Users Online
· Members Online: 0
· Total Members: 188
· Newest Member: meenachowdary055
Forum Threads
Latest Articles
Articles Hierarchy
SAP for Beginners
What is SAP? Definition of SAP ERP Software
What is SAP?
SAP stands for Systems Applications and Products in Data Processing.
SAP by definition is also named of the ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software as well the name of the company.
SAP Software was Founded in 1972 by Wellenreuther, Hopp, Hector, Plattner and Tschira.
SAP system consists of a number of fully integrated modules, which covers virtually every aspect of the business management.
SAP is #1 in the ERP market. As of 2010, SAP has more than 140,000 installations worldwide, over 25 industry-specific business solutions and more than 75,000 customers in 120 countries
Other Competitive products of SAP Software in the market are Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics etc.
What is SAP ERP? Why it is Required?
Following Video will explain the need of an ERP software like SAP in an enterprise
The very basic question to any beginners is why Enterprise Resource Planning also called ERP is required? To answer this, let’s examine this typical business scenario.
Suppose a client approaches sales team asking for a particular product. The sales team contacts to inventory department to check the availability of the product. To their surprise, sales team found out that the product is out of stock. So next time this don’t happen, they have to introduce a SAP ERP tool.
Before we actually see in detail, what ERP is and how ERP can help in your business process, we will understand how different departments are involved in the whole business process, right from the ordering of the raw material – to manufacturing goods – to delivering final goods to the customer.
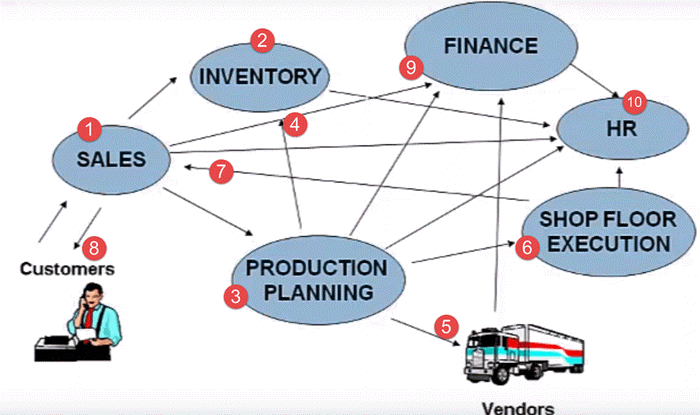
Here is the whole process that is followed by any business unit.
- Client contacts the sales team to check the availability of the product
- Sales team approaches the Inventory department to check for the availability of the product
- In case the product is out of stock, the sales team approaches the Production Planning Department to manufacture the product
- The production planning team checks with inventory department for availability of raw material
- If raw material is not available with inventory, the Production Planning team buys the raw material from the Vendors
- Then Production Planning forwards the raw materials to the Shop Floor Execution for actual production
- Once ready, the Shop Floor Team forwards the goods to the Sales Team
- Sales Team who in turn deliver it to the client
- The sales team updates the finance with revenue generated by the sale of the product. Production planning team update the finance with payments to be made to different vendors for raw materials.
- All departments approach the HR for any Human Resource related issue.
That is a typical business process for any manufacturing company. Some key inferences one could derive from the scenario would be.
- It has many departments or business units
- These departments or business units continuously communicate and exchange data with each other
- The success of any organization lies in effective communication, and data exchange, within these departments, as well as associated third party such as vendors, outsourcers, and customers.
Based on the manner in which communication and data exchanged is managed. Enterprise systems can be broadly classified as
2) Centralized System which are also called as ERP.
Decentralized System
Let's look at Decentralized system first, in a company with Decentralized System of Data Management, there are two major problems –
- Data is maintained locally at the individual departments
- Departments do not have access to information or data of other departments
To identify problems arising due to decentralized Enterprise management system lets look at the same business process again. The customer approaches the sales team for a product, but this time around he needs the product, on an urgent basis.
Since it is a decentralized process, the Sales Team do not have any real-time information access to the products availability. So they approach the Inventory department to check the availability of the product. This process takes time and customer chooses another vendor leading to loss of revenue and customer dissatisfaction.
Now, suppose the product is out of stock and the Sales Team approaches the Production Planning team to manufacture the product for future use. Production Planning Team checks the availability of the raw materials required.
In a decentralized system, raw material information is separately stored by Production Planning as well as Inventory Department. Thus, data maintenance cost (in this case Raw Material) goes up.
The raw material information is available in two different departments Inventory as well as Production Planning. When sales team check a particular raw material required to manufacture the product, it shows the raw material is available as per the inventory, but as per the database of the production planning team, the raw material is out of stock.
So, they go ahead and buy the raw material. Thus, material as well inventory cost goes up.
Once the raw material is available, the shop floor department suddenly realizes they are short of workers they approach the HR, who in turn hire temporary employees at higher than market rates. Thus LABOR Cost Increases.
The production planning department fails to update the finance department on the materials they have purchased. The finance department defaults the payment deadline set by the vendor causing the company loss of its reputation and even inviting a possible legal action.
These are just a few of many problems with decentralized systems.
Some Major problems with the decentralized system are –
- Numerous disparate information system generates individually over time which are difficult to maintain
- Integrating the data is time and money consuming
- Inconsistencies and duplication of data
- Lack of timely information leads to customer dissatisfaction , loss of revenue and reputation
- High Inventory, material, and human resource cost.
These are some major drawbacks for which we need a solution. Well the Solution lies in Centralized Systems i.e. ERP.
Centralized System
In a company, with Centralized System of Information and Data Management.
1) Data is maintained at a central location and is shared with various Departments
2) Departments have access to information or data of other Departments
Let’s look at the same business process again to understand how a Centralized Enterprise System helps to overcome problems posed by a Decentralized Enterprise System.
In this Case, all departments update a Central Information System.
- When Customer approaches the sales team to buy a product on an urgent basis. The Sales Team has real-time information access to the products in inventory which is updated by the Inventory Department in the Centralized System
- Sales Team respond to customer request on time leading to Increased Revenue and Customer Delight.
- In case, manufacturing is required the Sales Team update the Centralized Database, so that all the department remain informed about the product status.
- Production Planning Department is auto updated by the Centralized Database for requirements. Production Planning Team checks the availability of the raw materials required via Central Database, which is updated by the Inventory Department.
- Thus, Data Duplication is avoided, and accurate data is made available. The Shop Floor Team update their Man Power Status regularly in the Central Database, which can be accessed by the HR department.
- In case of shortage of workforce, HR team starts recruitment process with considerable lead time to hire a suitable candidate at market price.Thus labor cost goes down.
- While vendors can directly submit their invoices to the Central Enterprise System, which can be accessed by the finance department. Thus, payments are made on time, and possible legal actions are avoided
- SAP software is a type of Centralized System. SAP System is most popularly used ERP software.
Key benefits of the centralized system are:
- It Eliminates the duplication, discontinuity and redundancy in data
- Provides information across departments in real time.
- SAP System is Provides control over various business processes
- Increases productivity, better inventory management , promotes quality , reduced material cost, effective human resources management, reduced overheads boosts profits
- Better customer interaction and increased throughput. It also improves customer service
- Hence, a centralized enterprise management system is required.
- SAP Software is a centralized enterprise management system also known as Enterprise Resource Planning.
SAP Business Suite
What is SAP Business Suite?
SAP Business Suite is collection of fully integrated applications such as SAP customer relationship management (CRM), SAP Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), SAP product lifecycle management (PLM), SAP supplier relationship management (SRM), and SAP supply chain management (SCM) modules.
Most people relate SAP with its ERP offering. But SAP now offers variety of products to address varied needs of an organization. Lets have a look at them -
- SAP HANA:- High Performance Analytic Appliance uses in-memory computing, a breakthrough technology that enables analysis of very large, non-aggregated data at unprecedented speed in local memory (vs. disk-based database) enabling complex analyses, plans and simulations on real-time data.
- SAP Convergent Charging :- SAP Convergent Charging provides a rating and charging solution for high-volume processing in service industries. It delivers pricing design capabilities, high performance rating and convergent balance management.
- Customer Relationship Management:- Unlike other CRM software, the SAP Customer Relationship Management (SAP CRM) application, part of the SAP Business Suite, not only helps you address your short-term imperatives – to reduce cost and increase your decision-making ability – but can also help your company achieve differentiated capabilities in order to compete effectively over the long term.
- Enterprise Resource Planning:- A sound foundation is necessary to compete and win in the global marketplace. The SAP ERP application supports the essential functions of your business processes and operations efficiently and are tailored to specific needs of your industry like SAP ERP Financials, SAP ERP Human capital management,SAP ERP Operations,SAP ERP corporate services.
- SAP Environment, Health, and Safety Management :- It supports environmental, occupational and product safety processes, regulatory compliance, and corporate responsibility. This is accomplished by embedding corporate policies, compliance, and environmental, health and safety capabilities with global business processes for human resources, logistics, production and finance.
- SAP Global Batch Traceability :- It allows you to completely trace tracked objects, for example, a batch, across both SAP systems and non-SAP systems. In the event of a recall or withdrawal, SAP GBT ensures the timely compliance with legal reporting timelines. Furthermore, it helps you to minimize cost and corporate risk exposure. You can also analyze multiple objects, for example, batches, in one run.
- SAP Product Life Cycle Management:- To survive in an ever-changing global environment, creating and delivering innovative and market differentiating products and services is what distinguishes your company from the competition. The SAP Product Lifecycle Management (SAP PLM) application provides you with a 360-degree-support for all product-related processes – from the first product idea, through manufacturing to product service
- SAP Supplier Life Cycle Management:- SAP Supplier Lifecycle Management is a holistic approach to managing supplier relationships. It deals with the supply base as a whole to constantly determine the right mix of suppliers. It covers the lifecycle of individual suppliers ? from onboarding to a continuous development.
- Supply Chain Management :- You face enormous pressure to reduce costs while increasing innovation and improving customer service and responsiveness. SAP Supply Chain Management (SAP SCM) enables collaboration, planning, execution, and coordination of the entire supply network, empowering you to adapt your supply chain processes to an ever-changing competitive environment.
- Supplier Relationship Management:- With SAP SRM you can examine and forecast purchasing behavior, shorten procurement cycles, and work with your partners in real time. This allows you to develop long-term relationships with all those suppliers that have proven themselves to be reliable partners.
- Governance, Risk and Compliance:- Risk is unavoidable, but it can be managed. With governance, risk, and compliance (GRC), businesses can strategically balance risk and opportunity.
- Sales and operations planning:- SAP Sales and Operations Planning enables you to optimally and profitably meet long-term future demand. Typically, this process repeats every month and involves many participants including Sales, Marketing, Finance, Demand Planning, and Supply Chain Planning.
- SAP Transportation Management :- It supports you in all activities connected with the physical transportation of goods from one location to another.
- Extended Warehouse Management:- SAP Extended Warehouse Management gives you the option of mapping your entire warehouse complex in detail in the system, down to the storage bin level. Not only does this give you an overview of the total quantity of a product in the warehouse, but you can also always see exactly where a specific product is, at any time, in your warehouse complex. With EWM, you can optimize the use of various storage bins and stock movements, and can combine the storage of stocks from several plants in randomly-managed warehouses.
- Mobile Apps:- Mobile devices can also access SAP system.