Users Online
· Members Online: 0
· Total Members: 188
· Newest Member: meenachowdary055
Forum Threads
Latest Articles
Articles Hierarchy
Hadoop Tutorial: Master BigData
Hadoop Tutorial: Features, Components, Cluster & Topology
Apache HADOOP is a framework used to develop data processing applications which are executed in a distributed computing environment.
In this tutorial we will learn,
Similar to data residing in a local file system of personal computer system, in Hadoop, data resides in a distributed file system which is called as a Hadoop Distributed File system.
Processing model is based on 'Data Locality' concept wherein computational logic is sent to cluster nodes(server) containing data.
This computational logic is nothing but a compiled version of a program written in a high level language such as Java. Such a program, processes data stored in Hadoop HDFS.
HADOOP is an open source software framework. Applications built using HADOOP are run on large data sets distributed across clusters of commodity computers.
Commodity computers are cheap and widely available. These are mainly useful for achieving greater computational power at low cost.
Do you know? Computer cluster consists of a set of multiple processing units (storage disk + processor) which are connected to each other and acts as a single system.
Components of Hadoop
Below diagram shows various components in Hadoop ecosystem-
Apache Hadoop consists of two sub-projects –
-
Hadoop MapReduce : MapReduce is a computational model and software framework for writing applications which are run on Hadoop. These MapReduce programs are capable of processing enormous data in parallel on large clusters of computation nodes.
-
HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System): HDFS takes care of storage part of Hadoop applications. MapReduce applications consume data from HDFS. HDFS creates multiple replicas of data blocks and distributes them on compute nodes in cluster. This distribution enables reliable and extremely rapid computations.
Although Hadoop is best known for MapReduce and its distributed file system- HDFS, the term is also used for a family of related projects that fall under the umbrella of distributed computing and large-scale data processing. Other Hadoop-related projects at Apache include are Hive, HBase, Mahout, Sqoop , Flume and ZooKeeper.
Features Of 'Hadoop'
• Suitable for Big Data Analysis
As Big Data tends to be distributed and unstructured in nature, HADOOP clusters are best suited for analysis of Big Data. Since, it is processing logic (not the actual data) that flows to the computing nodes, less network bandwidth is consumed. This concept is called as data locality concept which helps increase efficiency of Hadoop based applications.
• Scalability
HADOOP clusters can easily be scaled to any extent by adding additional cluster nodes, and thus allows for growth of Big Data. Also, scaling does not require modifications to application logic.
• Fault Tolerance
HADOOP ecosystem has a provision to replicate the input data on to other cluster nodes. That way, in the event of a cluster node failure, data processing can still proceed by using data stored on another cluster node.
Network Topology In Hadoop
Topology (Arrangment) of the network, affects performance of the Hadoop cluster when size of the hadoop cluster grows. In addition to the performance, one also needs to care about the high availability and handling of failures. In order to achieve this Hadoop cluster formation makes use of network topology.
Typically, network bandwidth is an important factor to consider while forming any network. However, as measuring bandwidth could be difficult, in Hadoop, network is represented as a tree and distance between nodes of this tree (number of hops) is considered as important factor in the formation of Hadoop cluster. Here, distance between two nodes is equal to sum of their distance to their closest common ancestor.
Hadoop cluster consists of data center, the rack and the node which actually executes jobs. Here, data center consists of racks and rack consists of nodes. Network bandwidth available to processes varies depending upon location of the processes. That is, bandwidth available becomes lesser as we go away from-
- Processes on the same node
- Different nodes on the same rack
- Nodes on different racks of the same data center
- Nodes in different data centers
Hadoop Setup Tutorial - Installation & Configuration
Prerequisites:
You must have Ubuntu installed and running
You must have Java Installed.
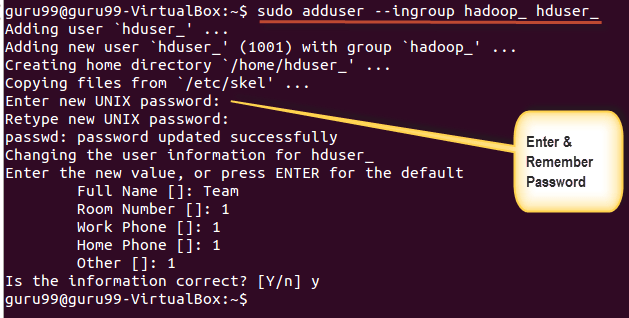
Step 1) Add a Hadoop system user using below command
sudo addgroup hadoop_
sudo adduser --ingroup hadoop_ hduser_
Enter your password , name and other details.
NOTE:
There is a possibility of below mentioned error in this setup and installation process.
"hduser is not in the sudoers file. This incident will be reported."
This error can be resolved by
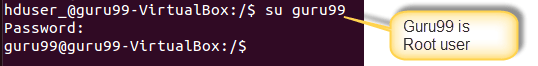
Login as a root user
Execute the command
sudo adduser hduser_ sudo
Re-login as hduser_
Step 2) . Configure SSH
In order to manage nodes in a cluster, Hadoop require SSH access
First, switch user, enter following command
su - hduser_
This command will create a new key.
ssh-keygen -t rsa -P ""
Enable SSH access to local machine using this key.
cat $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> $HOME/.ssh/authorized_keys
Now test SSH setup by connecting to locahost as 'hduser' user.
ssh localhost
Note:
Please note, if you see below error in response to 'ssh localhost', then there is a possibility that SSH is not available on this system-
To resolve this -
Purge SSH using,
sudo apt-get purge openssh-server
It is good practice to purge before start of installation
Install SSH using command-
sudo apt-get install openssh-server
Step 3) Next step is to Download Hadoop
Select Stable
Select the tar.gz file ( not the file with src)
Once download is complete, navigate to the directory containing the tar file
Enter , sudo tar xzf hadoop-2.2.0.tar.gz
Now, rename rename hadoop-2.2.0 as hadoop
sudo mv hadoop-2.2.0 hadoop
sudo chown -R hduser_:hadoop_ hadoop
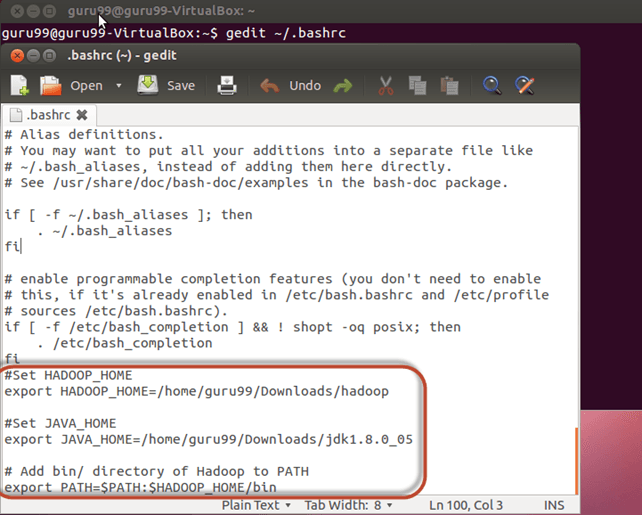
Step 4) Modify ~/.bashrc file
Add following lines to end of file ~/.bashrc
#Set HADOOP_HOME export HADOOP_HOME=<Installation Directory of Hadoop> #Set JAVA_HOME export JAVA_HOME=<Installation Directory of Java> # Add bin/ directory of Hadoop to PATH export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_HOME/bin
Now, source this environment configuration using below command
. ~/.bashrc
Step 5) Configurations related to HDFS
Set JAVA_HOME inside file $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh
With
There are two parameters in $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml which need to be set-
1. 'hadoop.tmp.dir' - Used to specify directory which will be used by Hadoop to store its data files.
2. 'fs.default.name' - This specifies the default file system.
To set these parameters, open core-site.xml
sudo gedit $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml
Copy below line in between tags <configuration></configuration>
<property> <name>hadoop.tmp.dir</name> <value>/app/hadoop/tmp</value> <description>Parent directory for other temporary directories.</description> </property> <property> <name>fs.defaultFS </name> <value>hdfs://localhost:54310</value> <description>The name of the default file system. </description> </property>
Navigate to the directory $HADOOP_HOME/etc/Hadoop
Now, create the directory mentioned in core-site.xml
sudo mkdir -p <Path of Directory used in above setting>
Grant permissions to the directory
sudo chown -R hduser_:Hadoop_ <Path of Directory created in above step>
sudo chmod 750 <Path of Directory created in above step>
Step 6) Map Reduce Configuration
Before you begin with these configurations, lets set HADOOP_HOME path
sudo gedit /etc/profile.d/hadoop.sh
And Enter
export HADOOP_HOME=/home/guru99/Downloads/Hadoop
Next enter
sudo chmod +x /etc/profile.d/hadoop.sh
Exit the Terminal and restart again
Type echo $HADOOP_HOME. To verify the path
Now copy files
sudo cp $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml.template $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml
Open the mapred-site.xml file
sudo gedit $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml
Add below lines of setting in between tags <configuration> and </configuration>
<property> <name>mapreduce.jobtracker.address</name> <value>localhost:54311</value> <description>MapReduce job tracker runs at this host and port. </description> </property>
Open $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml as below,
sudo gedit $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml
Add below lines of setting between tags <configuration> and </configuration>
<property> <name>dfs.replication</name> <value>1</value> <description>Default block replication.</description> </property> <property> <name>dfs.datanode.data.dir</name> <value>/home/hduser_/hdfs</value> </property>
Create directory specified in above setting-
sudo mkdir -p <Path of Directory used in above setting>
sudo mkdir -p /home/hduser_/hdfs
sudo chown -R hduser_:hadoop_ <Path of Directory created in above step>
sudo chown -R hduser_:hadoop_ /home/hduser_/hdfs
sudo chmod 750 <Path of Directory created in above step>
sudo chmod 750 /home/hduser_/hdfs
Step 7) Before we start Hadoop for the first time, format HDFS using below command
$HADOOP_HOME/bin/hdfs namenode -format
Step 8) Start Hadoop single node cluster using below command
$HADOOP_HOME/sbin/start-dfs.sh
Output of above command
$HADOOP_HOME/sbin/start-yarn.sh
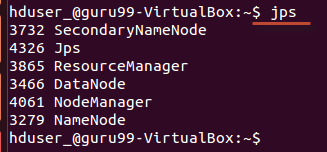
Using 'jps' tool/command, verify whether all the Hadoop related processes are running or not.
If Hadoop has started successfully then output of jps should show NameNode, NodeManager, ResourceManager, SecondaryNameNode, DataNode.
Step 9) Stopping Hadoop
$HADOOP_HOME/sbin/stop-dfs.sh
$HADOOP_HOME/sbin/stop-yarn.sh