Users Online
· Members Online: 0
· Total Members: 188
· Newest Member: meenachowdary055
Forum Threads
Latest Articles
Articles Hierarchy
SAP Basis
AP BAPI Tutorial - Step by Step Guide to Create BAPI in ABAP
What is BAPI?
Business Application Programming Interface(BAPI) are standardized programming interfaces (methods) enabling external applications to access business processes and data in the R/3 System.
They provide stable and standardized methods to achieve seamless integration between the R/3 System and external applications, legacy systems and add-ons.
BAPIs are defined in the BOR(Business object repository) as methods of SAP business object types that carry out specific business functions.They are implemented as RFC-enabled function modules and are created in the Function Builder of the ABAP Workbench.
Some BAPIs and methods provide basic functions and can be used for most SAP Business Objects.These are called STANDARDIZED BAPI's.
List of Standardized BAPIs:
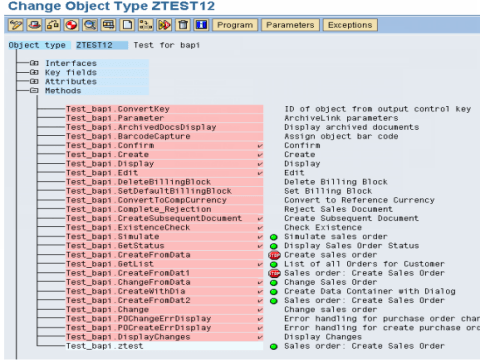
- BAPIs for Reading Data - GetList() , GetDetail() , GetStatus() , ExistenceCheck()
- BAPIs for Creating or Changing Data- Create() ,Change(),Delete() and Undelete() ,
- BAPIs for Mass Processing -ChangeMultiple(), CreateMultiple(), DeleteMultiple().
How to create a BAPI
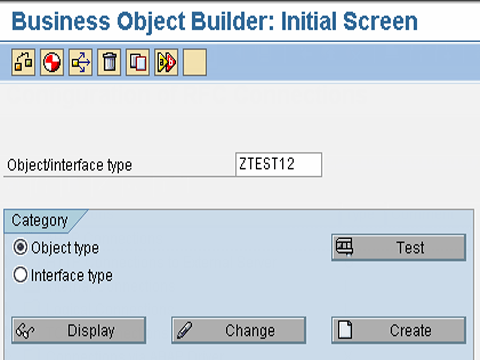
Step 1.Go to transaction swo1 (Tools->Business Framework -> BAPI Development ->Business Object builder ) .Select the business object, according to the functional requirement for which the BAPI is being created.
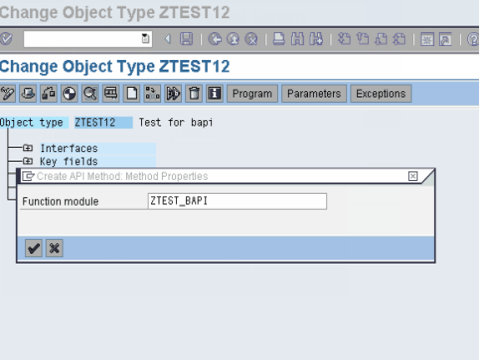
Step2.Open the business object in change mode. Then Select Utilities ->API Methods ->Add method.Then enter the name of the function module and select Continue.
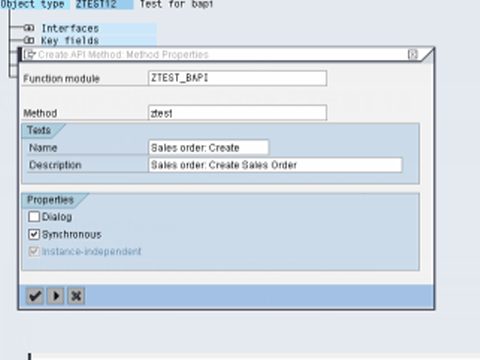
Step 3.In the next dialog box, following information needs to be specified :
- Method : Suggest an appropriate name for the method,
- Texts : Enter description for the BAPI,
- Radio buttons : Dialog, Synchronous, Instance-independent . BAPI 's are usually implemented synchronously.
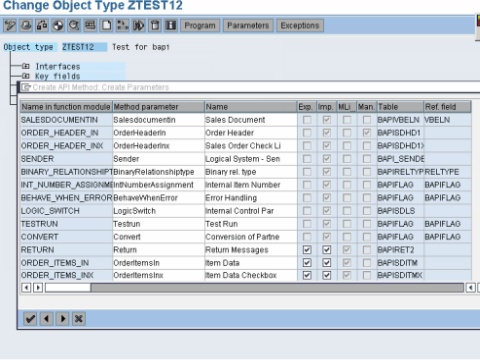
Step4.To create the method select Yes in the next dialog box.
Step5.After the program has been generated and executed, check the program in the method just created.Thus , a BAPI is created.
Testing the BAPI
You can test the BAPI by Testing the individual method of the Business Object in the Business Object Builder. ( or one can use the transaction 'SWUD' to test the method ) .
Releasing and freezing the BAPI
- To release the BAPI , first release the function module ( using transaction se37 ) .
- Set the status of the method to 'released' in the Business Object Builder ( using transaction SWo1 - Edit-> change status-> released. )
You can also use the BAPI Explorer (Transaction code BAPI) for 360' view on BAPI
60 SAP Basis interview questions
1) What is SAP Basis?
SAP basis acts as an operating system or a platform for SAP applications to run. It supports the entire range of SAP applications.
2) What is the difference between Developer Trace, System Log and System Trace?
a) System Trace: When you want to record internal SAP system activities, system trace is used. The trace is useful in diagnosis internal problems within SAP system and the host system.
b) System Log : To know the recent logs for application server and CI, System log is referred.
c) Developer Trace: In the event of problems, developer trace, records the technical information about the error or problem
For problem analysis and system monitoring Developer trace or System log is used.
3) In a situation where My SAP system is down (Users unable to login to SAP system), how to analyze the problem?
a) Check the Database status
b) SAP services
c) SAP management console ( Dispatcher, IGS and Message Server)
d) You need to find out trace root on the basis of point at serial no ( c ).
e) Check network connectivity if everything is ok
4) What is private mode?
In private mode, the heap data is exclusively allocated by the user and is no more shared or available across the system. This occurs when your extended memory is exhausted.
5) What is OSP$ mean?
Two users “OPS$adm” and “OPS$SAP” Service are created in your SAP system and to connect and communicate with database internally this user mechanism is used.
6) What are the different types of RFC and explain what Transactional RFC is?
RFC (Remote Function Call) is a mechanism to communicate and exchanging the information between other SAP systems. There are four types of RFC’s system
a) Synchronous RFC ( S RFC)
b) Asynchronous RFC (A RFC)
c) Transactional RFC ( T RFC)
d) Queued RFC (Q RFC)
Transactional RFC ( T RFC ) : This type of RFC is similar to asynchronous RFC, but by allocating a transaction ID (TID) it makes sure that the request sent multiple times due to an error must process only for once. In T RFC the remote system does not have to be available at the moment unlike asynchronous RFC.
7) What is OCM and how to apply OCM Patches?
OCM stands for online correction system, by using SPAM you can apply OCM Patches.
8) How to perform a SAP-export and import tables in SAP from OS level?
To export or import tables in SAP from OS level you have to follow three steps and by using R3trans utility in SAP
Step 1: Collect all list of tables to be exported
Step 2: Check whether enough disk space is available in the directory where you going to export.
Step 3: Create two control files for R3trans which will be used for import and export.
9) What is the difference between – support package, kernel and SAP note?
SAP Note: An error in a single transaction or program is removed by implementing a SAP note.
Kernel: Kernel contains the executable files (.EXE) like other applications and when a Kernel upgrade is done a new version of the EXE file replaces the older versions.
Support Package: SAP support packages is a bunch of corrections, this can be used by applying transaction SPAM
10) How can you find the list of objects that have been repaired in the system?
The list of objects that have been repaired can be found in the system having ADIRACCESS keys.
11) What is the purpose of table TADIR?
Table TADIR contains object directory entries.
12) Is it possible to install SAP patches when other users are online?
When other users are online we can’t install SAP patches, as support manager will not be able to update and it will terminate it. So it is always feasible to better apply support packs when there is no users login into the system.
13) Mention what is the difference between SDM and JSPM?
JSPM ( Java Support Package Manager) is used to apply support packages on deployed software components. In other words it’s a tool that allows you to install the components and support packages.
SDM ( Software Delivery Manager) is used for importing Java Support Packages. To deploy and manage software packages received from SAP, SDM tool is used.
JSPM uses SDM for the deployment purpose
14) What is the procedure to disable import all option from STMS in SAP?
To disable import all option from STMS in SAP, steps are:
a) Go to STMS T-code
b) Go to menu option overview
c) Select System
d) Choose SAP System
e) Go to transport tool tab
f) Create parameter “No_Import_All” with value set as 1
g) Save it
15) Mention the use of personalized tab and parameter tab in user master record?
Parameter Tab: It will allow access to assign T-code on which one has to work
Personalization Tab: It is required for RFC connection between systems other than user personal information
16) What is the different type of users in SAP?
Different types of users in SAP are
a) Dialog Users
b) System Users
c) Communication Users
d) Service Users
e) Reference Users
17) Explain what is the use of reference and service user in SAP?
- Service User: For “service user” initial password or expiration of password are not checked. Only admin has rights to change the password, users cannot. Multiple logins are possible.
Usage: Service users are for anonymous users. Minimum authorization should be given to such type of users
- Reference User: For this kind of users GUI login is not possible.
Usage: In case of emergency, with the help of reference user, it is possible to provide one user authorization to another user.
18) Explain how you can restrict multiple logins of user in SAP? What are the thing you have to take care of while writing the ID’s?
To restrict multiple logins you have to set the parameter as
Parameter should set in RZ10
a) login/multi_login_users= set to 1 to activate (If this parameter is set to value 1, multiple dialog logons to the R/3 system are blocked)
b) login/disable_multi_gui_login= List out the users that should be allow to logon for multiple times
While writing the user ID’s things to be taken care are, list the user IDs separated by commas “..” , between user IDs do not leave space characters and to see the changes restart the R/3 instance.
19) At OS level how you can change the number of work process? How you can analyze the status of work process at OS level?
To change the number of work process at the OS level, you can increase the no. of work processes by modifying the parameter rdisp/wp_no_=
Status of a WP at OS level can be checked by executing dpmon.
20) Explain how to define logon groups?
Logon groups can be defined using the Tcode smlg. In order to do that you have to create the group and then assign the instances for that particular group.
21) What is SAP single stack system?
A single stack system is defined by SAP system either with JAVA as runtime engine or SAP Netweaver as ABAP.
Eg: Single Stack System (Java) is SAP Enterprise Portal System (Ep)
Single Stack System (ABAP) is SAP ERP (ECC)
22) What are the tools to install JAVA patches?
To use the JAVA patches , SAP installer (SAPinst.exe) is employed. SDM and JSPM are the latest versions of tools used to deploy Java Patches.
23) Explain what is “Data Sets” in SAP?
To solve queries which cannot be solved by using the method interfaces, a set of information is used. This set of information is known as “ Data Sets”.
24) At O.S level where to check for system logs of SAP application?
To check the system logs of SAP application at OS level, SAPMMCà SAP systemsà SIDàSysLog
25) Explain what is LUW (logical unit of work)?
A list of steps among t-code in known as logical LUW
26) Explain what is heterogenous system copy and homogenous system copy ?
Homogenous system copy= Same OS + Same Database
Heterogeneous system copy= Different OS + Different database or same database
27) Explain what are the functional modules used in sequence in BDC?
Using BDC programming a data can be transferred successfully. There are 3 functional modules which can be used in a sequence.
a) BDC _OPEN_GROUP: Name of the client, sessions and user name are specified in these functional modules.
b) BDC_INSERT: It is used to insert the data for one transaction into a session.
c) BDC_CLOSE_GROUP: It is used to close the batch input session.
28) Explain what is an “OK” code is and what is the difference between “t-code” and “OK” code?
An “OK” code is used by a program to execute a function for example after a push button has been clicked.
Transaction code or “t-code” is a “shortcut” that helps a user to run a program.
29) Explain how client refresh is different than client copy?
Client refresh is overwriting or copying to existing client, while copying the newly created client is called client copy.
30) What is a background processing batch scheduler?
To check the schedule background jobs and to execute them parameters like rdisp/btctime is used. These parameters define background processing batch scheduler.
31) Explain what is SAP IDES?
SAP Internet Demonstration and Evaluation System or SAP IDES, this system demonstrate the functionality of various SAP solutions used by important customers.
32) Explain what is the purpose of TDEVC ?
The purpose of TDEVC contains development classes and packages.
33) How many types of work processes are there in SAP ?
There are seven types of work processes they are:
a) Dialog
b) Enque
c) Update
d) Background
e) Spool
f) Message
g) Server
h) Gateway
34) What is the role of “ Application Server” ?
Application Server takes the request from the user and if the request requires data then it connects to the database server and gives output.
35) What is process for applying patches?
Process for applying patches are:
a) Download patches from the service .sap.com to Trans Directory
b) Using CAR command extract the patches in the Trans Directory
c) Using SAPM, import patches into SAP level and Apply
36) How to perform the transport?
Transport can be done through STMS_IMPORT or through FTP.
37) What are the types of transport queries?
a) Customising Request
b) Workbench Request
c) Transport of Copies
d) Re-location
38) Explain what is business KPIs ?
Business KPIs are Key Performance Indicators. It indicates the performance of a company at a strategic level. They help in leading the company on the desired track by comparing company’s previous performance with the market leaders in the same market.
39) Explain what is the importance of table T000?
Table T000 contains a list of defined clients, where we can maintain transaction code SCC4.
40) What is SAPS ?
SAPS stands for SAP Application Performance Standard, which is a hardware independent unit which describes the performance of a system configuration in SAP environment.
41) Mention what is the difference between Central Instance & Application Server?
Central Instance has message server and dialog, update, spool, enque, gateway, background work processes.
Application server has dialog, update, spool, gateway and background work process.
42) In what ways you would know whether a system is Unicode or Non-unicode?
By code sm51 t-code we can see whether it is Unicode or non-unicode. In this code we can find the release notes button in the application tool bar if you click on that you can see the total information like Database, Kernel version, Unicode or non- Unicode.
43) In SAP basis what are the different types of transport requests?
Four types of transport requests are there
a) Customizing request
b) Workbench request
c) Transport request
d) Relocation
44) What is logical system? How to create and why?
For communication between systems within the landscapes logical system is required. It enables the system to recognize the target system as an RFC destination.
TCODE used is SPRO
45) How you can assign an object to 100 roles at time?
To assign an object to 100 roles at time,
a) Go to sell T-code from there go to the table agr_agrs.
b) You will be asked for Access key
c) Enter the objects that needs to be added to 100 roles
d) Select the range of roles in which the object needs to be added
e) Save or Activate whatever option is given
46) On a particular system how you can get a list of the users with development access on a particular system?
By using table “DEVACCESS” you can get a list of the users with development access.
47) How can you view locked transactions?
To view locked transactions you need to look in field CINFO, table TSTC. Within SAP you can either use SE11 or SE16 to browse the table contents. Make sure that you enter “A0” as the “HEX01 data element for SYST” starting value and “A9” as the ending value. This will list all the transactions locked in the system.
48) What is an ‘OK’ code? What are the differences an ‘OK’ code to a ‘T-code’?
OK code is used by a program to execute a function for example after a pushbutton has been clicked. A transaction code is a “shortcut” that helps a user run program.
49) How you can disable the ‘Import All’ button on STMS for the queues?
a) Login to your Transport Domain Controller
b) Run STMSàOverviewàSystem
c) Choose the system you want to disable ‘Import All’
d) Go to Transport Tool tab
e) Add/Create parameter “ No_IMPORT_ALL” set its value to 1
50) How you can apply SAP notes to SAP system?
a) Goto Tcode SNOTE
b) GOTO MenuàDownload SAPNote
c) Give the Note No
d) After downloading check the status, if implemented
e) Select Note, GOTO Menu SAPNoteàImplement Note
51) Mention what is the purpose of table USR02?
This table stores passwords and User IDS.
52) What is the difference between kernel replacement and support package?
Kernel replacement is the replacement of the SAP executable on the OS level, while support package contains fixes to the ABAP code within a SAP instance.
53) Which are the most frequent errors encountered while dealing with TRANSPORTS ?
Return code (4) indicates import ended with warning.
Return code (8) indicates not imported ended with error
Return code (12) indicates import is cancelled.
Return code (16) indicates import is cancelled.
54) How will go about doing a client copy ?
You can do a client copy using the SCCL transaction
55) List the difference between asynchronous and synchronous transport -
Synchronous Transport - Dialog or batch process are blocked until import is ended
Asynchronous Transport - Dialog or batch process is released after import is started.
55) How will determine whether your SAP server is Unicode or ASCII ?
Go to SM51 , Click Release Notes. Entry corresponding to ICU Version will tell you whether your system is ASCII or Unicode.
56) List the types of Transport requests?
There are 4 types of transport requests in SAP -
1. Customizing Request
2. Workbench Request
3. Transport of Copies
4. Relocation
57) What is the difference between Consolidation and Development route ?
In consolidation route - objects can be changed and they can transport from one system to other. This is the route between development to quality
In Development route - Objects can not be changed and they can not be transported from one system to other. This is the route between quality to production
58) How will you define logon groups ? What is Load Balancing in SAP ?
You can set the logon group using SMLG transaction.
59) What is supplementation language ?
Default SAP systems are pre-installed with English and German.
SAP does support many other language which may not full translate from the default English and German. To fill this gap , Supplementary language (a program) is installed.
60) Is SAP a database ?
NO . SAP is not a database but it uses databases from other vendors like Oracle. Although SAP has recently released its own database HANA
61) Which transaction do you use to check Buffer Statistics ?
ST02 , RZ10