Introduction of Django Filter Queryset
When the database connectivity is been established in Django, there is always a need of extracting the needed columns alone from the database and their corresponding rows, basically, the filter query set in django model filters is used for achieving this. When a value is expected to be retrieved from the database then the filter queryset section of the queryset oriented extraction comes into play. Mentioning a filter of a specific column will help us to filter and pull those corresponding values alone from the queryset retrieved. This option in django helps us to achieve abstract level filtering of needed values.
Syntax:
The syntax of filter queryset is as like below,
model.objects.filter(condition)
Creating a Queryset
Lest discuss how to create a queryset.
1. Create a models.py file in the application: The schematic structure of an database needs to be mentioned here in the moedels.py file.
Examples: (models.py)
from django.db import models
# Create your models here.
class sample(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=20,unique=True)
card_no = models.IntegerField()
def _str_(Self):
return self.name, self.id
We can notice the schematic structure is created as an class referring to the models import. All the expected fields of the model need to be declared in this class. also ensure the database configurations are in place so that no issues are generated while reaching the database,
Example: (SETTINGS.py)
TEMPLATES = [
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [Template_DIR,],
'APP_DIRS': True,
'OPTIONS': {
'context_processors': [
'django.template.context_processors.debug',
'django.template.context_processors.request',
'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth',
'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',
],
},
},
] WSGI_APPLICATION = 'educba.wsgi.application'
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.postgresql',
'NAME': 'postgres',
'USER': 'postgres',
'PASSWORD' : 'anand',
'HOST': '127.0.0.1',
'PORT': '5432',
}
}
2. Check for Migrations: After the models file is created verify the migrations expected using the make migrations command.
python manage.py makemigrations
3. Apply the Migrations: Next, apply all the needed migrations using the migrate command.
python manage.py migrate
4. Create the needed views in the views.py file: All needed views have to be generated.
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.http import HttpResponse
from Django_app1.forms import Valueform,fileform,emailform,requestcheckform
from django.core.exceptions import ViewDoesNotExist
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
from django.core.files.storage import FileSystemStorage
from django.contrib import messages
from django.core.mail import send_mail,EmailMessage
from Django_app1.models import sample
import requests
def requestmethods(request):
form = requestcheckform()
if request.method == 'POST':
# REQUEST OBJECT ATTRIBUTES
if request.POST['request_attribute'] == 'Request Header':
data_content = "data content of request method : " + str(request.headers)
messages.success(request,data_content)
elif request.POST['request_attribute'] == 'Request POST':
post_content = "post content of request method : " + str(request.POST)
messages.success(request,post_content)
elif request.POST['request_attribute'] == 'Request Files':
FILES_content = "FILES in request method : " + str(request.FILES)
messages.success(request,FILES_content)
elif request.POST['request_attribute'] == 'Request GET':
GET_content = "GET Content in request method : " + str(request.GET)
messages.success(request,GET_content)
elif request.POST['request_attribute'] == 'Request User':
Request_User = "User Details : " + str(request.user)
messages.success(request,Request_User)
elif request.POST['request_attribute'] == 'Request Body':
Request_body = "Request Body : " + str(request.body)
messages.success(request,Request_body)
elif request.POST['request_attribute'] == 'Request Content Type':
Request_Content_Type = "Request Content type : " + str(request.content_type)
messages.success(request,Request_Content_Type)
elif request.POST['request_attribute'] == 'Request Encoding':
Request_Encoding = "Request Encoding Used : " + str(request.encoding)
messages.success(request,Request_Encoding )
elif request.POST['request_attribute'] == 'Request Method':
Request_method = "Request Method posted : " + str(request.method)
messages.success(request,Request_method )
elif request.POST['request_attribute'] == 'Request Path':
Request_path = "Path of the request : " + str(request.path)
messages.success(request,Request_path )
elif request.POST['request_attribute'] == 'Request Cookies':
Request_Cookies = "Cookies associated to the Request : " + str(request.COOKIES)
messages.success(request,Request_Cookies )
elif request.POST['request_attribute'] == 'Request META':
Request_META = "HTTP headers info : " + str(request.META)
messages.success(request,Request_META )
# REQUEST METHODS
elif request.POST['request_attribute'] == 'Request port':
Request_port = "Request port number: " + str(request.get_port())
messages.success(request,Request_port )
elif request.POST['request_attribute'] == 'Request host':
Request_host = "Requested Host: " + str(request.get_host())
messages.success(request,Request_host)
elif request.POST['request_attribute'] == 'Request is_secure':
Request_secure = "Security level of the request: " + str(request.is_secure())
messages.success(request,Request_secure)
return render(request,'Request_methods_check.html',{"form":form})
def file_upload(request):
file = fileform()
print(" File Values in File Dictionary :", request.FILES)
if request.method == 'POST' and request.FILES['Uploaded_File']:
uploaded_file = request.FILES['Uploaded_File'] fs = FileSystemStorage()
filename = fs.save(uploaded_file.name, uploaded_file)
uploaded_File_Size = 'Size of Uploaded file : ' + str(uploaded_file.size)
content_type_of_uploaded_file = 'Content type of uploaded file : ' + str(uploaded_file.content_type)
uploaded_file_name = 'Name of Uploaded file : ' + str(uploaded_file.name)
uploaded_file_url = fs.url(filename)
print("uploaded file url",uploaded_file_url)
messages.success(request, '!!! File upload successful !!!')
messages.success(request,uploaded_File_Size)
messages.success(request,uploaded_file_name)
messages.success(request,content_type_of_uploaded_file)
return render(request, 'filehandeling.html', {"file":file})
return render(request, 'filehandeling.html',{"file":file})
def email_sending(request):
email = emailform()
if request.method == 'POST':
email_id = request.POST['email'] email_subject = request.POST['email_subject'] email_message = request.POST['email_message'] mail = send_mail(email_subject,email_message,'testmysmtpconnection@gmail.com',[email_id],fail_silently = False)
response = HttpResponse(mail)
print("Content of the resposne: ",response.content)
print("Charecterset of the response: ",response.charset)
print("Status code of the response: ",response.status_code)
print("Reason phrase of the response: ",response.reason_phrase)
print("Reason close status: ",response.closed)
return response
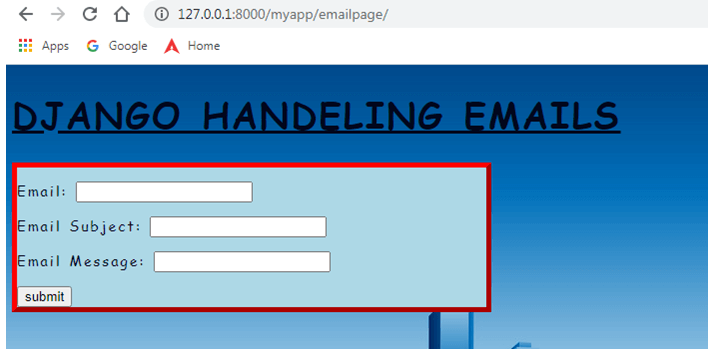
return render(request, 'emailpage.html',{"email":email})
def db_hit(request):
all_objects = sample.objects.all()
for i in all_objects:
print(i.card_no)
print(sample.objects.filter(card_no = 102))
return render(request, 'model.html')
6. Generate the needed Templates: The templates mentioning the webpage has to be created.
model.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" dir="ltr">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Django App1</title>
{% load static %}
<link href="{% static 'admin/css/font.css' %}" rel="stylesheet">
<style>
body {
background-image: url("{% static 'admin/img/background.jpg' %}");
background-color: #acccbb;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> <u> MODEL HANDELING </u> </h1>
</body>
</html>
email_page.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" dir="ltr">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Django App1</title>
{% load static %}
<link href="{% static 'admin/css/font.css' %}" rel="stylesheet">
<style>
body {
background-image: url("{% static 'admin/img/background.jpg' %}");
background-color: #acccbb;
}
.myDiv {
border: 5px outset red;
background-color: lightblue;
text-align: center;
font-family: "Comic Sans MS", cursive, sans-serif;
font-size: 14px;
letter-spacing: 2px;
word-spacing: 1.8px;
text-align: left;
color: #02071C;
font-weight: 200;
text-decoration: none;
font-style: normal;
font-variant: normal;
text-transform: capitalize;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> <u> DJANGO HANDELING EMAILS </u> </h1>
<div class="myDiv" style = "max-width:470px;">
<form method = 'POST' ">
{{ email.as_p }}
{% csrf_token %}
<input type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" value="submit" style="text-align:center">
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
7. Tag the view in urls.py file: This is the process of creating a url for the view.
- Import the library from django.conf.urls import url
- declare a url entry in the urlpatterns list
url(url_path, view_to_be_tagged, name_for_this_view)
urls.py:
from django.contrib import admin
from django.conf.urls import url
from Django_app1 import views
urlpatterns = [
url(r'formpage/',views.formView,name='form'),
url(r'fileupload/',views.file_upload,name='file_upload'),
url(r'emailpage/',views.email_sending,name='email_sending'),
url(r'requests/',views.Httpmethods,name='Request_check'),
url(r'requestmethod/',views.requestmethods,name='request_method'),
url(r'model/',views.db_hit,name='db_hit'),
]
Output: