in terms of rows of data. Column-oriented storages store data tables in terms of columns and column families.
The following Table gives some key differences between these two storages
| Column-oriented Database |
Row oriented Database |
|
|
|
|
|
|
What HBase consists of
HBase consists of following elements,
-
Set of tables
-
Each table with column families and rows
-
Each table must have an element defined as Primary Key.
-
Row key acts as a Primary key in HBase.
-
Any access to HBase tables uses this Primary Key
-
Each column present in HBase denotes attribute corresponding to object
HBase Architecture and its Important Components
HBase architecture consists mainly of four components
-
HMaster
-
HRegionserver
-
HRegions
-
Zookeeper
HMaster:
HMaster is the implementation of Master server in HBase architecture. It acts like monitoring agent to monitor all Region Server instances present in the cluster and acts as an interface for all the metadata changes. In a distributed cluster environment, Master runs on NameNode. Master runs several background threads.
The following are important roles performed by HMaster in HBase.
-
Plays a vital role in terms of performance and maintaining nodes in the cluster.
-
HMaster provides admin performance and distributes services to different region servers.
-
HMaster assigns regions to region servers.
-
HMaster has the features like controlling load balancing and failover to handle the load over nodes present in the cluster.
-
When a client wants to change any schema and to change any Metadata operations, HMaster takes responsibility for these operations.
Some of the methods exposed by HMaster Interface are primarily Metadata oriented methods.
-
Table ( createTable, removeTable, enable, disable)
-
ColumnFamily (add Column, modify Column)
-
Region (move, assign)
The client communicates in a bi-directional way with both HMaster and ZooKeeper. For read and write operations, it directly contacts with HRegion servers. HMaster assigns regions to region servers and in turn check the health status of region servers.
In entire architecture, we have multiple region servers. Hlog present in region servers which are going to store all the log files.
HRegions Servers:
When Region Server receives writes and read requests from the client, it assigns the request to a specific region, where actual column family resides. However, the client can directly contact with HRegion servers, there is no need of HMaster mandatory permission to the client regarding communication with HRegion servers. The client requires HMaster help when operations related to metadata and schema changes are required.
HRegionServer is the Region Server implementation. It is responsible for serving and managing regions or data that is present in distributed cluster. The region servers run on Data Nodes present in the Hadoop cluster.
HMaster can get into contact with multiple HRegion servers and performs the following functions.
-
Hosting and managing regions
-
Splitting regions automatically
-
Handling read and writes requests
-
Communicating with the client directly
HRegions:
HRegions are the basic building elements of HBase cluster that consists of the distribution of tables and are comprised of Column families. It contains multiple stores, one for each column family. It consists of mainly two components, which are Memstore and Hfile.
Data flow in HBase
Write and Read operations
The Read and Write operations from Client into Hfile can be shown in below diagram.
Step 1) Client wants to write data and in turn first communicates with Regions server and then regions
Step 2) Regions contacting memstore for storing associated with the column family
Step 3) First data stores into Memstore, where the data is sorted and after that it flushes into HFile. The main reason for using Memstore is to store data in Distributed file system based on Row Key. Memstore will be placed in Region server main memory while HFiles are written into HDFS.
Step 4) Client wants to read data from Regions
Step 5) In turn Client can have direct access to Mem store, and it can request for data.
Step 6) Client approaches HFiles to get the data. The data are fetched and retrieved by the Client.
Memstore holds in-memory modifications to the store. The hierarchy of objects in HBase Regions is as shown from top to bottom in below table.
| Table |
HBase table present in the HBase cluster |
| Region |
HRegions for the presented tables |
| Store |
It store per ColumnFamily for each region for the table |
| Memstore |
-
Memstore for each store for each region for the table
-
It sorts data before flushing into HFiles
-
Write and read performance will increase because of sorting
|
| StoreFile |
StoreFiles for each store for each region for the table |
| Block |
Blocks present inside StoreFiles |
ZooKeeper:
In Hbase, Zookeeper is a centralized monitoring server which maintains configuration information and provides distributed synchronization. Distributed synchronization is to access the distributed applications running across the cluster with the responsibility of providing coordination services between nodes. If the client wants to communicate with regions, the servers client has to approach ZooKeeper first.
It is an open source project, and it provides so many important services.
Services provided by ZooKeeper
-
Maintains Configuration information
-
Provides distributed synchronization
-
Client Communication establishment with region servers
-
Provides ephemeral nodes for which represent different region servers
-
Master servers usability of ephemeral nodes for discovering available servers in the cluster
-
To track server failure and network partitions
Master and HBase slave nodes ( region servers) registered themselves with ZooKeeper. The client needs access to ZK(zookeeper) quorum configuration to connect with master and region servers.
During a failure of nodes that present in HBase cluster, ZKquoram will trigger error messages, and it starts to repair the failed nodes.
HDFS:-
HDFS is Hadoop distributed file system, as the name implies it provides distributed environment for the storage and it is a file system designed in a way to run on commodity hardware. It stores each file in multiple blocks and to maintain fault tolerance, the blocks are replicated across Hadoop cluster.
HDFS provides a high degree of fault –tolerance and runs on cheap commodity hardware. By adding nodes to the cluster and performing processing & storing by using the cheap commodity hardware, it will give client better results as compared to existing one.
In here, the data stored in each block replicates into 3 nodes any in case when any node goes down there will be no loss of data, it will have proper backup recovery mechanism.
HDFS get in contact with the HBase components and stores large amount of data in distributed manner.
HBase vs. HDFS
HBase runs on top of HDFS and Hadoop. Some key differences between HDFS and HBase are in terms of data operations and processing.
Some typical IT industrial applications use HBase operations along with Hadoop. Applications include stock exchange data, online banking data operations, and processing Hbase is best-suited solution method.
Conclusion:-
Hbase is one of NoSql column-oriented distributed database available in apache foundation. HBase gives more performance for retrieving fewer records rather than Hadoop or Hive. It's very easy to search for given any input value because it supports indexing, transactions, and updating.
We can perform online real-time analytics using Hbase integrated with Hadoop eco system. It has an automatic and configurable sharding for datasets or tables, and provides restful API's to perform the MapReduce jobs.
After successful installation of HBase on top of Hadoop, we get an interactive shell to execute various commands and perform several operations. Using these commands, we can perform multiple operations on data-tables that can give better data storage efficiencies and flexible interaction by the client.
We can interact with HBase in two ways,
- HBase interactive shell mode and
- Through Java API
In HBase, interactive shell mode is used to interact with HBase for table operations, table management, and data modeling. By using Java API model, we can perform all type of table and data operations in HBase. We can interact with HBase using this both methods.
The only difference between these two is Java API use java code to connect with HBase and shell mode use shell commands to connect with HBase.
Quick overcap of HBase before we proceed-
- HBase uses Hadoop files as storage system to store the large amounts of data. Hbase consists of Master Servers and Regions Servers
- The data that is going to store in HBase will be in the form of regions. Further, these regions will be split up and stored in multiple region servers
- This shell commands allows the programmer to define table schemas and data operations using complete shell mode interaction
- Whichever command we use, it's going to reflect in HBase data model
- We use HBase shell commands in operating system script interpreters like Bash shell
- Bash shell is the default command interpreters for most of Linux and Unix operating distributions
- HBase advanced versions provides shell commands jruby-style object oriented references for tables
- Table reference variables can be used to perform data operations in HBase shell mode
For examples,
- In this tutorial, we have created a table in which 'education' represents table name and corresponds to column name "guru99".
- In some commands "guru99," itself represents a table name.
In this tutorial- you will learn,
General commands
In Hbase, general commands are categorized into following commands
- Status
- Version
- Table_help ( scan, drop, get, put, disable, etc.)
- Whoami
To get enter into HBase shell command, first of all, we have to execute the code as mentioned below
Once we get to enter into HBase shell, we can execute all shell commands mentioned below. With the help of these commands, we can perform all type of table operations in the HBase shell mode.
Let us look into all of these commands and their usage one by one with an example.
This command will give details about the system status like a number of servers present in the cluster, active server count, and average load value. You can also pass any particular parameters depending on how detailed status you want to know about the system. The parameters can be 'summary', 'simple', or 'detailed', the default parameter provided is "summary".
Below we have shown how you can pass different parameters to the status command.
hbase(main):002:0>status 'simple'
hbase(main):003:0>status 'summary'
hbase(main):004:0> status 'detailed'
If we observe the below screen shot, we will get a better idea.
Syntax: hbase(main):001:0>status
When we execute this command status, it will give information about number of server's present, dead servers and average load of server, here in screenshot it shows the information like- 1 live server, 1 dead servers, and 7.0000 average load.
- Version
Syntax:hbase(main):005:0> version
- This command will display the currently used HBase version in command mode
- If you run version command, it will give output as shown above
- Table help
Syntax: hbase(main) :007:0>table_help
This command guides
- What and how to use table-referenced commands
- It will provide different HBase shell command usages and its syntaxes
- Here in the screen shot above, its shows the syntax to "create" and "get_table" command with its usage. We can manipulate the table via these commands once the table gets created in HBase.
- It will give table manipulations commands like put, get and all other commands information.
- whoami
Syntax: hbase(main):006:0> Whoami
This command "whoami" is used to return the current HBase user information from the HBase cluster.
It will provide information like
- Groups present in HBase
- The user information, for example in this case "hduser" represent the user name as shown in screen shot
- TTL(Time To Live) - Attribute
In HBase, Column families can be set to time values in seconds using TTL. HBase will automatically delete rows once the expiration time is reached. This attribute applies to all versions of a row – even the current version too.
The TTL time encoded in the HBase for the row is specified in UTC. This attribute used with table management commands.
Important differences between TTL handling and Column family TTLs are below
- Cell TTLs are expressed in units of milliseconds instead of seconds.
- A cell TTLs cannot extend the effective lifetime of a cell beyond a Column Family level TTL setting.
Tables Managements commands
These commands will allow programmers to create tables and table schemas with rows and column families.
The following are Table Management commands
- Create
- List
- Describe
- Disable
- Disable_all
- Enable
- Enable_all
- Drop
- Drop_all
- Show_filters
- Alter
- Alter_status
Let us look into various command usage in HBase with an example.
- Create
Syntax: hbase> create <tablename>, <columnfamilyname>
Example:-
hbase(main):001:0> create 'education' ,'guru99'
0 rows(s) in 0.312 seconds
=>Hbase::Table – education
The above example explains how to create a table in HBase with the specified name given according to the dictionary or specifications as per column family. In addition to this we can also pass some table-scope attributes as well into it.
In order to check whether the table 'education' is created or not, we have to use the "list" command as mentioned below.
- List
Syntax:hbase(main):001:0>list
- "List" command will display all the tables that are present or created in HBase
- The output showing in above screen shot is currently showing the existing tables in HBase
- Here in this screenshot, it shows that there are total 8 tables present inside HBase
- We can filter output values from tables by passing optional regular expression parameters
- Describe
Syntax: hbase>describe <table name>
This command describes the named table.
- It will give more information about column families present in the mentioned table
- In our case, it gives the description about table "education."
- It will give information about table name with column families, associated filters, versions and some more details.
Here, in the above screenshot we are disabling table education
- Enable
Syntax: hbase>enable <tablename>
- This command will start enabling the named table
- Whichever table is disabled, to retrieve back to its previous state we use this command
- If a table is disabled in the first instance and not deleted or dropped, and if we want to re-use the disabled table then we have to enable it by using this command.
- Here in the above screenshot we are enabling the table "education."
- show_filters
Syntax:hbase>show_filters
This command displays all the filters present in HBase like ColumnPrefix Filter, TimestampsFilter, PageFilter, FamilyFilter, etc.
- drop
Syntax:hbase>drop <table name>
We have to observe below points for drop command
- To delete the table present in HBase, first we have to disable it
- To drop the table present in HBase, first we have to disable it
- So either table to drop or delete first the table should be disable using disable command
- Here in above screenshot we are dropping table "education."
- Before execution of this command, it is necessary that you disable table "education."
- drop_all
Syntax:Hbase>drop_all<"regex">
- This command will drop all the tables matching the given regex
- Tables have to disable first before executing this command using disable_all
- Tables with regex matching expressions are going to drop from HBase
- is_enabled
Syntax:hbase>is_enabled 'education'
This command will verify whether the named table is enabled or not. Usually, there is a little confusion between "enable" and "is_enabled" command action, which we clear here
- Suppose a table is disabled, to use that table we have to enable it by using enable command
- is_enabled command will check either the table is enabled or not
- alter
Syntax:- hbase> alter <tablename>, NAME=><column familyname>, VERSIONS=>5
This command alters the column family schema. To understand what exactly it does, we have explained it here with an example.
Examples:
In these examples, we are going to perform alter command operations on tables and on its columns. We will perform operations like
- Altering single, multiple column family names
- Deleting column family names from table
- Several other operations using scope attributes with table
- To change or add the 'guru99_1' column family in table 'education' from current value to keep a maximum of 5 cell VERSIONS,
- "education" is table name created with column name "guru99" previously
- Here with the help of an alter command we are trying to change the column family schema to guru99_1 from guru99
hbase> alter 'education', NAME=>'guru99_1', VERSIONS=>5
- You can also operate the alter command on several column families as well. For example, we will define two new column to our existing table "education".
hbase> alter 'edu', 'guru99_1', {NAME => 'guru99_2', IN_MEMORY => true}, {NAME => 'guru99_3', VERSIONS => 5}
- We can change more than one column schemas at a time using this command
- guru99_2 and guru99_3 as shown in above screenshot are the two new column names that we have defined for the table education
- We can see the way of using this command in the previous screen shot
- In this step, we will see how to delete column family from the table. To delete the 'f1' column family in table 'education'.
Use one ofthese commands below,
hbase> alter 'education', NAME => 'f1', METHOD => 'delete'
hbase> alter 'education', 'delete' =>' guru99_1'
- In this command, we are trying to delete the column space name guru99_1 that we previously created in the first step
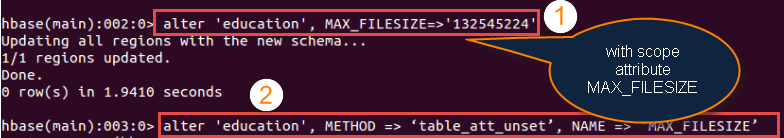
- As shown in the below screen shots, it shows two steps – how to change table scope attribute and how to remove the table scope attribute.
Syntax: hbase(main):002:0> alter <'tablename'>, MAX_FILESIZE=>'132545224'
Step 1) You can change table-scope attributes like MAX_FILESIZE, READONLY, MEMSTORE_FLUSHSIZE, DEFERRED_LOG_FLUSH, etc. These can be put at the end;for example, to change the max size of a region to 128MB or any other memory value we use this command.
Usage:
- We can use MAX_FILESIZE with the table as scope attribute as above
- The number represent in MAX_FILESIZE is in term of memory in bytes
NOTE: MAX_FILESIZE Attribute Table scope will be determined by some attributes present in the HBase. MAX_FILESIZE also come under table scope attributes.
Step 2) You can also remove a table-scope attribute using table_att_unset method. If you see the command
Syntax: hbase(main):003:0> alter 'education', METHOD => 'table_att_unset', NAME => 'MAX_FILESIZE'
- The above screen shot shows altered table name with scope attributes
- Method table_att_unset is used to unset attributes present in the table
- The second instance we are unsetting attribute MAX_FILESIZE
- After execution of the command, it will simply unset MAX_FILESIZE attribute from"education" table.
Data manipulation commands
These commands will work on the table related to data manipulations such as putting data into a table, retrieving data from a table and deleting schema, etc.
The commands come under these are
- Count
- Put
- Get
- Delete
- Delete all
- Truncate
- Scan
Let look into these commands usage with an example.
Example:
- hbase> count 'guru99', CACHE=>1000
This example count fetches 1000 rows at a time from "Guru99" table.
We can make cache to some lower value if the table consists of more rows.
But by default it will fetch one row at a time.
- hbase>count 'guru99', INTERVAL => 100000
hbase> count 'guru99', INTERVAL =>10, CACHE=> 1000
If suppose if the table "Guru99" having some table reference like say g.
We can run the count command on table reference also like below
- hbase>g.count INTERVAL=>100000
hbase>g.count INTERVAL=>10, CACHE=>1000
- Put
Syntax: hbase> put <'tablename'>,<'rowname'>,<'columnvalue'>,<'value'>
This command is used for following things
- It will put a cell 'value' at defined or specified table or row or column.
- It will optionally coordinate time stamp.
Example:
- Here we are placing values into table "guru99" under row r1 and column c1
hbase> put 'guru99', 'r1', 'c1', 'value', 10
- We have placed three values, 10,15 and 30 in table "guru99" as shown in screenshot below
-
Suppose if the table "Guru99" having some table reference like say g. We can also run the command on table reference also like hbase>g.put 'guru99', 'r1', 'c1', 'value', 10
-
The output will be as shown in the above screen shot after placing values into "guru99".
To check whether the input value is correctly inserted into the table, we use "scan" command. In the below screen shot, we can see the values are inserted correctly
Code Snippet: For Practice
create 'guru99', {NAME=>'Edu', VERSIONS=>213423443}
put 'guru99', 'r1', 'Edu:c1', 'value', 10
put 'guru99', 'r1', 'Edu:c1', 'value', 15
put 'guru99', 'r1', 'Edu:c1', 'value', 30
From the code snippet, we are doing these things
- Here we are creating a table named 'guru99' with the column name as "Edu."
- By using "put" command, we are placing values into row name r1 in column "Edu" into table "guru99."
- Get
Syntax: hbase> get <'tablename'>, <'rowname'>, {< Additional parameters>}
Here <Additional Parameters> include TIMERANGE, TIMESTAMP, VERSIONS and FILTERS.
By using this command, you will get a row or cell contents present in the table. In addition to that you can also add additional parameters to it like TIMESTAMP, TIMERANGE,VERSIONS, FILTERS, etc. to get a particular row or cell content.
Examples:-
For table "guru99"row 1 values in the time range ts1 and ts2 will be displayed using this command
- Delete
Syntax: hbase> delete <'tablename'>,<'row name'>,<'column name'>
- This command will delete cell value at defined table of row or column.
- Delete must and should match the deleted cells coordinates exactly.
- When scanning, delete cell suppresses older versions of values.
Example:
- hbase(main):)020:0> delete 'guru99', 'r1', 'c1''.
- The above execution will delete row r1 from column family c1 in table "guru99."
- Suppose if the table "guru99" having some table reference like say g.
- We can run the command on table reference also like hbase> g.delete 'guru99', 'r1', 'c1'".
- deleteall
Syntax: hbase>deleteall <'tablename'>, <'rowname'>
- This Command will delete all cells in a given row.
- We can define optionally column names and time stamp to the syntax.
Example:-
hbase>deleteall 'guru99', 'r1', 'c1'
hbase>deleteall 'guru99', 'r1', 'c1',
This will delete all the rows and columns present in the table. Optionally we can mention column names in that.
- Truncate
Syntax: hbase> truncate <tablename>
After truncate of an hbase table, the schema will present but not the records. This command performs 3 functions; those are listed below
- Disables table if it already presents
- Drops table if it already presents
- Recreates the mentioned table
- Scan
Syntax: hbase>scan <'tablename'>, {Optional parameters}
This command scans entire table and displays the table contents.
- We can pass several optional specifications to this scan command to get more information about the tables present in the system.
- Scanner specifications may include one or more of the following attributes.
- These are TIMERANGE, FILTER, TIMESTAMP, LIMIT, MAXLENGTH, COLUMNS, CACHE, STARTROW and STOPROW.
Examples:-
The different usages of scan command
|
Command
|
Usage
|
|
hbase> scan '.META.', {COLUMNS => 'info:regioninfo'}
|
It display all the meta data information related to columns that are present in the tables in HBase
|
|
hbase> scan 'guru99', {COLUMNS => ['c1', 'c2'], LIMIT => 10, STARTROW => 'xyz'}
|
It display contents of table guru99 with their column families c1 and c2 limiting the values to 10
|
|
hbase> scan 'guru99', {COLUMNS => 'c1', TIMERANGE => [1303668804, 1303668904]}
|
It display contents of guru99 with its column name c1 with the values present in between the mentioned time range attribute value
|
|
hbase> scan 'guru99', {RAW => true, VERSIONS =>10}
|
In this command RAW=> true provides advanced feature like to display all the cell values present in the table guru99
|
hbase(main):016:0> scan 'guru99'
The output as below shown in screen shot
In the above screen shot
- It shows "guru99" table with column name and values
- It consists of three row values r1, r2, r3 for single column value c1
- It displays the values associated with rows
Code Snippet:-
First create table and place values into table
create 'guru99', {NAME=>'e', VERSIONS=>2147483647}
put 'guru99', 'r1', 'e:c1', 'value', 10
put 'guru99', 'r1', 'e:c1', 'value', 12
put 'guru99', 'r1', 'e:c1', 'value', 14
delete 'guru99', 'r1', 'e:c1', 11
Input Screenshot:
If we run scan command Query:hbase(main):017:0> scan 'guru99', {RAW=>true, VERSIONS=>1000}
It will display output shown in below.
Output screen shot:
The output shown in above screen shot gives the following information
- Scanning guru99 table with attributes RAW=>true, VERSIONS=>1000
- Displaying rows with column families and values
- In the third row, the values displayed shows deleted value present in the column
- The output displayed by it is random; it cannot be same order as the values that we inserted in the table
Cluster Replication Commands
- These commands work on cluster set up mode of HBase.
- For adding and removing peers to cluster and to start and stop replication these commands are used in general.
|
Command
|
Functionality
|
|
add_peer
|
Add peers to cluster to replicate
hbase> add_peer '3', zk1,zk2,zk3:2182:/hbase-prod
|
|
remove_peer
|
Stops the defined replication stream.
Deletes all the metadata information about the peer
hbase> remove_peer '1'
|
|
start_replication
|
Restarts all the replication features
hbase> start_replication
|
|
stop_replication
|
Stops all the replication features
hbase>stop_replication
|
Summary:
HBase shell and general commands give complete information about different type of data manipulation, table management, and cluster replication commands. We can perform various functions using these commands on tables present in HBase.
Hbase is a column oriented NoSql database for storing a large amount of data on top of Hadoop eco system. Handling tables in Hbase is a very crucial thing because all important functionalities such as Data operations, Data enhancements and Data modeling we can perform it through tables only in HBase.
Handling tables performs the following functions
- Creation of tables with column names and rows
- Inserting values into tables
- Retrieving values from tables
In HBase, we can perform table operations in two ways
We already have seen how we can perform shell commands and operations in HBase. In this tutorial, we are going to perform some of the operations using Java coding through Java API.
Through Java API, we can create tables in HBase and also load data into tables using Java coding.
In this tutorial - we will learn,
HBase create table with Rows and Column names
In this section, we are going to create tables with column families and rows by
- Establishing connection with HBase through Java API
- Using eclipse for Java coding, debugging and testing
Establishing connection through Java API:
The Following steps guide us to develop Java code to connect HBase through Java API.
Step 1) In this step, we are going to create Java project in eclipse for HBase connection.
Creation of new project name "HbaseConnection" in eclipse.
For Java related project set up or creation of program: Refer /java-tutorial.html
If we observe the screen shot above.
- Give project name in this box. In our case, we have project name "HbaseConnection"
- Check this box for default location to be saved. In this /home/hduser/work/HbaseConnection is the path
- Check the box for Java environment here. In this JavaSE-1.7 is the Java edition
- Choose your option where you want to save file. In our case, we have selected option second "Create separate folder for sources and class files"
- Click on finish button.
- When you click on Finish button, it's going to create "HbaseConnection" project in eclipse
- It will directly come to eclipse home page after clicking finish button.
Step 2) On eclipse home page follow the following steps
Right click on project -> Select Build Path -> Configure build path
From above screenshot
- Right click on project
- Select build path
- Select configure build path
After clicking Configure Build path, it will open another window as shown in below screen shot
In this step, we will add relevant HBase jars into java project as shown in the screenshot.
- Important jars to be added hbase-0.94.8.jar, hadoop-core-1.1.2.jar
- Click on finish button
- Come to libraries
- Press option - Add External Jars
- Select required important jars
- Press finish button to add these files to 'src' of java project under libraries
After adding these jars, it will show under project "src" location. All the Jar files that fall under the project are now ready for usage with Hadoop ecosystem.
Step 3) In this step by using HBaseConnection.java, the HBase Connection would be established through Java Coding
- Select Run
- Select Run as Java Application
- This code will establish connection with HBase through Java API
- After Running this code 'guru99' table will be created in HBase with two column families named "education" and "projects". At present, the empty schema is only created in HBase.
From screen shot above we are performing following functions.
- Using HTableDescriptor we can able to create "guru99" table in HBase
- Using addFamily method, we are going to add "education" and "projects" as column names to "guru99" table.
The below coding is going to
- Establish connection with HBase and
- Create "guru99" table with two columns
Code Placed under HBaseConnection_Java document
// Place this code inside Hbase connection
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HColumnDescriptor;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HTableDescriptor;
Import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HBaseAdmin;
public class HBaseConnection
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
HBaseConfigurationhc = new HBaseConfiguration(new Configuration());
HTableDescriptorht = new HTableDescriptor("guru99");
ht.addFamily( new HColumnDescriptor("education"));
ht.addFamily( new HColumnDescriptor("projects"));
System.out.println( "connecting" );
HBaseAdminhba = new HBaseAdmin( hc );
System.out.println( "Creating Table" );
hba.createTable( ht );
System.out.println("Done......");
}
}
This is required code you have to place in HBaseConnection.java and have to run java program
After running this program, it is going to establish a connection with HBase and in turn it will create a table with column names.
- Table name is "guru99"
- Column names are "education" and "projects"
Step 4) We can check whether "guru99" table is created with two columns in HBase or not by using HBase shell mode with "list" command.
The "list" command gives information about all the tables that is created in HBase.
Refer "HBase Shell and General Commands" article for more information on "list" command.
In this screen, we going to do
- Code checking in HBase shell by executing "list" command.
- If we run "list" command, it will display the table created in HBase as below. In our case, we can see table "guru99" is created
Placing values into tables and retrieving values from table:
In this section, we are going to
- Write data to HBase table and
- Read Data from HBase table
For example, we will
- Insert values into table "guru99" that previously created in the Step (3) of Creation of Table with Rows and Column names
- And then retrieve this value from table "guru99"
Here is the Java Code to be placed under HBaseLoading.java as shown below for both writing and retrieving data.
Code Placed under HBaseLoading_Java document
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Get;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HTable;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Result;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.ResultScanner;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Scan;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;
public class HBaseLoading
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
// When you create a HBaseConfiguration, it reads in whatever you've set into your hbase-site.xml and in hbase-default.xml, as long as these can be found on the CLASSPATH
org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configurationconfig = HBaseConfiguration.create();
//This instantiates an HTable object that connects you to the "test" table
HTable table = newHTable(config, "guru99");
// To add to a row, use Put. A Put constructor takes the name of the row you want to insert into as a byte array.
Put p = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("row1"));
//To set the value you'd like to update in the row 'row1', specify the column family, column qualifier, and value of the table cell you'd like to update. The column family must already exist in your table schema. The qualifier can be anything.
p.add(Bytes.toBytes("education"),
Bytes.toBytes("col1"),Bytes.toBytes("BigData"));
p.add(Bytes.toBytes("projects"),Bytes.toBytes("col2"),Bytes.toBytes("HBaseTutorials"));
// Once you've adorned your Put instance with all the updates you want to make, to commit it do the following
table.put(p);
// Now, to retrieve the data we just wrote.
Get g = new Get(Bytes.toBytes("row1"));
Result r = table.get(g);
byte [] value = r.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("education"),Bytes.toBytes("col1"));
byte [] value1 = r.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("projects"),Bytes.toBytes("col2"));
String valueStr = Bytes.toString(value);
String valueStr1 = Bytes.toString(value1);
System.out.println("GET: " +"education: "+ valueStr+"projects: "+valueStr1);
Scan s = new Scan();
s.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("education"), Bytes.toBytes("col1"));
s.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("projects"), Bytes.toBytes("col2"));
ResultScanner scanner = table.getScanner(s);
try
{
for (Result rr = scanner.next(); rr != null; rr = scanner.next())
{
System.out.println("Found row : " + rr);
}
} finally
{
// Make sure you close your scanners when you are done!
scanner.close();
}
}
}
First of all, we are going to see how to write data, and then we will see how to read data from an hbase table.
Write Data to HBase Table:
Step 1) In this step, we are going to write data into HBase table "guru99"
First we have to write code for insert and retrieve values from HBase by using-HBaseLoading.java program.
For creating and inserting values into a table at the column level, you have to code like below.
From the screen shot above
- When we create HBase configuration, it will point to whatever the configurations we set in hbase-site.xml and hbase-default.xml files during HBase installations
- Creation of table "guru99" using HTable method
- Adding row1 to table "guru99"
- Specifying column names "education" and "projects" and inserting values into column names in the respective row1. The values inserted here are "BigData" and "HBaseTutorials".
Read Data from Hbase Table:
Step 2) Whatever the values that we placed in HBase tables in Step (1) , here we are going to fetch and display those values.
For retrieving results stored in "guru99"
The above screen shot shows the data is being read from HBase table 'guru99'
- In this, we are going to fetch the values that are stored in column families i.e "education" and "projects"
- Using "get" command we are going to fetch stored values in HBase table
- Scanning results using "scan" command. The values that are stored in row1 it will display on the console.
Once writing code is done, you have to run java application like this
- Right click on HBaseLoading.java -> Run As -> Java Application
- After running "HBaseLoading .java" the values going to insert into "guru99" in each column in HBase and in the same program it can retrieve values also.
Retrieving Inserted Values in HBase shell mode
In this section, we will check the following
- Values that are inserted into HBase table "guru99"
- Column names with values present in HBase Table guru99
From the above screen shot, we will get these points
- If we run "scan" command in HBase shell it will display the inserted values in "guru99" as follow
- In HBase shell, it will display values inserted by our code with column and row names
- Here we can see the column name inserted are "education" and "projects"
- The values inserted are "BigData" and "HBase Tutorials" into mentioned columns
Summary:
As we discussed in this article now, we are familiar with how to create tables, loading data into tables and retrieving data from table using Java API through Java coding. We can able to perform all type of shell command functionalities through this Java API. It will establish good client communication with HBase environment.
In our next article, we will see trouble-shooting for the HBase problems.
HBase: Limitations, Advantage & Problems
HBase architecture always has "Single Point Of Failure" feature, and there is no exception handling mechanism associated with it.
Problems with HBase
- In any production environment, HBase is running with a cluster of more than 5000 nodes, only Hmaster acts as the master to all the slaves Region servers. If Hmaster goes down, it can be only be recovered after a long time. Even though the client is able to connect region server. Having another master is possible but only one will be active. It will take a long time to activate the second Hmaster if the main Hmaster goes down. So, Hmaster is a performance bottleneck.
- In HBase, we cannot implement any cross data operations and joining operations, of course, we can implement the joining operations using MapReduce, which would take a lot of time to designing and development. Tables join operations are difficult to perform in HBase. In some use case, its impossible to create join operations that related to tables that are present in HBase
- HBase would require new design when we want to migrate data from RDBMS external sources to HBase servers. However, this process takes a lot of time.
- HBase is really tough for querying. We may have to integrate HBase with some SQL layers like Apache phoenix where we can write queries to trigger the data in the HBase. It's really good to have Apache Phoenix on top of HBase.
- Another drawback with HBase is that, we cannot have more than one indexing in the table, only row key column acts as a primary key. So, the performance would be slow when we wanted to search on more than one field or other than Row key. This problem we can overcome by writing MapReduce code, integrating with Apache SOLR and with Apache Phoenix.
- Slow improvements in the security for the different users to access the data from HBase.
- HBase doesn't support partial keys completely
- HBase allows only one default sort per table
- It's very difficult to store large size of binary files in HBase
- The storage of HBase will limit real-time queries and sorting
- Key lookup and Range lookup in terms of searching table contents using key values, it will limit queries that perform on real time
- Default indexing is not present in HBase. Programmers have to define several lines of code or script to perform indexing functionality in HBase
- Expensive in terms of Hardware requirements and memory blocks allocations.
- More servers should be installed for distributed cluster environments (like each server for NameNode, DataNodes, ZooKeeper, and Region Servers)
- Performance wise it require high memory machines
- Costing and maintenance wise it is also higher
Advantage of HBase:
- Can store large data sets on top of HDFS file storage and will aggregate and analyze billions of rows present in the HBase tables
- In HBase, the database can be shared
- Operations such as data reading and processing will take small amount of time as compared to traditional relational models
- Random read and write operations
- For online analytical operations, HBase is used extensively.
- For example: In banking applications such as real-time data updates in ATM machines, HBase can be used.
Limitations with HBase:
- We cannot expect completely to use HBase as a replacement for traditional models. Some of the traditional models features cannot support by HBase
- HBase cannot perform functions like SQL. It doesn't support SQL structure, so it does not contain any query optimizer
- HBase is CPU and Memory intensive with large sequential input or output access while as Map Reduce jobs are primarily input or output bound with fixed memory. HBase integrated with Map-reduce jobs will result in unpredictable latencies
- HBase integrated with pig and Hive jobs results in some time memory issues on cluster
- In a shared cluster environment, the set up requires fewer task slots per node to allocate for HBase CPU requirements
- Problem Statement: Master server initializes but region servers not initializes
- The Communication between Master and region servers through their IP addresses. Like the way Master is going to listen that region servers are running or having the IP address of 127.0.0.1. The IP address 127.0.0.1 which is the local host and resolves to the master server own local host.
Cause:
- In dual communication between region servers and master, region server continuously informs Master server about their IP addresses are 127.0.0.1.
Solution:
- Have to remove master server name node from local host that is present in hosts file
- Host file location /etc/hosts
What to change:
Open /etc./hosts and go to this location
|
127.0.0.1 fully.qualified.regionservernameregionservernamelocalhost.localdomain localhost
: : 1 localhost3.localdomain3 localdomain3
|
Modify the above configuration like below (remove region server name as highlighted above)
|
127.0.0.1 localhost.localdomainlocalhost
: : 1 localhost3.localdomain3 localdomain3
|
- Problem Statement: Couldn't find my address: XYZ in list of Zookeeper quorum servers
Cause:
- ZooKeeper server was not able to start, and it will throw an error like .xyz in the name of the server.
- HBase attempts to start a ZooKeeper server on some machine but at the same time machine is not able to find itself the quorum configuration i.e. present in HBase.zookeeper.quorum configuration file.
Solution:-
- Have to replace the host name with a hostname that is presented in the error message
- Suppose we are having DNS server then we can set the below configurations in HBase-site.xml.
- HBase.zookeeper.dns.interface
- HBase.zookeeper.dns.nameserver
- Problem Statement: Created Root Directory for HBase through Hadoop DFS
- Master says that you need to run the HBase migrations script.
- Upon running that, the HBase migrations script respond like no files in root directory.
Cause:
Solution:
- Problem statement: Zookeeper session expired events
Cause:
- HMaster or HRegion servers shutting down by throwing Exceptions
- If we observe logs, we can find out the actual exceptions that thrown
The following shows the exception thrown because of Zookeeper expired event
The highlighted events are some of the exceptions occurred in log file
Log files code as display below:
|
WARN org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn: Exception
closing session 0x278bd16a96000f to sun.nio.ch.SelectionKeyImpl@355811ec
java.io.IOException: TIMED OUT
at org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn$SendThread.run(ClientCnxn.java:906)
WARN org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Sleeper: We slept 79410ms, ten times longer than scheduled: 5000
INFO org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn: Attempting connection to server hostname/IP:PORT
INFO org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn: Priming connection to java.nio.channels.SocketChannel[connected local=/IP:PORT remote=hostname/IP:PORT]
INFO org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn: Server connection successful
WARN org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn: Exception closing session 0x278bd16a96000d to sun.nio.ch.SelectionKeyImpl@3544d65e
java.io.IOException: Session Expired
at org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn$SendThread.readConnectResult(ClientCnxn.java:589)
at org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn$SendThread.doIO(ClientCnxn.java:709)
at org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxn$SendThread.run(ClientCnxn.java:945)
ERROR org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegionServer: ZooKeeper session expired
|
Solution:
- The default RAM size is 1 GB. For doing long running imports, we have maintained RAM capacity more than 1 GB.
- Have to increase the session timeout for Zookeeper.
- For increasing session time out of Zookeeper, we have to modify the following property in "hbase-site.xml" that present in hbase /conf folder path.
- The default session timeout is 60 seconds. We can change it to 120 seconds as mentioned below
<property>
<name> zookeeper.session.timeout </name>
<value>1200000</value>
</property>
<property>
<name> hbase.zookeeper.property.tickTime </name>
<value>6000</value>
</property>
Hive is an open source data warehouse which is initially developed by Facebook for analysis and querying datasets but is now under Apache software foundation.
Hive is developed on top of Hadoop as its data warehouse framework for querying and analysis of data is stored in HDFS.
Hive is useful for performing operations like data encapsulation, ad-hoc queries, & analysis of huge datasets. Hive's design reflects its targeted use as a system for managing and querying structured data.
HBase Vs Hive
| Features |
HBase |
Hive |
| Data base model |
Wide Column store |
Relational DBMS |
| Data Schema |
Schema- free |
With Schema |
| SQL Support |
No |
Yes it uses HQL(Hive query language) |
| Partition methods |
Sharding |
Sharding |
| Consistency Level |
Immediate Consistency |
Eventual Consistency |
| Secondary indexes |
No |
Yes |
| Replication Methods |
Selectable replication factor |
Selectable replication factor |
HBase VS RDBMS
While comparing HBase with Traditional Relational databases, we have to take three key areas into consideration. Those are data model, data storage, and data diversity.
| HBASE |
RDBMS |
|
|
|
- Column-oriented databases
|
|
- Designed to store De-normalized data
|
|
- Wide and sparsely populated tables present in HBase
|
|
- Supports automatic partitioning
|
|
- Well suited for OLAP systems
|
|
- Read only relevant data from database
|
- Retrieve one row at a time and hence could read unnecessary data if only some of the data in a row is required
|
- Structured and semi-structure data can be stored and processed using HBase
|
|
- Enables aggregation over many rows and columns
|
|
1) Explain what is Hbase?
Hbase is a column-oriented database management system which runs on top of HDFS (Hadoop Distribute File System). Hbase is not a relational data store, and it does not support structured query language like SQL.
In Hbase, a master node regulates the cluster and region servers to store portions of the tables and operates the work on the data.
2) Explain why to use Hbase?
- High capacity storage system
- Distributed design to cater large tables
- Column-Oriented Stores
- Horizontally Scalable
- High performance & Availability
- Base goal of Hbase is millions of columns, thousands of versions and billions of rows
- Unlike HDFS (Hadoop Distribute File System), it supports random real time CRUD operations
3) Mention what are the key components of Hbase?
- Zookeeper: It does the co-ordination work between client and Hbase Maser
- Hbase Master: Hbase Master monitors the Region Server
- RegionServer: RegionServer monitors the Region
- Region: It contains in memory data store(MemStore) and Hfile.
- Catalog Tables: Catalog tables consist of ROOT and META
4) Explain what does Hbase consists of?
- Hbase consists of a set of tables
- And each table contains rows and columns like traditional database
- Each table must contain an element defined as a Primary Key
- Hbase column denotes an attribute of an object
5) Mention how many operational commands in Hbase?
Operational command in Hbases is about five types
- Get
- Put
- Delete
- Scan
- Increment
6) Explain what is WAL and Hlog in Hbase?
WAL (Write Ahead Log) is similar to MySQL BIN log; it records all the changes occur in data. It is a standard sequence file by Hadoop and it stores HLogkey’s. These keys consist of a sequential number as well as actual data and are used to replay not yet persisted data after a server crash. So, in cash of server failure WAL work as a life-line and retrieves the lost data’s.
7) When you should use Hbase?
- Data size is huge: When you have tons and millions of records to operate
- Complete Redesign: When you are moving RDBMS to Hbase, you consider it as a complete re-design then mere just changing the ports
- SQL-Less commands: You have several features like transactions; inner joins, typed columns, etc.
- Infrastructure Investment: You need to have enough cluster for Hbase to be really useful
8) In Hbase what is column families?
Column families comprise the basic unit of physical storage in Hbase to which features like compressions are applied.
9) Explain what is the row key?
Row key is defined by the application. As the combined key is pre-fixed by the rowkey, it enables the application to define the desired sort order. It also allows logical grouping of cells and make sure that all cells with the same rowkey are co-located on the same server.
10) Explain deletion in Hbase? Mention what are the three types of tombstone markers in Hbase?
When you delete the cell in Hbase, the data is not actually deleted but a tombstone marker is set, making the deleted cells invisible. Hbase deleted are actually removed during compactions.
Three types of tombstone markers are there:
- Version delete marker: For deletion, it marks a single version of a column
- Column delete marker: For deletion, it marks all the versions of a column
- Family delete marker: For deletion, it marks of all column for a column family
11) Explain how does Hbase actually delete a row?
In Hbase, whatever you write will be stored from RAM to disk, these disk writes are immutable barring compaction. During deletion process in Hbase, major compaction process delete marker while minor compactions don’t. In normal deletes, it results in a delete tombstone marker- these delete data they represent are removed during compaction.
Also, if you delete data and add more data, but with an earlier timestamp than the tombstone timestamp, further Gets may be masked by the delete/tombstone marker and hence you will not receive the inserted value until after the major compaction.
12) Explain what happens if you alter the block size of a column family on an already occupied database?
When you alter the block size of the column family, the new data occupies the new block size while the old data remains within the old block size. During data compaction, old data will take the new block size. New files as they are flushed, have a new block size whereas existing data will continue to be read correctly. All data should be transformed to the new block size, after the next major compaction.
13) Mention the difference between Hbase and Relational Database?
| Hbase |
Relational Database |
- It is schema-less
- It is a column-oriented data store
- It is used to store de-normalized data
- It contains sparsely populated tables
- Automated partitioning is done in Hbase
|
- It is a schema based database
- It is a row-oriented data store
- It is used to store normalized data
- It contains thin tables
- There is no such provision or built-in support for partitioning
|